Rock West Composites delivers composite assembly fixtures for NASA PASS program
Nine-by-nine-foot fixtures were designed with tight tolerances for thermal and moisture stability, supporting NASA’s push to enable in-orbit construction of hardware for future space programs.
Rock West Composites (RWC, San Diego, Calif., U.S.) has delivered three composite 9 × 9-foot assembly fixtures for NASA’s (Washington, D.C., U.S.) precision assembly space structure (PASS) program supporting the on-orbit servicing assembly and manufacturing (OSAM) efforts. These fixtures are part of NASA’s push for next-generation manufacturing technology that will enable in-orbit construction of high-precision hardware, such as reflectors and antennas, for programs such as Artemis.
The fixtures were fabricated from M63 PAN fiber in PMT-F7 and a 350ºF curing toughened epoxy resin from Patz Materials and Technologies (Benicia, Calif., U.S.). RWC helped define the requirements and designed the hardware to meet their challenging operational parameters. According to the company, there are nine holes and nine slots on nine fittings which required a positional tolerance of 0.002 inch. The nine fittings also required a flatness across the fixture of 0.002 inch. The panels are required to interface with a strut assembly and have very low coefficients of thermal and moisture expansion to ensure high precision and repeatability.
RWC used a spliced panel design to meet the 9 × 9-foot sizing. Innovative soft fixturing with fine tuning adjustment capability was used to meet tight tolerances in a cost-effective manner. A laser tracker was used to verify tolerances during manufacture.
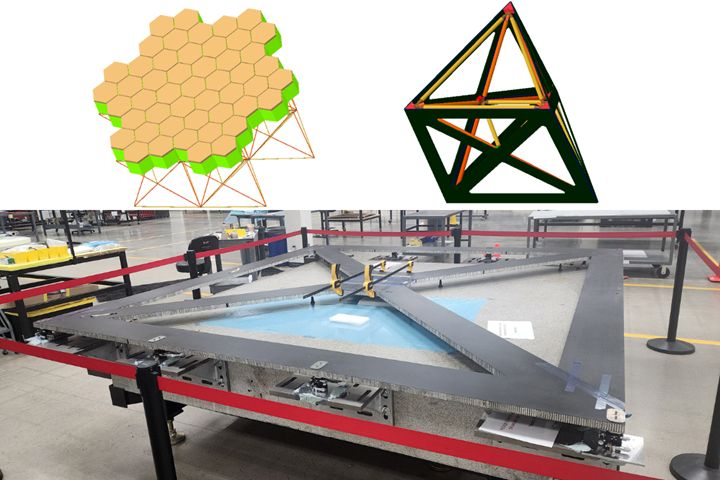
CAD image of NASA PASS Reflector assembled (top left), CAD image of segment of structural supports with assembly fixture (top right) and panel in manufacturing on adjustable fixtures for precision tuning (center). Photo Credit: NASA Langeley (top right and left) and RWC (center)
“We are proud to be part of this program supporting NASA’s mission infrastructure and pushing forward space technology,” Jeremy Senne, the head of RWC’s Space market segment, says. “When we can find ways to innovate our manufacturing process that ultimately save our customer time and money, it’s a win-win. We hope to recycle this process for similar large and tight tolerance structures to continue to push the envelope of what’s possible.”
RWC develops and manufactures composite products for multiple industries including aerospace, defense, space, radomes, commercial, industrial, medical, energy and sporting goods. The company specializes in carbon fiber and radio frequency-transparent composite materials.
Related Content
-
Carbon fiber satellite arm reduces weight, simplifies assembly onto naval vessels
Satcom developer EM Solutions partnered with ACS Australia to replace an aluminum arm design with a 65% lighter, one-piece, corrosion-resistant carbon fiber/epoxy alternative.
-
NASA launches composite solar sail into space
Sunlight-based propulsion system, supported by carbon fiber-reinforced booms, will undergo weeks-long testing to demonstrate and verify its capabilities.
-
On the radar: Cryogenic testing of composites for future hydrogen storage
Netherlands, U.K., France, Germany and the U.S. build up test capability, look at thermoset and thermoplastic composite materials.