Automated Tape Laying (ATP) / Automated Fiber Placement (AFP)
Automated Tape Placement (ATP) and Automated Fiber Placement (AFP) are advanced manufacturing techniques revolutionizing the production of composite structures. These robotic technologies precisely lay down continuous fibers or tape onto molds or mandrels to create intricate, high-performance composite components. ATP involves the automated placement of composite tape, while AFP handles the precise laying of individual tows of fibers.

Latest ATL/AFP Articles
VIEW ALLAddcomposites announces AFP-XS global install base milestone
More than 50 of the production-ready AFP solution for small- to medium-scale composite part manufacturing have been installed and is rapidly growing thanks to its affordability and versatility.
Read MoreMikrosam robotic filament winding cell to aid Cidetec composites projects
Delivery of the single-spindle robotic setup with an ATP head will advance the R&D organization’s work in CUBIC, GENEX and Carbo4power initiatives targeting sustainable composites development.
Read MoreMikrosam equips BTU Germany with single-tape AFP head for Type 5 pressure vessels
Delivery of upgraded placement head provides additional automated layup flexibility, quality control for the university’s latest projects advancing Type 4 and 5 hydrogen storage.
Read MoreCompoTech highlights fiber laying technologies to achieve CFRP preform, component versatility
Automated fiber laying (AFL) placement and winding machine technologies enhance OEM capabilities to produce reliable, commercially viable custom composite products.
Read MoreCarbon Axis releases the AFP head XPlace mk3
This standalone version enables the user to easily integrate AFP technology into existing robots or gantry systems.
WatchPlant tour: Airbus, Illescas, Spain
Airbus’ Illescas facility, featuring highly automated composites processes for the A350 lower wing cover and one-piece Section 19 fuselage barrels, works toward production ramp-ups and next-generation aircraft.
Read MoreKnowledge Centers

Discover the types of sensors being used in composites, the physics on which they�re based, their installation, promised benefits and challenges, as well as the potential they offer for even further developments in smart structures.
LEARN MORE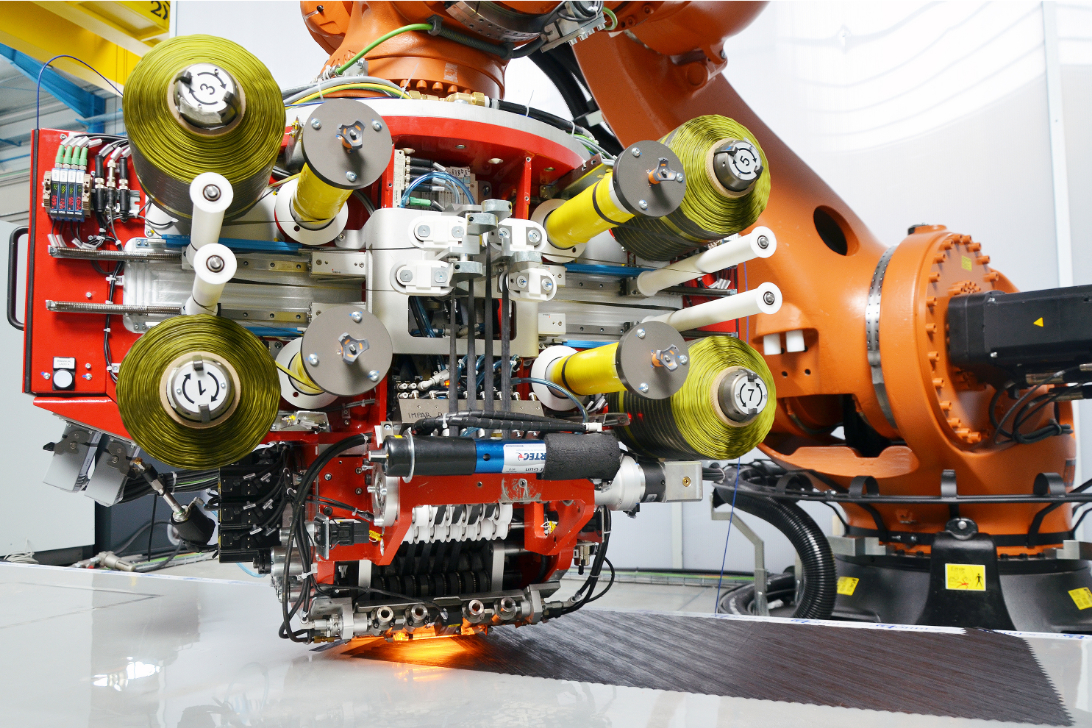
In the Automated Composites knowledge center, CGTech brings you vital information about all things automated composites, from the manufacturing processes to the vendors and necessary tools.
LEARN MORE
Review the state of the art in design, simulation, failure analysis, digital twins, virtual testing and virtual inspection.
LEARN MORELatest ATL/AFP News And Updates
CompoTech uses integrated loop technology to create high-performance mountain bike
CompoTech features its CDuro Epona mountain bike fitted with custom suspension forks, manufactured using its AFL winding and integrated loop technologies.
Read MoreRocket Lab begins installation of large AFP machine for rocket production
The 99-ton AFP machine, custom-designed and built by Electroimpact, is claimed to be the largest of its kind, expecting to save around 150,000 manufacturing hours in the Neutron rocket’s production process.
Read MoreModular AFP automation family supports adaptable production handling
CAMX 2024: Broetje-Automation’s Staxx family of AFP solutions create an ecosystem of functionality, versatility and scalable automation.
Read MoreModular, upgradeable, automated composites manufacturing equipment
CAMX 2024: Mikrosam highlights its filament winding automation, AFP and ATL, modular prepreg slitting and rewinding machine, and towpreg production lines for productivity and reduced costs.
Read MorePlug-n-play AFP/ATL equipment, adaptive mold and integration solutions eases adoption
CAMX 2024: Addcomp distributes its AFP-XS systems and now adaptive molds, works with customers to design and install custom systems and develops its capabilities with new partnerships.
Read MoreRTS technology by iCOMAT ramps up with $22.5 million funding
Additional financing is being secured to service automated fiber steering demand, build first RTS production facility in Gloucester.
Read MoreFeatured Posts
Combining multifunctional thermoplastic composites, additive manufacturing for next-gen airframe structures
The DOMMINIO project combines AFP with 3D printed gyroid cores, embedded SHM sensors and smart materials for induction-driven disassembly of parts at end of life.
WatchPlant tour: Aernnova Composites, Toledo and Illescas, Spain
RTM and ATL/AFP high-rate production sites feature this composites and engineering leader’s continued push for excellence and innovation for future airframes.
Read MoreThe next evolution in AFP
Automated fiber placement develops into more compact, flexible, modular and digitized systems with multi-material and process capabilities.
Read MorePlant tour: BeSpline/Addcomp, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada
Composites automation specialist increases access to next-gen technologies, including novel AFP systems and unique 3D parts using adaptive molds.
Read MoreThe potential for thermoplastic composite nacelles
Collins Aerospace draws on global team, decades of experience to demonstrate large, curved AFP and welded structures for the next generation of aircraft.
WatchManufacturing the MFFD thermoplastic composite fuselage
Demonstrator’s upper, lower shells and assembly prove materials and new processes for lighter, cheaper and more sustainable high-rate future aircraft.
Read MoreFAQ: ATL/AFP
What is the difference between AFP and ATL?
AFP involves the precise placement of continuous fibers onto a mold surface in a predetermined pattern, often in complex shapes, while ATL uses preimpregnated tape to lay down fiber strips onto a surface, typically in straight or curvilinear paths.
What materials can be used in AFP/ATL?
Both AFP and ATL commonly work with materials like carbon fibers, fiberglass, aramid, and thermoplastic or thermoset matrices tailored to specific application requirements.
What are the advantages of AFP/ATL over traditional manufacturing methods?
These technologies offer enhanced precision, reduced material waste, improved structural integrity, and the ability to create complex parts with optimized fiber orientations, resulting in lighter and stronger components.
Are there limitations to AFP/ATL?
Challenges can include high initial equipment costs, complexities in programming intricate designs, and the need for skilled operators to ensure precise placement and quality control.




















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)