NCC sensor technology unlocks digital potential for liquid resin processes
Research and testing of dielectric sensors performed by the NCC, Meggitt and Cranfield University accurately captures resin infusion data, shows promise for composites manufacturing.
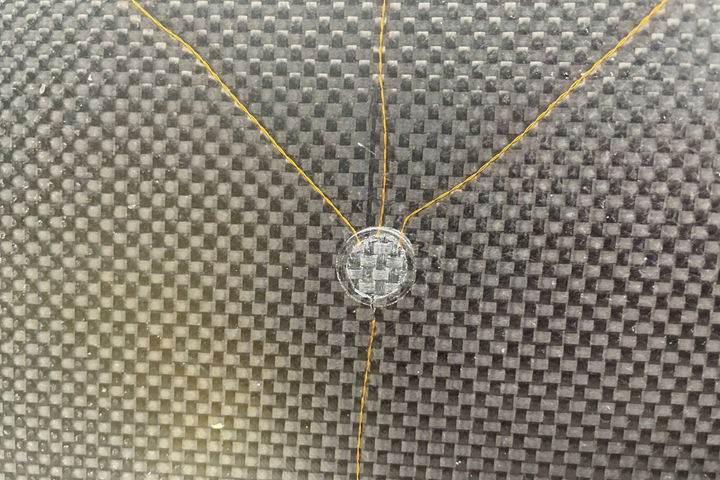

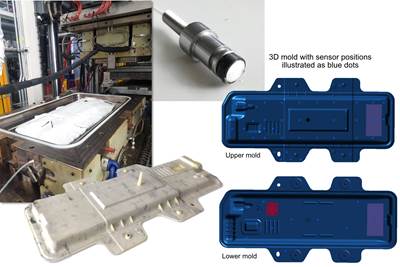
Dielectric sensors in a carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) component. Photo Credit: NCC
The National Composites Centre (NCC, Bristol, U.K.), in collaboration with Cranfield University (U.K.) and aerospace engineering specialists, Meggitt (Christchurch, Dorset, U.K.), has successfully developed and demonstrated a novel sensor technology for capturing data during liquid resin processes.
Initial research into dielectric sensors, which originated at Cranfield University led by Dr. Alex Skordos, Reader in Composites Process Science at the School of Aerospace, Transport and Manufacturing, was further developed at the composites research center through the NCC’s Technology Pull-Through (TPT) program — which partners with universities to evaluate and mature their low-TRL research ready for industry adoption —and then applied in industry by Meggitt.
The sensor system, a step toward the digitalization of resin transfer molding (RTM), provides accurate data capture of resin infusion. The NCC says this can be used to validate computer simulations of the process, enabling industry to reduce the number of initial experimental trials and facilitate a “right first time” approach, crucially reducing the time and cost spent manufacturing components.
Sensor trials, conducted at typical aerospace material processing conditions of 7 Bar and 180°C, showed the sensors could precisely detect resin as it flowed inside the preform, as well as its cure progression — both of which are invisible as the process occurs. Furthermore, the sensors provided no adverse effects on either the process or part quality.
Hearing of the trials’ success, Meggitt approached the NCC for use of the sensor technology in an ATI-funded project the company was conducting with the NCC’s fellow High Value Manufacturing Catapult center, the University of Sheffield Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre (AMRC, Rotherham, U.K.), producing industrial-scale aircraft components.
“We were interested in applying this sensor technology as a way of building in a smart function to the RTM process for monitoring part production,” notes Dr. Peter Karapapas, principal engineer at Meggitt. “This is with the aim of minimizing the time and effort required in post-production NDT [non-destructive testing] and inspection on future components as we move towards digital manufacturing. The sensors were robust and effective during the demonstration on the large-scale composite housing part designed for a civil aviation jet engine air-oil heat exchanger.”
The NCC team worked alongside the AMRC and Meggitt to successfully integrate the sensors into a closed RTM tool, with no modifications to the tool being required. In trials, the sensors successfully captured data on the resin flow progression and degree of cure, agreeing with results from previous reports and theoretical models.
“A large part of the NCC’s role within the composites industry is to enable the transition of technologies from academic research to being ready for industry to use and benefit from. This project is an excellent example of this, with it being developed in our Technology Pull-Through program, and now being used by Meggitt,” concludes Dr. Enrique Garcia, CTO at the NCC.
Related Content
JEC World 2022, Part 1: Highlights in sustainable, digital, industrialized composites
JEC World 2022 offered numerous new developments in composites materials, processes and applications, according to CW senior editor, Ginger Gardiner, most targeting improved sustainability for wider applications.
Read MoreEngine vane demonstrates potential for gapped, unidirectional dry fiber for infusion
GKN Aerospace and its partners developed an aircraft demonstrator component made with TeXtreme’s latest Gapped UD material, proving out a dry, infusible tape meant to compare in performance to UD prepreg.
Read MoreTwenco develops sensors for smart molds and process control in resin infusion and composites welding
Non-invasive DEA and NDT Analyzer for multi-parameter monitoring, QA and control, including real time simulation feed and 3D process visualization across and through composite parts.
Read MorePlant tour: ÉireComposites, Galway, Ireland
An in-house testing business and R&D focus has led to innovative materials use and projects in a range of markets, from civil aerospace to renewable energy to marine.
Read MoreRead Next
In-situ composites sensors for increased production rates, smart processes and life cycle monitoring
Com&Sens FBG sensors are embedded into pressure vessels, rudders and bridges, with new edge and surface connection technology, aimed at cost-effective serial production and monitoring of composite structures.
Read MoreCustomizing ultrasonic sensors for composites process optimization and control
University of Augsburg developed sensors for the CosiMo project’s digital twin and closed-loop process control of EV battery box cover demonstrator, and now moves forward with the AI Production Network for industry collaboration.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read More