Fiber-reinforced Pocan E compounds range highlights tracking resistance, insulation
Rating in the highest insulation class, the short glass fiber-reinforced PBT range from Lanxess is especially suited to compact electrical and electronic assemblies, and EVs.
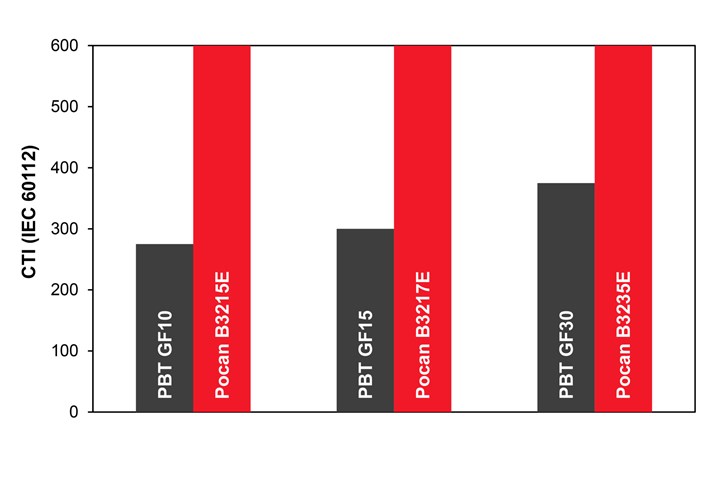
Comparison of conventional PBT types and Pocan E PBT types optimized for E/E applications. Photo Credit: Lanxess
Specialty chemicals company Lanxess (Cologne, Germany) has developed new polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) compounds. Under the name Pocan E, the company is now offering a product range comprising short glass fiber-reinforced grades that are especially suited to applications in e-mobility, as well as in electrical and electronic assemblies thanks to their tracking resistance and insulation properties.
In terms of tracking resistance, Lanxess says the new compounds score a 600 rating in the CTI A test (Comparative Tracking Index – IEC 60112) and therefore meet the requirements of the highest insulation class according to IEC 60664-1. A high tracking resistance reduces the risk of short circuiting and, in the worst-case scenario, damage to the device, defects that can be caused by undesirable creepage currents — what occurs when electrically conductive paths, facilitated by impurities, form on the surface of insulating materials, such as thermoplastics. Lanxess notes that while the CTI A value is 600, a plastic can also be used where higher voltages of up to 1,500 volts (direct current) are present — high voltage is often required for rapid charging of electric vehicles (EVs), for example.
The PBT compounds also is said to provide additional advantages such as optimized mechanical properties, as well as optimized flowability, hydrolysis resistance and flame-retardant properties. The new compounds are also suitable for coloring, which is important for various safety relevant components such as high-voltage connectors that must be clearly color-coded.
According to Lanxess, the fundamental advantage of all new structural materials in the Pocan E range is that their electrical insulation properties are scarcely dependent on temperature or humidity in the typical operating conditions of high-voltage connectors and terminals, for example. In addition, the resulting components are said to boast a particularly high level of dimensional stability, are almost completely resistant to stress cracks and are distinguished by their high chemical resistance.
Compounds with a CTI A test score of 600 include Pocan B3215E, Pocan B3217E and Pocan B3235E. They are reinforced with 10%, 16% and 30% short glass fibers by weight, respectively, and offer improved flowability compared to corresponding standard materials, making it easier to produce delicate and thin-walled component geometries in the injection molding process.
Hydrolytically stabilized and highly tracking-resistant compounds include the Pocan B3233HRE and Pocan B3216XHRE. The latter is reinforced with 16% short glass fibers by weight. In specimen tests based on U.S. Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE/USCAR-2 Rev. 7) stringent long-term hydrolysis tests, the material achieves “Class 5,” which is said to be the best possible rating. Pocan B3233HRE, which contains 30% short glass fibers by weight, achieves the “Class 4” rating in the USCAR hydrolysis test. Another of the compound’s strong points is said to be good flowability, which is maintained at high processing temperatures.
The new Pocan E range also includes Pocan BFN4231HRE, a PBT compound containing 25% short glass fibers by weight that is reported to be both flame-retardant and hydrolysis stabilized. The halogen-free, flame-retardant structural material meets the requirements of the UL 94 flammability test of testing institute Underwriters Laboratories Inc. (Northbrook, Ill., U.S.), achieving a V-0 classification with a test specimen thickness of 0.75 mm. Its high hydrolysis resistance is demonstrated by its “Class 3” rating in the specimen tests according to SAE/USCAR-2 Rev. 7.
Related Content
Carbon Mobile, SABIC to develop, deploy advanced carbon fiber in connected devices
Collaboration aims to deliver the next generation of thinner, lighter, stronger and more sustainable composite materials used in consumer electronics and automotive industries.
Read MoreNanocomposite films boost heat dissipation in thin electronics
Scientists from Japan develop cellulose nanofiber-carbon fiber composite films with high in-plane heat conductivity to assist in heat dissipation in electronic devices.
Read MoreMCVE 3DFlaxtronics enables functional composites for printed electronics
The novel process produces intelligent, highly functional films embedded in flax fiber organosheets with a bio-sourced PA 10-10 resin to advance electronic parts and components development.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Electronics (2024)
Increasingly, prototype and production-ready smart devices featuring thermoplastic composite cases and other components provide lightweight, optimized sustainable alternatives to metal.
Read MoreRead Next
Lanxess composite advances electric vehicle charging infrastructure
Halogen-free glass fiber-reinforced Durethan BKV20FN01 was used in the manufacture of charging cable connectors, demonstrates high tracking resistance and flame retardance.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: The tale of the thermoplastic cryotank
In 2006, guest columnist Bob Hartunian related the story of his efforts two decades prior, while at McDonnell Douglas, to develop a thermoplastic composite crytank for hydrogen storage. He learned a lot of lessons.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Energy (2024)
Composites are used widely in oil/gas, wind and other renewable energy applications. Despite market challenges, growth potential and innovation for composites continue.
Read More