CEO Jin-Ho Jeong. Photo Credit: CATACK-H
Founded in 2017 by CEO Jin-Ho Jeong, CATACK-H (HwaSeong, South Korea) is a chemical treatment-based, carbon fiber composite recycling start-up that currently serves the Korean region, but plans to expand as early as January 2021.
According to Hendrik Neuhaus, international operations manager, the company’s process involves the use of chemical solvents to break down epoxy-based resins in carbon fiber-reinforced plastic (CFRP) parts to recover fibers to reuse as a chopped or milled fiber product.

The current HwaSeong, South Korea facility.
Photo Credit: CATACK-H
At its 65,000-square-foot facility two hours’ drive south of Seoul, CATACK-H currently has capacity to process 300 tons per year of carbon fiber fabrics such as uncured prepregs on a continuous processing line. The company plans to quickly scale this up to 1,000 tons per year with the installation of a second, 700 tons/year line for batch treatment of “harder” materials like cured prepregs and end-of-life (EoL) CFRP parts, expected to go online in January. Current capabilities are for thermoset-based composites, but according to Neuhaus, the company will soon also add processing technology for thermoplastic composites.
Beyond the HwaSeong plant, the company plans to open a new, larger Korean facility by summer 2022, with an additional 4,000 tons/year of processing capacity. So far, the company mainly processes scrap sourced from Korean manufacturers, but longer-term plans include expansion, both of sourcing and of additional recycling facilities, in Europe and North America, as well.

Photo Credit: CATACK-H
Two strengths that set CATACK-H apart, according to Neuhaus, are the company’s sustainable practices, and the high quality and high mechanical properties of the fibers it produces. “The technology is 100% eco-friendly with very little use of energy,” he says, “and doesn’t cause any surface damage to the fibers, so the quality is very high.”
Currently, CATACK-H strives for sustainability three ways:
- Its materials are treated at relatively low temperatures (less than 210°F), requiring less energy compared to high-temperature recycling processes, according to Neuhaus.
- In this process, resins can also be recovered and reused, alongside fibers. During treatment, the polymers’ molecular structure is broken down into smaller units and condensed into another material which can be used, for example, as an ingredient in urethane foam.
- The chemicals CATACKH uses for its treatment process can be reused for six to seven recovery cycles, and Neuhaus says the company is constantly working on improving this chemical formula even further to decrease processing time for even lower energy consumption.
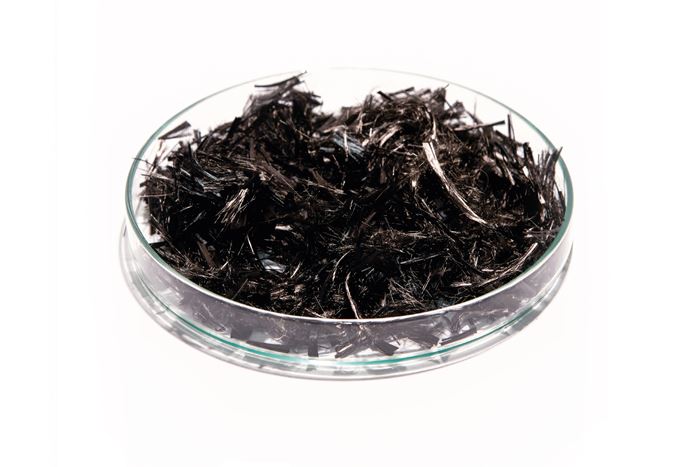
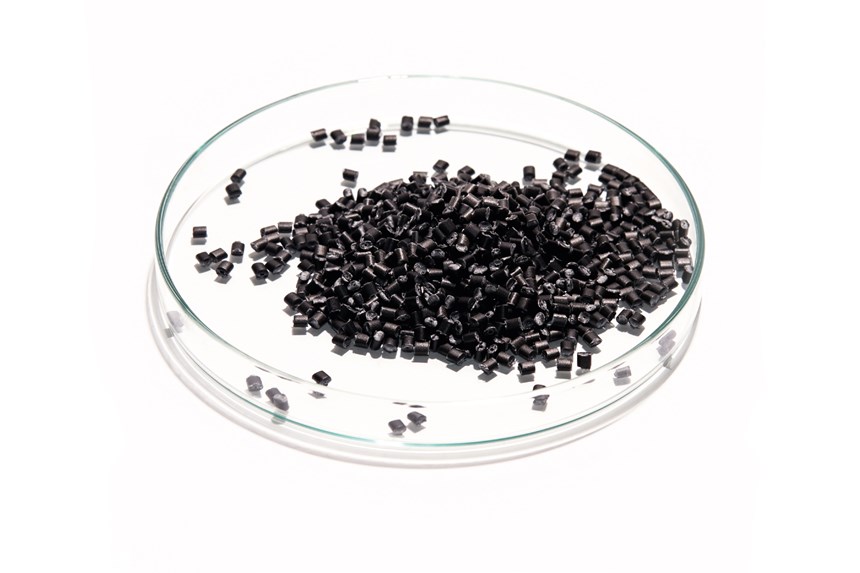
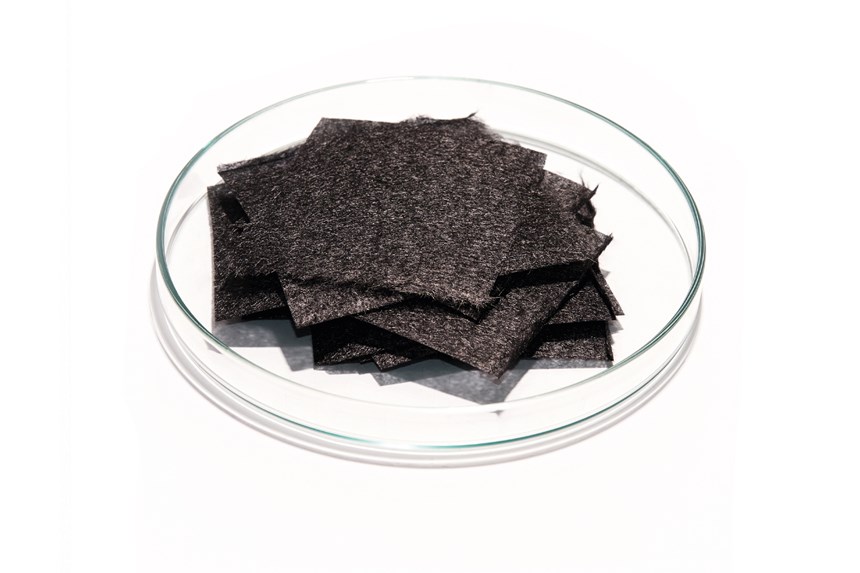
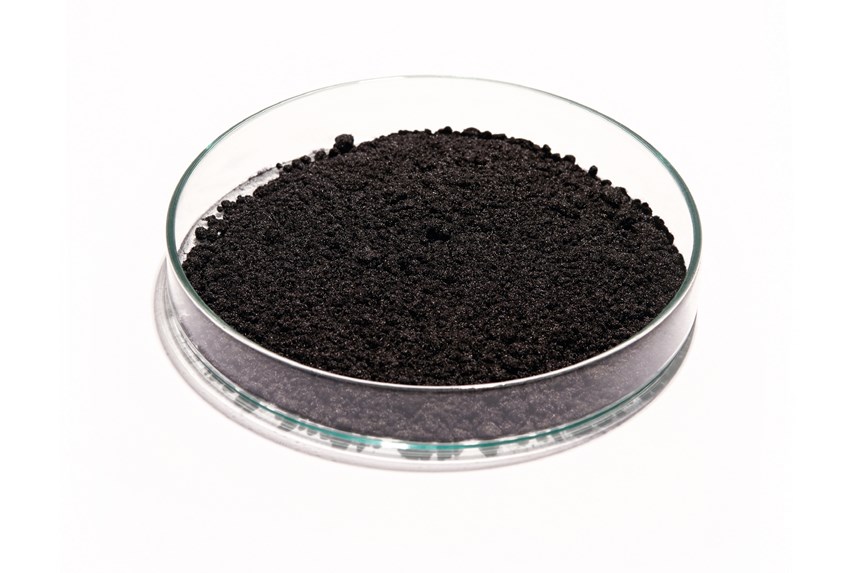
After recovering the fibers and resins from scrap materials, the company produces chopped and precision-cut carbon fiber and milled carbon fiber products, as well as thermoplastic pellets, 3D printing filaments and dry carbon fiber nonwovens (such as carbon paper). It also offers a resin remover powder. Neuhaus says future plans include production of recycled carbon fiber automotive components. “Beyond that, we continue to invest in technology and equipment to supply new types of materials and new forms of applications,” he says.
CATACK-H carbon fiber products
As the company scales up, it will require more waste material. Neuhaus says CATACK-H is looking for “any kind of epoxy-based CFRP,” including dry carbon fibers and fabrics, uncured and cured prepregs, and finished parts. “We also have the technology to recycle carbon fiber/glass fiber pressure tanks (such as hydrogen tanks), and are researching how to recycle wind blades,” he says. Companies interested in partnering with or in learning more about CATACK-H are encouraged to reach out to Neuhaus at neuhaus@catackh.com or to visit catackh.com.
Related Content
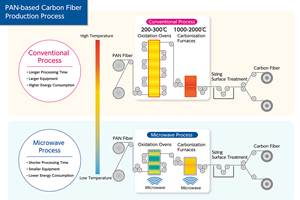
Microwave heating for more sustainable carbon fiber
Skeptics say it won’t work — Osaka-based Microwave Chemical Co. says it already has — and continues to advance its simulation-based technology to slash energy use and emissions in manufacturing.
Read MoreTU Munich develops cuboidal conformable tanks using carbon fiber composites for increased hydrogen storage
Flat tank enabling standard platform for BEV and FCEV uses thermoplastic and thermoset composites, overwrapped skeleton design in pursuit of 25% more H2 storage.
Read MoreJEC World 2023 highlights: Innovative prepregs, bio-resins, automation, business development
CW’s Jeff Sloan checks in with JEC innovations from Solvay, A&P, Nikkiso, Voith, Hexcel, KraussMaffei, FILL, Web Industries, Sicomin, Bakelite Synthetics, Westlake Epoxy and Reliance Industries.
Read MoreInfinite Composites: Type V tanks for space, hydrogen, automotive and more
After a decade of proving its linerless, weight-saving composite tanks with NASA and more than 30 aerospace companies, this CryoSphere pioneer is scaling for growth in commercial space and sustainable transportation on Earth.
Read MoreRead Next
The state of recycled carbon fiber
As the need for carbon fiber rises, can recycling fill the gap?
Read MoreCommercial-scale carbon fiber recycling comes to Tennessee
Accepting carbon fiber waste materials now, Carbon Fiber Recycling will recycle 2,000 tons of carbon fiber waste per year at its Tennessee facility.
Read MoreCW’s 2024 Top Shops survey offers new approach to benchmarking
Respondents that complete the survey by April 30, 2024, have the chance to be recognized as an honoree.
Read More

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)