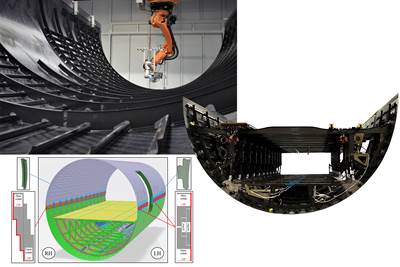
Automated Tape Laying (ATP) / Automated Fiber Placement (AFP)
Automated Tape Placement (ATP) and Automated Fiber Placement (AFP) are advanced manufacturing techniques revolutionizing the production of composite structures. These robotic technologies precisely lay down continuous fibers or tape onto molds or mandrels to create intricate, high-performance composite components. ATP involves the automated placement of composite tape, while AFP handles the precise laying of individual tows of fibers.
Latest ATL/AFP Articles
VIEW ALLElectroimpact offers variable spot size laser AFP 4.0 technology
Patented process technology increases quality, reliability and machine utilization for composite laminate production.
Read MoreAdvanced towpreg makes debut on IMOCA hydrofoil boat
JEC World 2024: Avel Robotics’ IMOCA hydrofoil, fresh off the water, is being highlighted at Toray Carbon Fiber Europe’s booth, showcasing a successful collaboration in using towpreg and AFP for efficient race boat development.
Read MoreBroetje-Automation demonstrates rCF placement via AFP
Through the ScrapSeRO project, the system integrator and machine builder successfully processed recycled composites, in addition to more traditional materials, via its highly flexible Staxx One system.
Read MoreAutomated end-to-end composite solutions for tape laying, fiber placement
JEC World 2024: Fives invites attendees to learn more about its specialization in providing composites precision and performance, whether its through its Cincinnati, Forest-Liné and Lund lines or its ACE and COAST engineering suites.
Read MoreCoriolis introduces hybrid CPico AFP machine
This compact cell brings together 3D printing, AFP and milling aided by a comprehensive software program, further simplifying the manufacture of complex thermoplastic composite aerostructures in the future.
WatchPlant tour: BeSpline/Addcomp, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada
Composites automation specialist increases access to next-gen technologies, including novel AFP systems and unique 3D parts using adaptive molds.
Read MoreKnowledge Centers

Closed mold processes offer many advantages over open molding. This knowledge center details the basics of closed mold methods and the products and tools essential to producing a part correctly.
LEARN MORELatest ATL/AFP News And Updates
Coriolis highlights C1.2 compact AFP system for multi-material applications
New developments regarding productivity, maintenance and ergonomics make this enhanced composite placement system well suited for the production of complex parts.
WatchCTC commissions Carbon Axis XCell machine for LaiLa project
The XCell AFP machine is being used to investigate innovative fiber deposition concepts and improve lightweight production via Industry 4.0.
Read MoreFives introduces COAST in-process composite inspection technology
COAST is capable of precise measurement and defect detection on contoured composite surfaces during the AFP process, reducing costs and increasing AFP accessibility.
Read MoreAddcomposites highlights novel composites manufacturing developments
AFP-XS and AddPath updates, new AFP and continuous AM systems, upcoming webinars and blog content are available to interested industry members.
Read MoreIFW’s AFP installation enhances thermoplastic structure production
Commissioned AddComposites AFP manufacturing cells with humm3 flashlamps are located at IFW’s Stade and Garbsen facilities to expand R&D services.
Read MoreBroadband flash lamp heat source improves material deposition
CAMX 2023: Humm3 technology is a broadband flash lamp heat source for AFP, ATL, filament winding and more composite applications, delivering power previously only available from lasers.
Read MoreFeatured Posts
The potential for thermoplastic composite nacelles
Collins Aerospace draws on global team, decades of experience to demonstrate large, curved AFP and welded structures for the next generation of aircraft.
WatchManufacturing the MFFD thermoplastic composite fuselage
Demonstrator’s upper, lower shells and assembly prove materials and new processes for lighter, cheaper and more sustainable high-rate future aircraft.
Read MoreHeat mapping simulation to improve AFP parts
An optical model developed for Coriolis Composites’ SimuReal AFP process simulation software enables verification of energy distributions during AFP to better define heating laws.
Read MorePlant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
Read MoreNine factors to consider when designing composites cure tooling
Gary Bond discusses the common pitfalls and compromises when designing good cure tooling and their holistic significance for a robust composite production process.
Read MorePEEK vs. PEKK vs. PAEK and continuous compression molding
Suppliers of thermoplastics and carbon fiber chime in regarding PEEK vs. PEKK, and now PAEK, as well as in-situ consolidation — the supply chain for thermoplastic tape composites continues to evolve.
Read MoreFAQ: ATL/AFP
What is the difference between AFP and ATL?
AFP involves the precise placement of continuous fibers onto a mold surface in a predetermined pattern, often in complex shapes, while ATL uses preimpregnated tape to lay down fiber strips onto a surface, typically in straight or curvilinear paths.
What materials can be used in AFP/ATL?
Both AFP and ATL commonly work with materials like carbon fibers, fiberglass, aramid, and thermoplastic or thermoset matrices tailored to specific application requirements.
What are the advantages of AFP/ATL over traditional manufacturing methods?
These technologies offer enhanced precision, reduced material waste, improved structural integrity, and the ability to create complex parts with optimized fiber orientations, resulting in lighter and stronger components.
Are there limitations to AFP/ATL?
Challenges can include high initial equipment costs, complexities in programming intricate designs, and the need for skilled operators to ensure precise placement and quality control.




















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)