Recycled carbon fiber for lower-priced lightweight in heavy trucks?
Though its recent SuperTruck project used CFRP to slash over 3,200 lb, Volvo says it needs lower cost materials like recycled carbon fiber.
Share
SOURCE: Inhabitat.com
Volvo Trucks USA (Greensboro, NC) unveiled its SuperTruck earlier this year — the third out of four SuperTruck vehicles in the US Dept. of Energy’s (DOE) $80 million program of the same name. Launched in 2009, the program aimed to develop Class 8 tractor trailers with 50% greater fuel efficiency. All four SuperTrucks used carbon fiber composites, though to varying degrees.

Enhancements that were developed on Volvo’s SuperTruck and then carried over to its production vehicles include a new aerodynamic bumper, flared chassis fairings and an aerodynamically enhanced roof. Volvo Trucks North America president Goran Nyberg said his company’s SuperTruck routinely achieved more than 12 mpg during testing while loaded and has now surpassed 13 mpg with some additional tinkering.
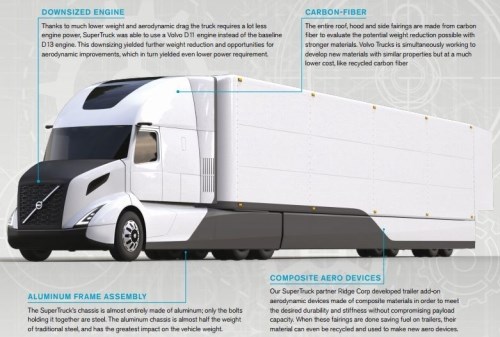
Lightweight materials played a significant role. For example, the aluminum trailer frame is 45% lighter than the 2009 production steel frame. According to senior project manager Pascal Amar, who oversaw this first SuperTruck project, designers didn’t just swap out steel for aluminum but instead designed the frame to take advantage of the lighter metal’s properties.
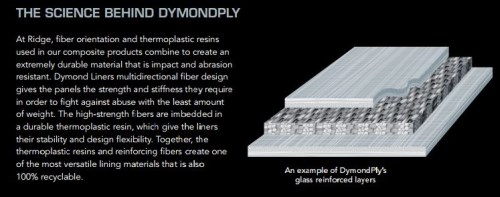
Composites also played a role. The roof, hood and side fairings are made from carbon fiber materials. According to Volvo Trucks USA’s webpage on the SuperTruck, aerodynamic trailer add-on fairings were developed and built by partner Ridge Corp. (Columbus, OH, US), maker of DymondPly and DymondGuard glass fiber-reinforced thermoplastic wall liners and Green Wing Aerodynamic Side Skirts. The SuperTruck fairings reportedly lower overall truck weight vs. 2009 models and minimize drag for dramatic fuel savings.
SOURCE: Ridge Corp.
The aluminum frame shaves 900 lb out of a total 4,700 lb weight loss, but the installation of new drivetrain technologies put back about 1,500 lb, resulting in a net weight savings of 3,200 lb.
Though Volvo depended on carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) to meet SuperTruck program goals, it says the material’s price tag is too high and it is working to develop new composite materials with similar properties at lower costs, like recycled carbon fiber.
Other SuperTrucks and CFRP
Navistar (Lisle, IL, US) was the last to unveil its SuperTruck, reportedly using CFRP in the cab’s upper body panels, roof, back panel and dash panel. Its partner Wabash National (Lafayette, IN, US) developed a lightweight trailer that cut 1525 lb. It also used an aluminum frame but added composite leaf springs to its design, as well as composite sidewalls, closures and support structure for the aerodynamic skirt.
Daimler Trucks North America and subsidiary Freightliner (Portland, OR, US) did not detail use of composites in their SuperTruck, except for carbon fiber cabinets in the cab. However, the team did specify a list of lightweighting partners including MSI-ACPT, Maxion Inmagusa (Castaños Municipality, Coahuila, Mexico), Oregon State University, Strick Trailers (Monroe, IN, US) and carbon fiber supplier Toray.
The Peterbilt (Denton, TX, US) and Cummins (Columbus, IN, US) supertruck reportedly featured CFRP in the front of the trailer skirts and the trailer front’s “horse collar”.
SuperTruck II
Building on the SuperTruck initiative’s success, DOE has announced SuperTruck II and selected the following four teams, each of which will receive $20 million in federal funding to be matched dollar-for-dollar by each recipient:
- Cummins will design and develop a new more-efficient engine and advanced drivetrain and vehicle technologies.
- Daimler Trucks North America will develop and demonstrate a tractor-trailer combination using a suite of technologies including active aerodynamics, cylinder deactivation, hybridization, and the electrification of accessories.
- Navistar will design and develop a vehicle and powertrain with electrified engine components that can enable higher engine efficiency and a significantly more aerodynamically reengineered cab.
- Volvo Technology of America will develop and demonstrate a tractor trailer combination with lightweight cab that achieves the freight efficiency goal using alternative engine designs and a variety of system technologies.
SuperTruck II projects will research, develop and demonstrate technologies to improve heavy-truck freight efficiency by more than 100%, relative to a manufacturer’s best-in-class 2009 truck, with an emphasis on technology cost-effectiveness and performance. Though SuperTruck II will build on lessons learned during the first project, it will produce completely new trucks.
Volvo Trucks’ Nyberg explained that because this second project requires truck makers to demonstrate a one- to two-year payback on technologies used, his company will have to eliminate some of the costlier systems that were deployed on the first SuperTruck. This requisite quick payback also suggests that more of the improvements that make the final cut will also proceed to production vehicles.
So what does the market look like for heavy trucks? According to an April 2016 report by Stifel Financial Corp. (St. Louis, MO, US), the forecast will be down from 2015:
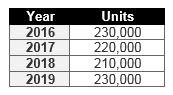
SOURCE: Stifel Financial Corp.
Meanwhile, Stifel reported that the medium duty truck segment, which is less volatile, was up in 2016.
An alternative source of market info, FTR (Bloomington, IN, US) announced an upturn earlier this month, with net orders for Class 8 trucks in North America projected to hit 19,300 units for November, a 41% increase over October. That still annualizes out to only 191,000 units, but FTR says inventories have finally dropped and manufacturing is regaining strength, connoting continued upward movement through early 2017. The table below shows Class 8 market share by manufacturer.
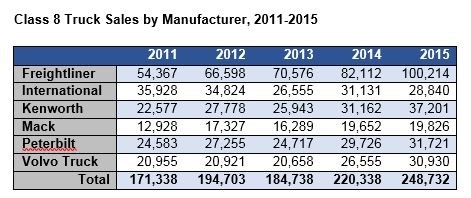
SOURCE: Ward’s Automotive Group, Motor Vehicle Facts and Figures 2015
http://cta.ornl.gov/vtmarketreport/heavy_trucks.shtml
Related Content
SMC composites progress BinC solar electric vehicles
In an interview with one of Aptera’s co-founders, CW sheds light on the inspiration behind the crowd-funded solar electric vehicle, its body in carbon (BinC) and how composite materials are playing a role in its design.
Read MoreAutomotive chassis components lighten up with composites
Composite and hybrid components reduce mass, increase functionality on electric and conventional passenger vehicles.
Read MoreCarbon fiber, bionic design achieve peak performance in race-ready production vehicle
Porsche worked with Action Composites to design and manufacture an innovative carbon fiber safety cage option to lightweight one of its series race vehicles, built in a one-shot compression molding process.
Read MoreRecycling hydrogen tanks to produce automotive structural components
Voith Composites and partners develop recycling solutions for hydrogen storage tanks and manufacturing methods to produce automotive parts from the recycled materials.
Read MoreRead Next
Developing bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read MoreAll-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read More























