Airbus PERIOD project to pioneer satellite factory in space
PERIOD consortium to prepare concept for in-orbit demonstrator for satellite assembly and manufacturing in space, with potential for composite materials.
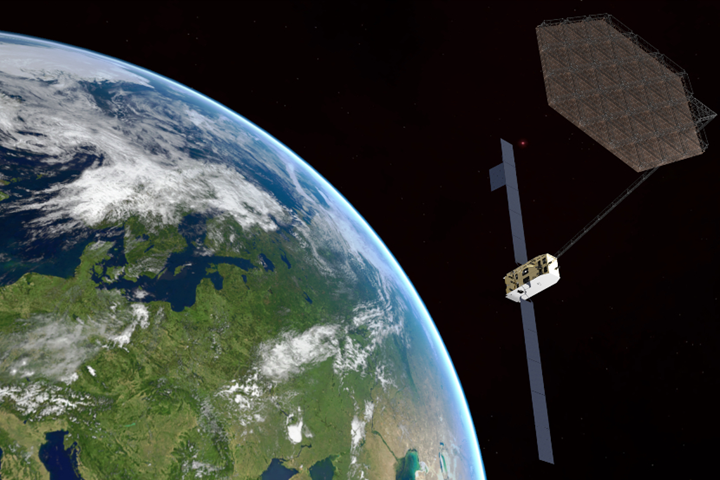

Illustration of Space Manufacturing—large antenna reflector. Photo Credit: Airbus
Airbus (Toulouse, France) announced on March 11 that it has been selected by the European Commission to study spacecraft manufacturing in space through the Horizon 2020 Programme. The PERIOD (PERASPERA In-Orbit Demonstration) project focuses on satellite assembly and manufacturing in orbit. This A/B1 phase study contract, worth €3 million, will last two years, with the objective to continue with a demonstrator in orbit.
More specifically, this “orbital factory” envisioned by PERIOD will reportedly pioneer construction of major components such as antenna reflectors, assembly of spacecraft components and satellite payload replacements, directly in space; among the materials that will be manufactured in space, Airbus says its colleagues and partners have not ruled out or privileged any materials so far, therefore giving potential to both metallic and composite structures.
Airbus says this project is the precursor to future manufacturing of large structures in orbit, revolutionizing the way space systems are designed, built and operated. The aerospace company also notes that it has significant advantages over the traditional approach — where everything is produced on Earth and subsequently transported to space — since objects made in space are freed from the constraints and requirements of launch (launcher mass and volume limitations, structural strength to withstand launch).
To achieve this goal, Airbus Defence and Space (Bremen, Germany), is leading a team of seven European innovators, bringing their own expertise in fields such as robotic operation, virtual reality and in-space assembly: DFKI, EASN-TIS, GMV, GMV-SKY, ISISPACE, SENER Aeroespacial and Space Applications Services.
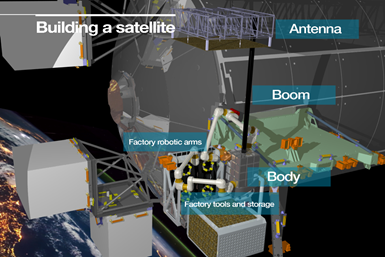
PERIOD demonstrator option using ISS for in-orbit manufacture and assembly. Photo Credit: Airbus.
By validating disruptive capabilities, PERIOD will demonstrate the value of in-space servicing, manufacturing and assembly. It will also help Europe develop capability and industrial infrastructure to put it at the leading edge of the in-orbit servicing and manufacturing market. PERIOD will stimulate future research and generate new market opportunities, leading to jobs and growth in forward-looking technology.
When discussing its potential, Airbus says the future space factory, as well as the demonstrator, could be orbited by a launcher and would then activate and start producing in orbit as a free flyer. An alternative demonstration mission, offering more flexibility and for a lower cost, would be to use ISS infrastructure.
“Airbus has been working on in-orbit manufacturing technologies for more than a decade and the PERIOD program will help Europe move its combined technological know-how to the next level,” says Silvio Sandrone, head of Space Exploration future projects at Airbus. “Future large-scale space systems can only be manufactured and assembled in orbit, so it’s crucial that Europe is at the forefront of this key capability.”
Airbus teams are already involved in a number of other in-space research programs including Metal3D, a metal 3D printer due to be deployed to space next year, in a project funded by the European Space Agency (ESA), and the MANTOS project, which demonstrated robotic and AI-based assembly operations with the support of German Space Agency (DLR).
Related Content
-
ASCEND program update: Designing next-gen, high-rate auto and aerospace composites
GKN Aerospace, McLaren Automotive and U.K.-based partners share goals and progress aiming at high-rate, Industry 4.0-enabled, sustainable materials and processes.
-
Plant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
-
PEEK vs. PEKK vs. PAEK and continuous compression molding
Suppliers of thermoplastics and carbon fiber chime in regarding PEEK vs. PEKK, and now PAEK, as well as in-situ consolidation — the supply chain for thermoplastic tape composites continues to evolve.













