Carbon fiber-based BMC wears well
Carbon fiber and ceramic are combined with a proprietary resin system to create a novel, extremely high-wear bulk molding compound (BMC) for centrifugal pump application.

ZeMC2, Zeon Technologies and Asbury Carbons worked together to develop 3858A, a carbon fiber/ceramic bulk molding compound (BMC) that is conductive and uncommonly wear-resistant.
ZeMC2 reports that it was approached by a manufacturer of centrifugal pumps who was looking for a new bushing material capable of outperforming the typical metal or plastic industry standards. Centrifugal pumps can range in size from a few gallons per minute to more than 10,000 gpm, and can be found in a range of applications including irrigation, flood water evacuation, water circulation, refinery “offsite” loading and transfer, chemical transfers, and more.
The typical design of centrifugal pumps locates a bushing (or sets of bushings) around the outside of a spinning shaft to provide mechanical stabilization to the shaft while rotating at high RPM. These bushings are typically made out of a metal or plastic material and have a life span of one to two years. Primary modes of failure of typical bushings are related to the high stress — thermal and mechanical stress — developed during operation. Mechanical wear, chemical erosion and debris impact are also well-known failure modes.
In the particular application studied, the pump design required a start up and dry run for 1 hour, generating extremely high temperatures and associated stresses on the bushing materials. Clearance tolerances for the shaft bearings ranged from 1/1000-1/20,000 of an inch. The pump manufacturer was looking for a thermally stable, conductive and lubricious material. Traditional wear bushings would expand, melt, or bind in the application as they lacked the necessary properties, ultimately resulting in a variety of failure modes including:
- Pump seizure
- Shaft wobble due to gap
- Shaft wear due to binding
- Catastrophic failures
- Pump performance decreases
ZeMC2 and Zeon Technologies developed a proprietary resin that was combined with Asbury’s novel carbon fiber materials, and ceramic, to create a new BMC with outstanding performance capabilities. The BMC is called 3858A and supplied by ZeMC2. It exhibits significantly improved thermal stability through a range of operating temperatures, as well as improved strength and toughness made possible by Asbury’s graphite and carbon fiber material solutions. 3858A can be machined and press fit, is chemically inert and conductive, and can be manufactured in virtually any bulk feedstock size.
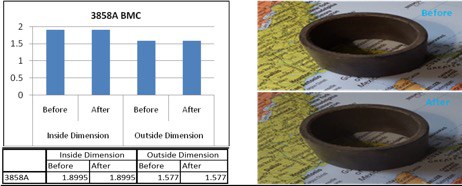
After four years of service in a cetrifugal pump, bushings fabricated with 3858A BMC, featuring a proprietary thermoset resin, showed no change in inside or outside dimension. Similar tests with polyphenelene sulfide (PPS), polyamide-imide (PAI) and polyimide showed dimensional degradation.
After 2,000 operating hours in extreme application conditions (dry run, high/low temperatures), 3858A samples were analyzed and benchmarked against competitive materials. In short: 3858A significantly outperformed other competitive materials (PPS, PAI, PI), showing no sign of degradation. After four years in the field, the companies says, bushings show no measurable or visible wear.
Mechanical properties of 3858A:
- Specific gravity: 1.84
- Mold shrinkage: 0.001 mm/mm
- Water absorption: 0.4%
- Flex strength: 90.1 MPa
- Compressive strength: 243 MPa
- Izod un-notched: 11.59J
- Tg: 221°C
- CTE: 10-5
















