SAMPE 2011 Long Beach Product Showcase
Huge show, huge new product offerings … huge success.
The annual Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering’s (SAMPE) Convention & Exhibition returned, for the first time since 2008, to its long-time base in Long Beach, Calif., after a first-ever Pacific Northwest showing last year in Seattle, Wash. The four-day event, held May 23-26 at the Long Beach Convention Center, met with considerable success. The SAMPE 2011 exhibit hall was sold out this year, with 356 exhibitors (including 106 first-time exhibitors) representing 555 companies. Attendance figures indicated the show took a large leap; the official count topped 7,100, with delegates coming from 48 U.S. states, the District of Columbia and 27 other countries.
Organized by SAMPE’s Orange County Chapter, the SAMPE conference was cochaired by Joyce Lentz, president of National Aerospace Supply Co. (San Juan Capistrano, Calif.), and Darrell Reed, quality control engineer at Exova OCM Test Labs (Anaheim, Calif.). Eight tutorials and more than 250 technical papers were presented by M&P practitioners and researchers.
"SAMPE is on an upward trend," commented Dr. Allan Crasto, associate director at UDRI (Dayton, Ohio) and sitting SAMPE international president. "We seem to have fully recovered from the impact of the recession.”
On Tuesday, conference delegates attended a keynote presentation on “Understanding and Managing Risk in Human Space Flight Developments and Operations” by Dr. Mike Ryschkewitsch, chief engineer at NASA. He discussed NASA’s approach to certification of systems for human spaceflight.
Wednesday’s keynoter, Andreas Wüllner, managing director of SGL Automotive Carbon Fibers GmbH (Munich, Germany), filled in the background on the events that led to the much-publicized decision by the SGL/BMW joint venture to build its now nearly complete captive carbon fiber production plant in Moses Lake, Wash. Wüllner reported that the carbon fiber manufacturing facility is complete and that testing of the first production line will begin this summer, followed by the plant’s official opening sometime in third quarter 2011. In his presentation, “SGL Carbon Group – BMW: A Visionary Joint Venture for Carbon Fiber Composites in Automotive Applications,” he updated the audience on the development of the BMW all-electric i3 and hybrid electric i8 vehicles, both of which make use of resin transfer molded SGL carbon fiber composites in the passenger cell, called the Life Module. During the Q&A after his address, Wüllner was asked about repair of carbon fiber composites on the two car models in the event of damage. Wüllner said that BMW is establishing dedicated global repair facilities designed specifically to repair damaged composite structures. He would not say, however, whether body panels (hood, roof, door panels, etc.) on the i3 and i8 would be made of composites.
In addition to keynote presentations, conference attendees had their pick of distinguished lectures, panels and sessions to attend. Topics included natural materials, out-of-autoclave technology, design and analysis, tooling, repair and nondestructive evaluation, to name a few.
SAMPE 2012 will mark the society’s return to its East Coast hub. The convention will be held May 21-24 in Baltimore, Md. at the Baltimore Convention Center.
On the show floor
Given the abundance of exhibitors this year, HPC staffers anticipated that a number of newsworthy developments might be on display. They were correct in that assumption. On the following pages, you’ll find a sampling of what was available.
Automated mold cleaning/polishing
Abrasive Warehouse & Equipment (Houston, Texas and Ontario, Calif.) showed systems designed and built by Walther Trowal GmbH & Co. KG (Haan, Germany) to polish mold surfaces and /or remove coatings and contaminates from those surfaces. The Multi Vibrator MV uses clamping fixtures to hold components, such as mold tools, in a bowl filled with an abrasive, fine media. Vibration is used to activate the media in a predictable way to accomplish polishing or cleaning. West Coast regional manager Michel Kraber pointed out a new starch-based abrasive that is capable of cleaning composite tool surfaces without damaging them.
New name & off-angle scrims
Adfors (Grand Island, N.Y.), the new name and brand for Saint-Gobain Technical Fabrics, showed its line of off-angle specialty scrims, using aramid, polyester, carbon and a wide range of other high-tenacity performance fibers. Laid scrims and other products are used for cost-effective structural reinforcement with less bulk and weight, says the company, in applications such as technical sailcloth.
Material modeling software
AlphaSTAR Corp. (Long Beach, Calif.) introduced visitors to its recently released MCQ Composites material modeling software. Developed to enable rapid design, modeling and analysis of advanced composites, the program reportedly assesses material behavior that does not require finite element modeling by means of a unit cell (meshless) approach. Applicable to all un-notched laminates where a uniform stress persists, the software can model all types of composite architecture, including tapes, 2-D and 3-D wovens and braids. Unlike some software packages, MCQ does not require the input of actual tested fiber/matrix properties. Functions include laminate analysis (strength, stiffness, electrical and thermal properties prediction); rapid, accurate calculation of A- and B-basis allowables; prediction of design failure envelope; nonlinear material characterization and optimization; and much more.
Entry-level automated cutter
Autometrix Precision Cutting Systems (Grass Valley, Calif.) demonstrated the cutting accuracy and utility of its Advantage flatbed cutting system. Designed for knife or rolling-blade operation, the system cuts at a maximum rate of 22 inches/sec (560 mm/sec). Advantage is the low-end option of three units designed to bridge the gap between hand cutting and high-end automated cutting. It sports a carbon-composite beam, a stepper-driven direct-drive rack and pinion, optimized speed control for smooth operation, and blade and pen-tool options. The cutter is complemented by two upgrades: the M-4, with a maximum 46-inch/sec (1,160 mm/sec) cutting speed; and the M-8, with 66-inch/sec (1,680 mm/sec) capability. The systems each come with the company’s 2-D CAD design software. According to technical sales rep Joel Myers, demand is high for affordable cutting solutions that can be used in trial development. The entry-level system, therefore, is priced at an affordable $30,000.
Hot bonder for composite repairs
BriskHeat Corp. (Columbus, Ohio) exhibited its new hot bonder, the ACR MiniPro. The single-zone, low-profile composite repair device weighs less than 18 lb/8 kg and has a color touch screen and a USB data port to facilitate easy software updates. The company says it also can design and manufacture custom heat blankets and hot-drape formers for unusual repair situations.
Hot-melt prepregging technology
C.A. Litzler Co. Inc. (Cleveland, Ohio) showed for the first time at a U.S. trade event its recently acquired S-wrap hot-melt prepregging technology. Pioneered by Steven Vellman’s Western Advanced Engineering Co. (WAECO, Orange, Calif.), the trademarked S-wrap prepreg process is generally credited as the first method to advance prepregging reliability and repeatability beyond the "black art" arena. The S-wrap machine reportedly can increase production to 100 ft/min (30.5 m/min) vs. competing designs that run at 15 ft/min (4.6 m/min). Litzler recently bought WAECO’s technical assets, and Vellman has stayed on to engineer and promote new technology. WAECO machines include systems for development and production scenarios. The machines range from 12-inches to 60-inches (305-mm to 1,524-mm) wide, including online and offline filmers. Litzler personnel also confided that a unique new (pat. pend.) thermoplastic prepreg machine is on the horizon.
Compounds for tool backing
CASS Polymers (Madison Heights, Mich.) debuted a tooling concept that uses a sandwich structure, featuring composite facesheets and either of two “tooling dough” cores from the company’s ADTECH division. ADTECH EL-323 TC room-temperature or EL-325 HTTC high-temperature, pliable epoxy tooling compound is applied to the back of a fiber-reinforced epoxy tool face to any thickness greater than 0.25 inch/6.35 mm, without excessive exotherm. The cured compound forms a dimensionally stable, tough, lightweight core that can be machined as well as drilled and tapped. A fiber-reinforced epoxy back face completes a sandwich that will exhibit high stiffness. EL-323 TC has a convenient mix ratio of 1:1 by volume, cleans up with soap and water and contains no corrosive or noxious aromatic amines. EL-325 HTTC has a mix ratio by weight of 100 parts resin to 25 parts hardener and contains no MDA or VCHD, but its corrosive hardener requires that technicians wear gloves. Each tooling dough can be mixed by hand or via mechanical dough-type mixer.
Anisoptropic, noncrimp fabrics
Chomarat North America (Anderson, S.C.) drew attention to its engineered anisotropic C-Ply fabrics. Designed for composite structures that will be subjected to bending and twisting, these “unbalanced building blocks” are based on a laminate layer that combines axial fiber (0°) and an off-axis fiber printed at 25°, developed at Stanford University by Professor Steven Tsai. Assembled as stitched bi-angle noncrimp fabrics, these materials bring benefits to laminate design that cannot be duplicated with conventional balanced (quasi-isotropic) laminates (see Tsai’s discussion of this emerging technology in "Improving laminates through anistropy and homogenization," listed under "Editor's Picks," at top right). The company reports that the construction can be adapted to all composite molding processes (closed and open mold) and all types of reinforcement fibers.
Aerospace marine fastening solutions
Click Bond Inc. (Carson City, Nev.) focused on both aerospace and the marine industry at its booth. The company recently received American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) certification for many of its adhesive studs and cable-tie mount products, including its large, adhesively bonded deck stud, which is used in a U.S. Navy application to fasten deck plates on an amphibious vessel. The stud reportedly withstands 9,000 lb/4,000 kg in shear force.
Software upgrade adds manufacturability
Collier Research Corp. (Newport News, Va.) used the show to introduce a new update, Version 6, to its flagship software product, HyperSizer. The optimization program analyzes dimensions and layups to reduce the structural weight of components in the aerospace, wind energy, shipbuilding and transportation industries; the new version adds manufacturability to the program, reducing the number of ply drop-offs and emphasizing continuous plies for more effective layup and part production, says company principal Craig Collier. The analysis data can be exported easily to CATIA or FiberSIM for interface with layup software.
Self-heating RTM tooling
Compose (Bellignat, France), a tooling company, showcased its expertise in a wide range of tool concepts for composites. These included its Autonomous Tool Concept, a self-heated, out-of-press tool for resin transfer molding (RTM), equipped with the company’s patented IronJaw clamping system. On display was a complex aircraft door demonstrator, a part made in one piece from a 3-D stitched carbon preform in a multipart, autonomous RTM tool. The demonstrator was produced as part of a development project with Group Latecoere (Toulouse, France).
Diamond and CBN grinding wheels and tools
Superabrasives manufacturer Continental Diamond Tool Corp. (New Haven, Ind.) showcased its portfolio of diamond and cubic boron nitrite (CBN) grinding wheels and tools. Diamond and CBN abrasives are bonded to tools with phenolic resin, powered metals or electroplating. The company specializes in design and production of drilling, dressing, cutting and grinding products. Company representatives emphasized their fully equipped machine shop and extensive materials inventory, which reportedly enable technicians to design and deliver custom machine tools in 7 to 10 days, not the industry-typical two months. Plated products usually feature a single layer of diamonds or CBN bonded by a nickel alloy. Metal-bonded tools feature diamond or CBN sintered in position by a powdered metal coating that holds its shape and distributes heat generated by grinding.
New oven-control/data-acquisition system
Oven and thermal processing equipment supplier Despatch Industries (Lakeville, Minn.) reported that it is developing a new control and data-acquisition system for its oven products. The control system can fully control the vacuum bagging process, and the data system records all necessary information from the thermocouples, vacuum transducers and other monitors to document the cure cycle. The company also recently announced new orders from China (see the “Biz Brief” under "Editor's Picks").
Conductive quartz fabric
Eeonyx Corp. (Pinole, Calif.) has a new addition to its EeonTeX product line. AQ503-SD-P is a quartz plain-weave fabric (99.99 percent pure fused silica) coated with a thermally stable, electrically conductive ink. The ink can be applied in selective areas or patterns (via screen printing or pad printing), permitting customers to develop resistive-heating elements in composite laminates (e.g., for deicing applications), as well as radar-absorbing composites (for stealth applications) and static-free composites. The fabric’s areal weight is 3.58 oz/yd2 without the coating. Available in 40-inch/1,016-mm widths with a 5-mil thickness, the fabric can be coated for surface resistivity ranging between 60 and 1,500 ohms, and it performs adequately at service temperatures as high as 250°C/482°F.
Graphite machining services
Electro-Tech Machining Inc. (ETM, Long Beach, Calif.) demonstrated its expertise in the machining of graphite used for composite tooling for carbon/carbon structures and specialty graphite parts, such as fuel-cell bipolar plates. The company also supplies materials for electrical discharge machining (EDM), including graphite electrode materials and EDM wires. Further, it has a large-envelope, 5-axis CNC vertical machining center with full CAD/CAM 3-D surfacing support, as well as laser tracker inspection capabilities that reportedly ensure production of high-precision tools.
Automotive sector joint development project
Evonik (Parsippany, N.J.), in a newly designed booth, highlighted its involvement in a new joint-development project for the automotive sector, working with partners Johnson Controls GmbH (Burscheid, Germany), Jacob Plastics GmbH (Wilhelmsdorf, Germany) and Toho Tenax Europe GmbH (Heinsberg, Germany), together with the University of Aachen’s Institute for Textile Technology and Automotive Institute. The three-year CAMISMA project aims to reduce the weight of a standard automotive metallic system by 40 percent, with the use of multiple material systems. In particular, research will focus on a seat panel structure. Evonik’s high-temperature polyamide 12 resin, trademarked VESTAMID, is one element of the new material system approach.
Tape-layed production parts
Fiberforge Corp. (Glenwood Springs, Colo.) displayed an 11.8 inch by 17.4 inch by 1.2 inch (298.5 mm by 441.3 mm by 30.5 mm) bezel, codeveloped with Marquez (Montréal, Québec, Canada), that is the structural bone of the seven-piece window assembly on the Bombardier (Montréal, Canada) Global Express business aircraft. The part’s specialized bidirectional laminate sequence uses 19 plies of unidirectional S-2 Glass-reinforced polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) to achieve tightly limited deflection in two directions, enabling a hermetic seal. (S-2 Glass supplied by AGY Holdings Inc., Aiken, S.C.) Also on display: A half-scale demonstrator of the new all-carbon/polyetheretherketone (PEEK) floor panel for Sikorsky’s (Stratford, Conn.) C-53K Super Stallion helicopter, developed for the U.S. Marine Corps. The company is gearing up for full production of the complete full-size panel that measures approximately 2.5 ft by 4 ft (0.76m by 1.2m). The complex panel includes welded and bonded parts, each layed up by the company’s proprietary Relay Station tape-laying system, which is available for licensing to composites manufacturers.
Software update: Bettter delamination prediction
Firehole Composites (Laramie, Wyo.) attracted visitors interested in the company’s Helius:MCT software, now offered with Cohesive Zone Modeling (CZM), which enables better prediction of delamination. According to the company, CZM has been shown to be the most accurate method for predicting the initiation and progression of composite delamination, based on experimental test results that compare favorably with the analysis.
Paste and sprayable modeling materials
Distributor Freeman Manufacturing & Supply Co. (Avon, Ohio) put the spotlight on two new offerings: RenPaste 4618-1 with Ren 4619 hardener, a two-part seamless modeling paste is an intermediate-temperature material intended for aerospace and marine model/plug builds. Odorless during cure and machinable after 24 hours, the paste reportedly produces a fine, seamless surface with high dimensional stability. When it is applied over an expanded aluminum base, the combination produces lightweight, easy-to-handle tools. Applied in layers up to 0.75-inch/19-mm thick, the paste can be built up in stages (cured between coats) to greater thicknesses. Postcured tools can be used to form and cure parts up to 225°F/107°C. The second offering was Master Works M2, a “milling media” (tooling paste) for pattern (plug) builds, developed by William Ivor Stone Ltd. (Ludlow, U.K.). Designed for use with Master Works spray equipment, the two-component material is water based (water cleanup) and can be applied at a 2:1 ratio over rough-milled expandable polystyrene (EPS) foam forms to provide a machinable surface coat at any desired thickness (it also can be hand carved). Cure involves low exotherm (+30°C), and the material achieves a Shore D hardness of ~50. The cured material yields no toxic dust or odor during milling and accepts a variety of surface coatings.
Robotic inspection cell
Robotic systems integrator Genesis Systems Group LLC (Davenport, Iowa) specializes in factory automation of robotic assembly and handling systems for welded, mechanical and adhesive assembly processes and machine-tending applications. The company showed its NSpect robot nondestructive inspection (NDI) system, a two-station, single-robot work cell designed for automated NDI processes. It features a Kuka KR30HA 6-axis robot, FlawInspecta ultrasonic array imaging system, Allen Bradley PLC-based control system and ANDSCAN Robot postprocess analysis software. The NSpect family of NDI systems has been developed to provide a cost-effective, accurate inspection solution for large volumes of composite components.
Compact cutting system
Gunnar Advanced Cutting Solutions (Arlington, Wash. and Rebstein, Switzerland) specializes in cutting systems for niche applications in which cut quantities are too small for the major flatbed cutting system providers, says sales manager Joe Gnagey. Gunnar booth personnel observed that in addition to the company’s composites customers, show traffic was peppered with metal-based manufacturers that are looking at composites, with a trend toward small cutting tables that enable experiments with materials on a small scale. Accordingly, the company’s affordable and compact, fully computerized TTC119 flatbed single layer cutter with vacuum table was demonstrated on the show floor. Compatible with all major CAD systems and able to read major cutting file formats (DXF, HPGL, ISO, Gerber and Lectra), the machine’s maximum cutting speed is 1,500 mm/sec (59 inches/sec).
Multiple aerostructures capabilities
The Hampson Group, which encompasses seven U.S. facilities, including Coast Composites Inc. (Santa Ana, Calif.), Composites Horizons Inc. (Covina, Calif.) and Texstars Inc. (Grand Prairie, Texas), exhibited the Group’s multiple capabilities for the production of aerostructures. Notable news included Composites Horizons’ recent acquisition of a new 5-axis CNC machining center with rotary table, manufactured by FIDIA SpA (San Mauro Torinese, Italy) and a new autoclave to support its high-temperature part and assembly fabrication. The company is the primary supplier of the PMTR-15 augmenter flaps on the F-16 military jet.
Weight-saving carbon fabrics
Hexcel (Stamford, Conn.) showcased its range of composite materials and applications, including a composite forward engine mount link that was shown for the first time. Using HexPly 8552 prepreg with HexTow IM7 carbon fiber, Blair Composites (Medford, N.Y.) manufactured the link for a commercial aircraft. It offers a 63 percent weight reduction compared to an equivalent metallic component at a competitive cost, while delivering structural performance that exceeded initial expectations. Hexcel also promoted PrimeTex, a range of carbon fabrics processed for a smooth weave with a high degree of closure, which results in outstanding visual quality. Fiber tows are spread in both warp and weft directions, providing a more uniform weave and a thinner, more closely woven fabric that leads to weight savings, better mechanical properties and less porosity in the laminate.
Smaller, lighter ultrasound camera
Imperium Inc. (Beltsville, Md.) showed the latest version of its Acousticam ultrasound camera, now one-third the size of the older version and redesigned to be lighter and more ergonomic. The new electronics provide a clearer image, and the operator can now “scan and stitch” together multiple images via encoder to produce a larger mosaic image of any imperfections in the laminate. With wireless capability, the data can be viewed remotely as a technician scans the part surface. The camera is used by The Boeing Co. (Seattle, Wash.) and other aircraft OEMs.
Built-to-order machining cells
Ingersoll Machine Tools Inc. (Rockford, Ill.) highlighted its Mongoose and Lynx Automated Fiber Placement Systems. Built to order, the systems accommodate the specific customer’s part geometry, material type and production rate. Machine design options include vertical and horizontal platforms, medium-to-large work envelopes, a variety of tool handling methods and modular construction of subcomponents, which permits shorter lead times for system assembly. www.ingersoll.com
New machinery expands part production
ITT-Integrated Structures (N. Amityville, N.Y. and Salt Lake City, Utah), a producer of primary aerospace structural assemblies of complex design in thermoset and thermoplastic composites, revealed that it recently purchased a MAG Cincinnati (Erlanger, Ky.) Viper 6000 automated fiber placement (AFP) machine for production of parts for numerous programs at its Salt Lake City facility. Another machine may be purchased within the next year, says the company.
Two-needle, single-side stitching machine
Keilmann Group (Lorsch, Germany), manufacturer of stitching equipment for fabrication of composite preforms and other industrial applications, emphasized at the show its two-needle, one-sided stitching technology. It is used in the manufacture of the composite landing gear braces for the Boeing 787, in which it penetrates 2 inches/50.8 mm of carbon fiber fabric. Company representative Guido Jaeger says there are 11,000 stitches per brace. The braces are manufactured by Messier-Dowty (Vélizy, France). Keilmann’s technology also is used to produce preforms for structures under development by NASA and The Boeing Co. (Seattle, Wash.) as they explore next-generation aircraft structures (see story, this issue, p. XX).
Heat-reducing carbide router bits
LMT Onsrud LP (Waukegan, Ill.) featured its new 66-900 Series high-performance routers for composites. The coated carbide bits are suitable for either hand-fed or CNC applications. Although the bits are similar to typical “burrs,” they offer several advantages. Composite material is cut into distinct chips, rather than ground away, which reduces heat on the laminate. Deep cutting flutes increase the chip flow and reduce bit wear for longer tool life. And the geometry produces a smooth edge on the part for greatly reduced secondary operations. In CNC router mode, higher speeds and feed rates are possible, increasing productivity and lowering costs, reports the company.
Laser-based metrology
Laser ply placement and kitting system provider Magestic Systems Inc. (Westwood, N.J.) has expanded its horizons into laser-based metrology. Its new TruPLY Compensation system uses laser technology to evaluate the thickness consistency of autoclaved prepreg parts. The company also introduced its TruPLAN software suite, which makes it possible to run multiple what-if scenarios. The program uses multiple algorithms to assess the cost impact of unique design features and surface definitions across multiple manufacturing processes, such as automated fiber placement (AFP) vs. automated tape laying (ATL) vs. hand layup. Also new is the TruFIBER programming suite. According to spokesman Dylan McLean, it can save hours in the calculation of ply placement paths when using AFP or ATL, helping the user determine whether the material placement that satisfies design requirements can be manufactured. The programs enable designers to confront design-to-manufacturing issues earlier in the development process, giving them an accurate assessment of the design/manufacturing trade-offs that must be negotiated.
Dispensable edge/core filler
Magnolia Plastics Inc. (Chamblee, Ga.) presented two new products at the show, dubbed 7001 and 7002. Intended for edge and core fill applications, the new dispensable epoxy-based materials offer ultralight weight thanks to glass microspheres, saving significant weight for aerospace interior parts. With a specific gravity of only 0.6, the products meet the FAA’s FAR-25 853 flammability requirements.
Toolmaker expands manufacturing capabilities
Major Tool & Machine (Indianapolis, Ind.) announced its expansion into high-speed machining, occasioned by the recent purchase and installation of a Jobs LinX Linear Motor High Speed 5-axis machining center (supplied by JOBS SpA, Placenza, Italy) and two Cincinnati U5 5-axis Portal Mills (from MAG Cincinnati, Hebron, Ky.). The 500,000 ft2 (46,452m2) shop employs 300 people. The company is a specialist in Invar tooling for aerospace composites manufacturers and also machines aluminum and composite tools.
Full-service resin transfer molding
Matrix Composites (Rockledge, Fla.) highlighted its expertise and pioneering role in closed mold resin transfer molding (RTM) for aircraft structures. A full-service job shop, Matrix works with epoxy, bismaleimide and polyimides to produce parts with very complex geometries and is currently involved in an undisclosed project with a military customer. www.matrixcomp.com
Release liner papers
Mondi Akrosil LLC (Menasha, Wis.) exhibited its line of release liner papers for the production of prepregs. Available in various types and widths of coated kraft paper, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene, the release “values” can be customized precisely to meet customer requirements, says the company. Individual packing, slitting or printing options are also available.
Small-scale vacuum mixer
Myers Engineering Inc. (Bell, Calif.) showcased its new Laboratory Mini-Vacuum mixer for laboratory-scale or formulation trial mixing applications. Available with a single- or multiple-shaft design, the disperser blade works to produce high shear dispersion to blend particularly difficult, high-viscosity materials. The vacuum design reduces any air entrapment to eliminate frothing and off-gassing. The company also produces a wide range of larger-scale mixers for production environments.
Nano-enhanced resin infusion film
Nanoledge Inc. (Boucherville, Quebec, Canada) introduced its LEO resin film series, a collection of nano-enhanced epoxy films for use in resin film infusion processes. Nanoparticle dispersions in the film provide enhanced toughness for epoxy parts that might otherwise be too brittle for an application. Formulated in film, the hot-melt product is sandwiched with fiber reinforcement during layup, avoiding lengthy flow paths that, during infusion processes, can create conditions in which filler particles can be filtered out of the resin as it flows through the dense fiber reinforcement. The resin flows very short distances during consolidation, maintaining uniform distribution of the nanotoughener.
New composites design center
The National Composite Center (Kettering, Ohio) called attention to its new Composites Manufacturing Design Center (CMDC). The Center will offer all composites businesses access to its structural design, optimization and manufacturability simulation capabilities. The move is expected to minimize the financial burden on small to midsized manufacturers by giving them access to design and simulation software and training and the opportunity to form collaborative research and development relationships with other users without having to purchase the software programs.
Portable, handheld flaw detector
The new Raptor imaging flaw detector from nondestructive testing (NDT) device manufacturer NDT Systems (Huntington Beach, Calif.) is a portable, handheld device that toggles easily between flaw detection and imaging modes and displays results on a 5.7-inch/145-mm VGA screen. It features a square and spike pulser; live A-, B- and C-scan capability; dual gates; 20-point DAC; support for SD cards up to 32 GB; timed and encoded B-scan; and peak echo hold screen-freeze and store capabilities. The probes are available as single or dual element, and the display modes include RF, +HW, -HW and FW. The unit measures 5.75 inches wide by 9.5 inches long by 3 inches deep (146 mm by 241 mm by 76 mm) and uses a rechargeable lithium-ion battery. www.ndtsystems.com
Composites design software
NEi Software Inc. (Westminster, Calif.) says to keep an eye out in Q3 2011 for release 10.1 of NEi Nastran, its composites design software. The new version will feature more fully integrated 3-D functionality, including 3-D micromechanics with progressive ply failure analysis. This feature includes multicontinuum theory (MCT) micromechanics, which highlights failure among all plies in a structure, not just the first ply. NEi says this allows the designer to meet specific load and mechanical requirements without overdesigning, which the company says is common when only first-ply failure data are available.
Core business acquisition
Core material manufacturer Nida-Core was acquired by 3M (St. Paul, Minn.) earlier this year, and during the past few months, 3M has been busy integrating the product line into its portfolio. For now, the Nida-Core name exists as a product line within the 3M Industrial Tapes and Adhesives Div., although 3M representatives said that the Nida-Core name eventually will be replaced. Meanwhile, 3M has introduced under its Nida-Core product line a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) closed-cell foam core with a polyester scrim that promotes adhesion on core materials. The scrim melts into the core during molding and, according to 3M, increases peel strength by more than 24 times, compared to unscrimmed PET core.
Epoxy-compatible surfacing film and epoxy prepreg
Park Electrochemical Corp. (Waterbury, Conn.) introduced two new products. The first, Aeroglide Surfacing Film, an epoxy‐based composite surfacing film, can be oven- or autoclave-cured at either 250°F/120°C or 350°F/180°C. Designed to minimize porosity in part surfaces, the standard 0.030 lb/ft2 film features woven glass-fiber reinforcement and is available in a variety of weights on 50-inch/1,270-mm wide rolls. Said to provide high-quality paintable surfaces, the film can be cocured with most epoxy prepregs. Further, it has an outlife of 45 days at ambient temperature and up to a one-year shelf life at 0°F/-17.8°C. The second new product, Easycure E-710 Epoxy Prepreg, features a modified epoxy system with a low cure-temperature range between 160°F and 250°F (70°C and 120°C). Advantages include a low cure temperature, good low-pressure consolidation and 60-day out-time at ambient temperature. It also comes in a flame-retardant version, Easycure E‐710FR, which meets the requirements of U.S. DOT FMVSS 302.
Cutting systems and cutting software
From down under, Pathfinder Australia Pty. Ltd. (Tullamarine, Victoria, Australia) brought its Pathfinder K-series knife-type cutting system. Available in 30-mm, 50-mm and 70-mm (1.2-inch, 2-inch and 2.7-inch) cutting heights and in widths of up to 3.8m/12.5 ft, the system has 12 basic configurations with more than 25 specialized options to suit almost any application. Custom systems can include multiple cutting tools and/or single- to multiple-ply capabilities on a single machine. New this year is PathWorks CAD software, available either integrated within the cutting system software (PathCut) or as standalone program. Features include automatic reading of standard industry files, photo digitizing, pattern design, magnetic pattern nesting, fully automatic pattern nesting and industry-specific wizards. Training for the system reportedly requires as little as 60 minutes.
Batch-type surface-treatment systems
In the Plasmatreat North America Inc. (Mississauga, Ontario, Canada) booth, Mikki Larner of Plasma Technology Systems (Belmont, Calif.) detailed the benefits of the company’s cold-gas plasma treatment systems. Depending on the plasma composition, the systems can clean surfaces of contaminants; provide activation and functionalization (alter the surface chemistry of polymers, making them more receptive to bonding with adhesives or coatings); or enable plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. On display was a batch system (scalable from 1.5 ft3 to 125 ft3 or 0.4m3 to 3.5m3) that features side-mounted electrodes. The system permits multiple part placement on trays for maximum efficiency. Also available are tumbler systems and roll-to-roll systems in widths ranging from 2 inches to 60 inches (50.8 mm to 1,524 mm).
Multiple moldmaking capabilities
Prospect Mold (Cuyahoga Falls, Ohio) demonstrated its production capabilities in the realm of highly complex, multipiece closed molds for composites. Serving a variety of markets since 1945, including aerospace, automotive and consumer goods, the company says it has the design skills and a large array of machining centers for producing closed RTM molds, vacuum and compression molds, fixtures and jigs and injection molding tools.
Cure monitoring equipment
RT Instruments (Woodland, Calif.) announced several new developments for those who characterize materials, including Lambient Technologies’ (Boston, Mass.) two dielectric cure-monitoring systems for thermosets. The LT-451 Cure Monitor and the TF-631 High Speed Dielectric Cure Monitor offer a simple method for observing the effects of chemical reaction rate, formulation and process parameters during the cure of thermoset polymers. Testable materials include epoxy, polyurethane and polyester resin and composites. The 631 model is optimized for QA/QC and studies of rapidly curing materials (e.g., polyurethanes). Both systems come with CureView software for instrument control, cure monitoring and data analysis. Also new for lab testing: Lambient’s LTP-350 MicroPress Miniature Press. Designed for pneumatic consolidation and cure of a wide range of composites, the portable system features independent controls for upper and lower platens and can be operated in either isothermal or ramp-and-hold modes. Temperatures range from ambient to as high as 350°C/660°F. The maximum applied force is 2,000 lb/909 kg, and the standard platen is 3-inches (75-cm) square.
Multiaxial and unidirectional noncrirmp fabrics
SAERTEX USA LLC (Huntersville, N.C.) exhibited its range of multiaxial fabrics for composite applications. Although wind is a major market for the company, general manager Stefan Maier said that more aerospace business is on the company’s horizon. He cited the recent agreements with Bombardier Aerospace through which SAERTEX will supply high-performance multiaxial and unidirectional noncrimp fabrics (NCFs) for the production of major primary structures for the new CSeries and Learjet 85 aircraft. The volume of orders during the next 10 years could exceed €250 million.
Ceramics from reinforced polymers
Starfire Systems (Schenectady, N.Y.) exhibited an array of ceramic composite materials, trademarked Polymer-to-Ceramic Technology (PTCC). The materials, designed for aircraft brakes and other friction applications, structural applications and thermal applications, are carbon-fiber-reinforced ceramic composites that rely only on pyrolysis to form a ceramic matrix from a thermosetting resin. This method avoids the use of dangerous precursors and conversion reactions that could compromise fiber integrity. The resulting ceramic machines easily and achieves high thermal stability. Sales director Al Cornell says the material, in prepreg form, will soon be used to make ceramic armor. Also new: Starfire SMP-10, which is reportedly the only single-component liquid precursor to silicon carbide (SiC) on the market. According to the company, it produces high-purity ceramic materials in short cycles, contains no solvents and requires none for processing. No chlorides, acids or other corrosives are generated during cure or pyrolysis. The finished ceramics are stable to 1800°C/3272°F in air and 2200°C/3992°F in inert gases.
Personnel changes
TenCate Advanced Composites (Morgan Hill, Calif.) has been active lately on the personnel front. Michael Favaloro, formerly with Ticona (Erlanger, Ky.), has joined TenCate as director, industrial sales and marketing, North America. And Steve Mead, who until two years ago managed sales and marketing at Fiberforge (Glenwood Springs, Colo.) and subsequently left the composites industry, is back as vice president of sales and marketing, North America at TenCate.
Thermocouples for autoclaves
TE Wire and Cable (Saddle Brook, N.J.) exhibited its line of AccuClave thermocouples, manufactured by the company since 1941. The very-small-diameter thermocouple wires are small enough to prevent leak paths in the vacuum-bagged composite layup, says the company. The wires are also available in a flat style, called AccuFlex, which further reduces any chance for markoff on the part edge.
Void fillers for aircraft interiors
3M Aerospace (Minneapolis, Minn.) introduced EC-3550 and EC-3555, the company’s new void fillers for aircraft interior applications. EC-3550 is slower curing than EC-3555, and both have a density of 0.58 g/cm3. They are said to be voidless. They also adhere to tapes, will not chip and meet all current fire retardant and flame, smoke and toxicity requirements for interior aircraft use. Both fillers are two-component products and are applied via cartridge.
Video-based testing system
Tinius Olsen (Horsham, Pa.) demonstrated its Video Extensometer, which replaces bonded strain-gage technology and other analog strain measurement techniques. The noncontact method evaluates strain live or via recorded video images. The sample is misted with contrasting white and black paints to give the coupon a visual texture, then it is placed in a test frame where test loads are applied. Strain is measured and calculated based on the change in image pixels. The software can calculate strain values in both the x and y axes. The Single Camera system uses a monochrome video camera, producing real-time point-to-point data accurate to ASTM E83 and ISO 9513 Class 0.5 standards. The Multi Camera system enhances Extensometer results with two to as many as eight cameras. This system can work on both tension and compression tests, can view and measure specimen strain from multiple sides, can make r and N value determinations and can be used with any test frame and frame software. According to district sales manager John Strauss, composite materials supplier Hexcel (Stamford, Conn.) is planning to invest in the technology in third quarter 2011.
High-temp hydraulic presses
TMP Inc., a Division of French (Piqua, Ohio) reported a good response from showgoers as it put the spotlight on the positives of its progress since its 2009 acquisition by Piqua-based French Oil Machinery Co. after 25 years of custom building high-temperature hydraulic presses and associated automation for compression, transfer and vacuum molding of all types of composites and thermoplastics for more than 1,000 customers in 16 countries. “Our acquisition … and subsequent restructuring confirms our commitment to the composites industry and allows us to better support our customers through focused sales efforts and increased product offerings of both TMP and French press design,” said TMP’s vice president, Dave Sledz. The company also offers laminating presses, intensive mixers and related components, controls and auxiliary equipment as well as machine service and rebuilding/upgrading.
Thermoplastics and thermoplastic composites
Tri-Mack Plastics Manufacturing Corp. (Bristol, R.I.) is a specialist in high-temperature engineering thermoplastics and thermoplastic composites. The company emphasized its expertise in injection molding, precision machining, injection toolmaking and parts manufacturing. Key parts of its mission include design for manufacturing and metal-to-composites conversion. It has extensive experience with high-temperature composite parts for jet engines and therefore says it can design complex parts with metal inserts and its EZ Fit thermoplastic bushings.
Video-based test systems
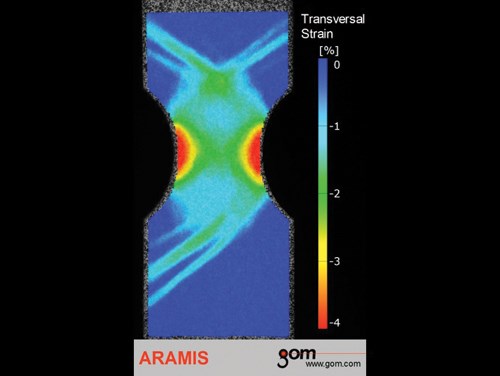
In the United Testing Systems Inc. (Huntington Beach, Calif.) booth, Trilion Quality Systems (Plymouth Meeting, Pa.) demonstrated the Aramis Optical 3D Deformation Analysis System. Designed and built by GOM mbH (Braunschweig, Germany), the noncontact and material-independent device can provide accurate data on 3-D surface coordinates, 3-D displacement and velocity, surface strain values and strain rates for static or dynamically loaded samples. Grey value distributions are calculated for subsets in each camera’s image, and a mathematical model of the sensor setup, the digital image correlation method and a triangulation calculation are combined to derive 3-D coordinates and convert them to precise x, y and z displacement values. Coupons are misted with white or black paint to introduce contrast, then they are loaded into a United test frame. Two cameras record the image in stereo (just as the human eye sees it) as loads are applied. Measurements are reportedly accurate to the micron level. Trilion’s application engineer Eric Schwartz notes that the system is designed for field use and need not be limited to lab scenarios.
Heated platens for press forming
Heated platen specialist Venango Machine Co. (Wattsburg, Pa.) emphasized its expertise in the field of (cartridge and strip) platen manufacture — heated via steam, hot oil or electricity. The company’s heat-tube platen technology reportedly distributes heat energy uniformly via a multilayered lattice of cartridge heaters/heat tubes. In platens for which heating and cooling must be expedited, strip- or cartridge-type electrical heating elements can be combined with water-cooling networks. Where temperature consistency over the entire platen surface is a critical need, the company offers MultiZone Platens, which feature thermocouple-based zoned temperature control and active temperature modification to reduce temperature variation across the platen surface. In tests, the MultiZone system reportedly held the variation to 2°F, compared to 24°F for a single-zone platen and 10°F for a heat-tube platen.
Platform for measuring devices
Metrology software company Verisurf Software Inc. (Anaheim, Calif.) demonstrated how its Verisurf program acts as a common platform for multiple measurement devices, including coordinate measurement machines (CMMs), laser trackers and inspection probes. The system reads all CAD file formats, permitting end-users to work with any CAD model, says the company, and it offers easily understood coordinate measurement capability in real time. At the booth, the software was running a laser projection system for part layup. The company reported that the software can work with any laser projection system.
New name and Web site
Bleeder and breather cloths manufacturer The Warm Co. (Lynnwood, Mass.) has updated its name and image in an effort to more accurately convey to the market the nature and scope of its products. The company is now called Warm Industrial Nonwovens and has a new Web site:
Patternless moldmaking services
Cast-tooling supplier Waukesha Foundry Inc. (Waukesha, Wis.) emphasized its long history with Invar (iron/nickel alloy) tooling. Its trademarked Cast Invar methods, says the company, provide a reliable means to form thin, lightweight tool faces of Invar 36 or Invar 42. In-house radiographic testing ensures the vacuum integrity of welds in large outgoing cast tool faces. Capabilities include patternless mold processing, in which robotic machining cells convert customer CAD data directly to toolpaths so that mold geometry can be machined precisely into the sand mold blanks. This eliminates the expense and equipment required for conventional patternmaking and thus reduces lead time and total tool cost. (Waukesha is one of several featured toolmakers in this issue’s “Tooling Update,” ).
Precision rollers for web converters
Webex Inc. (Neenah, Wis.), a manufacturer of large precision rollers for web handling and converting industries, offered its engineering and part expertise to showgoers involved in converting. The company also produces its own carbon fiber rolls and idlers, trademarked FeatherLight, which are made in a filament winding process.
Tackifier for epoxy prepregs/infusion processes
Zyvax Inc. (Ellijay, Ga.) revealed that one of the company’s newest products, StayZ Spray Interface Tackifier, is part of an undisclosed specification for Sikorsky Aircraft Corp. (Stratford, Conn.), and it will soon be included in an overall military specification. The company describes the tackifier as an innovative new formulation for all epoxy prepregs and infusion processes. It combines the sticky application of contact cement with the structural bond of epoxy in an aerosol can. The adhesive not only holds material in place, but it also cures with the matrix, eliminating the possibility that the adhesive could interfere with and weaken interlayer bonding in the laminate.
Read composites inductry product news from this year's other big trade event, the JEC Composites Show in Paris, by clicking on the articles under "Editor's Picks," at top right.
Related Content
Zeiss, Imperial College London summer school enhances materials, sustainability learning
Twenty-four next-generation students attended the Imperial College London this August to advance their scientific knowledge, with workshops, lectures, activities and a composites competition.
Read MoreBelzona opens fifth European SuperWrap Training Centre
Global training facilities provide intensive, first-class installer and supervisor training for proper use and application of Belzona composite pipe and tank repair systems.
Read MoreThe Native Lab launches composites course training membership plan
Courses that touch on the fundamentals of composite materials, design, analysis and more are available for individuals and companies alike through TNL’s online platform.
Read MoreToray, University of Chicago speed up polymer recycling R&D
A jointly developed multi-scale computational predictive technique can accurately predict viscoelasticity from the chemical structures of polymers, ramping up product maturation.
Read MoreRead Next
JEC Paris 2011 highlights
The news from this annual Parisian in-gathering of composites professionals is heavily weighted toward automotive lightweighting.
Read MoreJEC Paris 2011 Review
This annual Paris trade event’s statistics signal an advanced composites resurgence.
Read MoreImproving laminates through anisotropy and homogenization
Dr. Stephen Tsai, professor research emeritus in the Department of Aeronautics & Astronautics at Stanford University, discusses the merits of unbalanced (anisotropic) layers in composite laminates.
Read More