Cevotec’s Fiber Patch Placement wins Industry of the Future award
The additive fiber layup technology enables automated production of complex fiber composites.

Source | Cevotec
Cevotec (Taufkirchen bei München, Germany) has been awarded a “Processes of the Future” award for its Fiber Patch Placement solution for automated production of complex composite parts. The award was presented at the Industry of the Future Challenge in Vernon, France, by representatives from SKF (Gothenburg, Sweden), Atos (Bezons, France) and ArianeGroup (Courcouronnes, France).
The 2019 Industry of the Future Challenge was set up to promote Industry 4.0 solutions that make future industrial production smarter and the materials used more sustainable, increasing the potential of tomorrow’s industrial facilities.
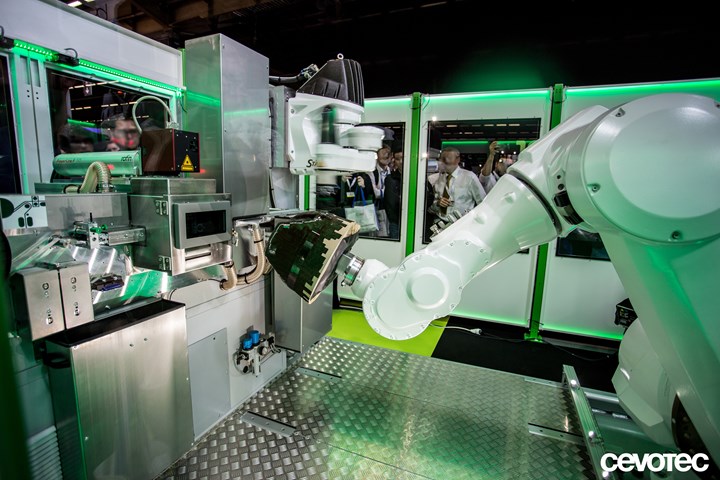
Source | Cevotec
Cevotec’s Fiber Patch Placement solution is an additive fiber layup technology that enables the automated production of complex fiber composites, extending the industrial application of composite lightweight technology to more components. Cevotec worked closely with SKF and ArianeGroup to apply the technology to identified production challenges of the partners.
“Fiber composites offer great lightweight and functional potential but are increasingly difficult to process when part design or fiber architecture are complex. Today’s often manual processes limit industrial-scale composites application,” explains Thorsten Groene, managing director of Cevotec.
“Manufacturers urgently need smart automation solutions to improve cost efficiency, quality and yield of their composites production. ... Our production systems enable composite manufacturers to do exactly that: produce more with less, that is: save time and money.”
Key application areas for Fiber Patch Placement are multimaterial sandwich components, parts with complex geometries and tailored reinforcement patches. Time and cost savings for manufacturers, compared to as-is processes, typically range from 20-60%, according to Cevotec. The company says it is also currently involved in several development programs with aerospace composites manufacturers.
Related Content
-
Pultrusion: The basics
A primer describing what pultrusion is, its advantages and disadvantages, and typical applications.
-
Sulapac introduces Sulapac Flow 1.7 to replace PLA, ABS and PP in FDM, FGF
Available as filament and granules for extrusion, new wood composite matches properties yet is compostable, eliminates microplastics and reduces carbon footprint.
-
TU Munich develops cuboidal conformable tanks using carbon fiber composites for increased hydrogen storage
Flat tank enabling standard platform for BEV and FCEV uses thermoplastic and thermoset composites, overwrapped skeleton design in pursuit of 25% more H2 storage.

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)







.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)





