CSP fine-tunes CF-RTM process, launches production programs
The carbon fiber RTM press will be installed at the CSP facility in Palmela, Portugal in order to run the company's first commercial applications using this technology.
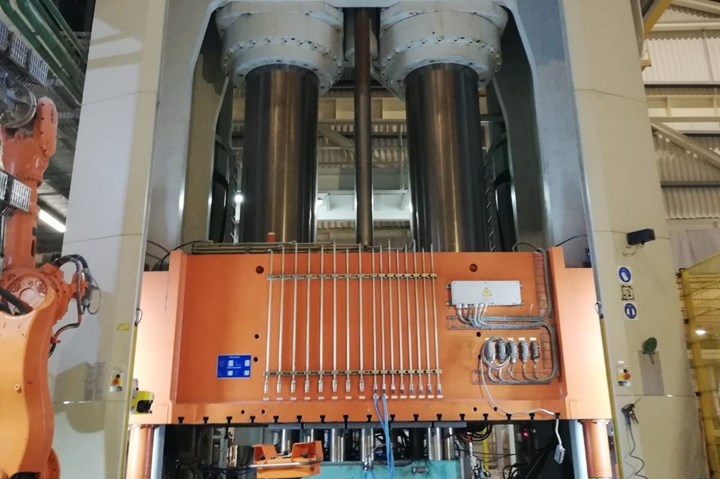

Photo Credit: Business Wire
After winning a JEC Innovation Award in 2016 for its Lincoln MKS Decklid Concept — a TCA Ultra Lite outer panel and a carbon fiber resin transfer molding (RTM) inner prototype — Continental Structural Plastics (CSP, Auburn Hills, Michigan) says it has fine-tuned its carbon fiber RTM (CF-RTM) process to the point that a premium automaker will be using the technology for closures on future vehicle platforms. These doors, reports the company, will feature both inner and outer panels as well as structural reinforcements molded using CSP’s advanced CF-RTM process.
When CSP set up its Center of Excellence for Lightweight Technologies and Carbon Fiber Processes in Pouancé, France, in 2013, the goal was to develop processes to make the use of carbon fiber in high-volume applications affordable and feasible. Since then, the CSP team in Europe has been working on developing a high-performance CF-RTM process that would result in high-strength, ultra-lightweight components to help OEMs address stringent CO2 emissions regulations. Specifically, the team has been focused on improving cycle time, utilizing automated preforming and lowering the cost of the carbon fiber materials.
“We have been targeting a three-minute cycle time using 100% recycled carbon fiber. With our multi-material decklid concept, we demonstrated this was totally possible,” says Marc Philippe Toitgans, director of Research and Development at CSP Europe. “Now we are proud to say we have collaborated with major OEMs in the United States and Europe on carbon fiber RTM programs and will see the first commercial applications of this technology very soon.”
From CAE analysis, flow simulation, preform process, mold design and full automation, CSP says it has built best-in-class expertise to support major structural and Class A CF-RTM programs for closures and other BIW applications. CSP’s key differentiators are based on:
- 100 bars of injection pressure, and up to 1,500 tons of pressure for closure applications.
- High fiber content (greater than 50%) for structural applications.
- 20-second injection time.
- Management of variable thicknesses.
- Weight savings of up to 30% when compared to aluminum.
To support several carbon fiber RTM programs that will begin as soon as the end of 2020, CSP and parent company Teijin Ltd. (Tokoyo, Japan) are investing in a dedicated CF-RTM production line in Palmela, Portugal. The initial investment of €5.5 million will include the installation of compression presses, RTM injection units and a bonding cell.
“We are excited to be working hand-in-hand with our customers in Europe to demonstrate our RTM capabilities,” says Ricardo Barros, CSP/Inapal program manager. “The level of industrialization and automation we are installing in Palmela is second to none for similar carbon fiber applications.”
In addition to reducing component weight and cycle times, the CSP team in Europe has been pursuing a number of methodologies that will result in more sustainable manufacturing processes. Working toward a net-zero emission target, CSP Europe is working on tomorrow’s CF-RTM process with a primary focus on natural or recycled fibers, thermoplastic/bio-sources, advanced resins and reduced scrap and waste.
“Our goal is to keep working on a sustainable value proposition with a focus on net-zero CO2 emissions,” adds Philippe Bonte, president of CSP Europe. “We will achieve this via advanced manufacturing technologies and the use of renewable materials with the aim of becoming a positive contributor to the global environment.”
Related Content
Plant tour: Teijin Carbon America Inc., Greenwood, S.C., U.S.
In 2018, Teijin broke ground on a facility that is reportedly the largest capacity carbon fiber line currently in existence. The line has been fully functional for nearly two years and has plenty of room for expansion.
Read MoreInfinite Composites: Type V tanks for space, hydrogen, automotive and more
After a decade of proving its linerless, weight-saving composite tanks with NASA and more than 30 aerospace companies, this CryoSphere pioneer is scaling for growth in commercial space and sustainable transportation on Earth.
Read MorePlant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
Read MoreCryo-compressed hydrogen, the best solution for storage and refueling stations?
Cryomotive’s CRYOGAS solution claims the highest storage density, lowest refueling cost and widest operating range without H2 losses while using one-fifth the carbon fiber required in compressed gas tanks.
Read MoreRead Next
Continental Structural Plastics develops composite EV battery enclosures
CSP’ lightweight composite and multi-material battery covers meet stringent static, dynamic and regulatory requirements for automakers.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read More

















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)