Firefly Aerospace doubles Texas facilities to support composite rockets
Company grows test stands, further implements AFP and seven-axis robotic powermill machinery to produce rockets up to nine times faster at 1/7th of the cost.
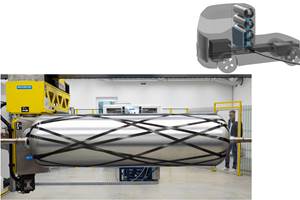
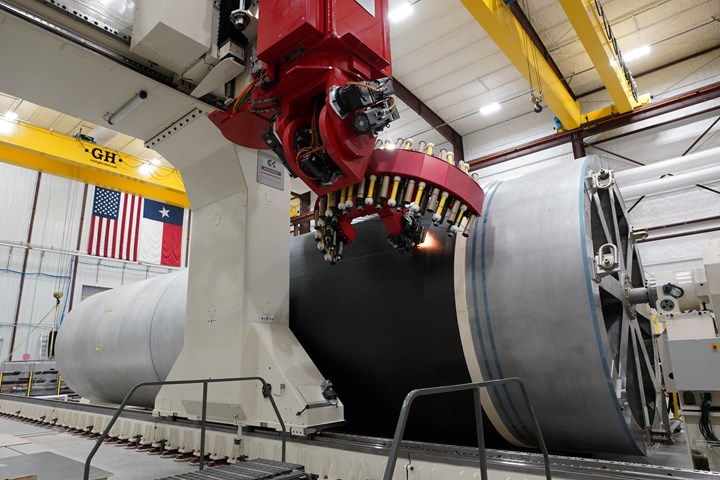
Newly installed Ingersoll automated fiber placement (AFP) machine. Source (All Images) | Firefly Aerospace
On Feb. 28, Firefly Aerospace Inc. (Cedar Park, Texas, U.S.) held an official ribbon cutting in celebration of the company’s Rocket Ranch expansion in Briggs, Texas. Firefly more than doubled the size of its manufacturing facilities, added two new test stands, and installed state-of-the-art machinery to support the production of Northrop Grumman’s (Falls Church, Va., U.S.) Antares 330 and the medium launch vehicle (MLV) the companies are co-developing together, which are leveraging Firefly’s composite technologies.
Firefly’s expanded manufacturing space from 92,000 to 207,000 square feet includes two new, large-scale buildings for rocket production, assembly and integration. The company also built a higher thrust engine stand to test Firefly’s Miranda and Vira engines with up to 230,000 pounds of thrust and five times the load capacity as Firefly’s current Reaver and Lightning engine stand. Designed to accommodate three engine bays as production cadence increases, the new stand provides redundant, high-accuracy thrust and mass flow rate data to further improve mission assurance.
The expansion also includes a new, 100-foot structural test stand to conduct pressurized axial loading to mimic flight loads. In total, Firefly now has six test stands at its Briggs location to support the robust testing performed across all vehicle lines.
“After Firefly signed the MLV agreement with Northrop Grumman, we went immediately to work on our Briggs expansion, which has been completed in less than a year’s time,” Bill Weber, CEO of Firefly Aerospace, says. “Along with the expansion, we’re taking advantage of automated machinery to further advance our rapid production schedule while improving efficiencies and lowering costs.”
Firefly is using a new automated fiber placement (AFP) machine, sourced from Ingersoll Machine Tools Inc. (Rockville, Ill., U.S.), a brand of Camozzi Group’s Machine Tool Division, to rapidly fabricate the carbon fiber composite structures, including barrels, domes and other structures, for the first stage of Antares 330 and both stages of MLV. Now operational, the AFP machine was recently used to build Firefly’s first carbon fiber barrel for MLV development testing.
“Firefly’s new AFP machinery, which is already widely used and proven in the aircraft industry, is a significantly more efficient and cost-effective approach to rocket production and can be utilized for composite parts across our vehicle lines,” Dan Fermon, COO of Firefly Aerospace, notes. “These high-speed robotic machines can lay up more than 200 pounds of carbon fiber per hour, allowing us to produce all the large carbon [fiber] composite structures for Alpha in just 7 days and MLV in just 30 days. This is about nine times faster and seven times cheaper than our former process.”
In addition to the AFP machine, Firefly is also installing a seven-axis robotic powermill to drill and trim carbon fiber structures with high speed and accuracy. This multi-axis machine, also procured from Ingersoll Machine Tools, can rotate rocket barrels up to 5.5 meters (18 feet) in diameter with a built-in dust collection system.
Other recent facility expansions include two new mission operations centers at Firefly’s spacecraft facility in Cedar Park, Texas, to support a growing number of launch, lunar and on-orbit missions. Firefly also expanded its Cedar Park headquarters with a mezzanine to accommodate nearly twice as many employees.
Related Content
Infinite Composites: Type V tanks for space, hydrogen, automotive and more
After a decade of proving its linerless, weight-saving composite tanks with NASA and more than 30 aerospace companies, this CryoSphere pioneer is scaling for growth in commercial space and sustainable transportation on Earth.
Read MorePartners recycle A350 composite production waste into adjustable-length rods for MFFD
Herone, Spiral RTC, Teijin Carbon Europe and Collins Aerospace Almere recycle A350 thermoplastic composite clips/cleats waste into rods for the all-thermoplastic composite Multifunctional Fuselage Demonstrator’s crown.
Read MoreRocket Lab begins installation of large AFP machine for rocket production
The 99-ton AFP machine, custom-designed and built by Electroimpact, is claimed to be the largest of its kind, expecting to save around 150,000 manufacturing hours in the Neutron rocket’s production process.
Read MoreCryo-compressed hydrogen, the best solution for storage and refueling stations?
Cryomotive’s CRYOGAS solution claims the highest storage density, lowest refueling cost and widest operating range without H2 losses while using one-fifth the carbon fiber required in compressed gas tanks.
Read MoreRead Next
Firefly Aerospace completes composite Blue Ghost lunar lander
First of two lunar missions under NASA’s CLPS initiative will launch in 2024 and conduct diverse technology demonstrations and scientific investigations on the moon’s surface.
Read MoreFirefly Aerospace's Alpha, launch services company selected by NASA for VADR missions
The composites-intensive Alpha launch vehicle will be used in NASA missions to deliver payloads such as CubeSats.
Read MoreRock West Composites support moon lander mission
Intuitive Machines’ IM-1 Nova-C lunar lander features multiple configurations of struts manufactured by Rock West Composites.
Read More



















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)