GE to develop largest, most powerful wind turbine
The Haliade-X will feature a 12 MW direct drive generator and 107m-long blades.
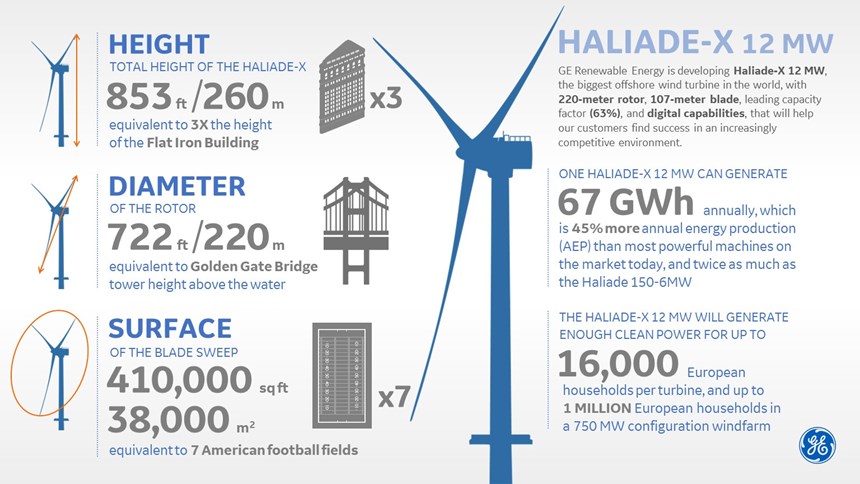
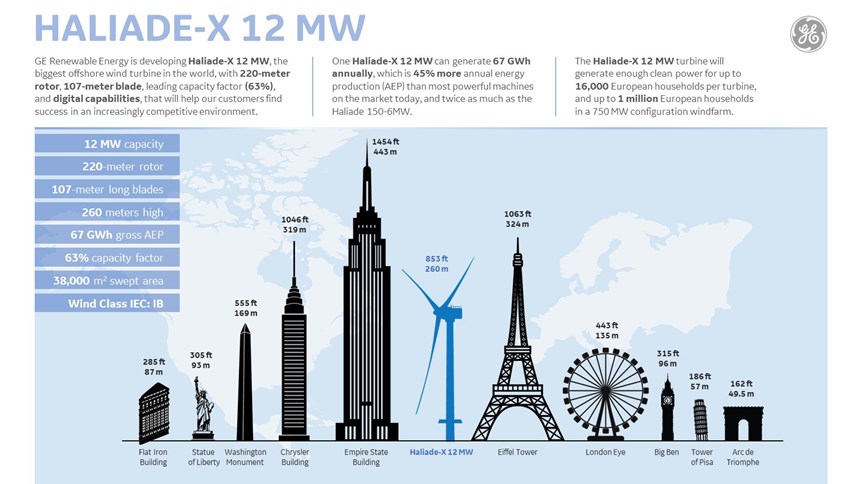
GE Renewable Energy (Paris, France) unveiled March 1 its plan to develop the largest, most powerful offshore wind turbine: the Haliade-X. Featuring a 12 MW direct drive generator and an industry leading gross capacity factor of 63%1 the Haliade-X will produce 45% more energy than any other offshore turbine available today2. GE will invest more than $400 million over the next three to five years in development and deployment of the Haliade-X.
John Flannery, chairman and CEO of GE, says, "We want to lead in the technologies that are driving the global energy transition. Offshore wind is one of those technologies and we will bring the full resources of GE to make the Haliade-X program successful for our customers."
Towering 260 meters over the sea, more than five times the size of the iconic Arc de Triomphe in Paris, France, the Haliade-X 12 MW carries a 220m rotor. Designed and manufactured by LM Wind Power, the 107m-long blades will be the longest offshore blades to date and will be longer than the size of a soccer field. One Haliade-X 12 MW turbine will generate up to 67 GWh annually2, enough clean power for up to 16,000 households per turbine, and up to 1 million European households in a 750 MW windfarm configuration.
Jérôme Pécresse, president and CEO of GE Renewable Energy says, "The renewables industry took more than 20 years to install the first 17 GW of offshore wind. Today, the industry forecasts that it will install more than 90 GW over the next 12 years. This is being driven by lower cost of electricity from scale and technology. The Haliade-X shows GE's commitment to the offshore wind segment and will set a new benchmark for cost of electricity, thus driving more offshore growth."
The ability to produce more power from a single turbine means a smaller number of turbines in the total farm, which translates to less capital expenditure for the balance of plant and reduced risk in project execution as the installation cycle time is reduced. It also simplifies operation and maintenance of the wind farm. All of this reduces the investment and operation cost for developers, makes offshore wind projects more profitable, and ultimately lowers cost of electricity for consumers.
To design and build the Haliade-X platform, GE Renewable Energy is relying on an unprecedented collaboration across the GE portfolio, leveraging the knowledge of GE's Onshore wind team, with 50,000 turbines in the field; the blade expertise of LM Wind Power; the GE Power and GE Aviation engineers for peer reviews of component and systems design; the Global Research Center for control systems and component validation; and GE Digital for supporting digital modelling, analytics and app development. The program is a GE-wide effort.
GE Renewable Energy aims to supply its first nacelle for demonstration in 2019 and ship the first units in 2021.
1. "Capacity factor" compares how much energy was generated against the maximum that could have been produced at continuous full power operation during a specific period of time.
2. Based on wind conditions on a typical German North Sea site.
Related Content
Polar Technology develops innovative solutions for hydrogen storage
Conformable “Hydrogen in a Box” prototype for compressed gas storage has been tested to 350 and 700 bar, liquid hydrogen storage is being evaluated.
Read MoreJEC World 2023 highlights: Recyclable resins, renewable energy solutions, award-winning automotive
CW technical editor Hannah Mason recaps some of the technology on display at JEC World, including natural, bio-based or recyclable materials solutions, innovative automotive and renewable energy components and more.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Batteries and fuel cells (2024)
As the number of battery and fuel cell electric vehicles (EVs) grows, so do the opportunities for composites in battery enclosures and components for fuel cells.
Read MoreNCC reaches milestone in composite cryogenic hydrogen program
The National Composites Centre is testing composite cryogenic storage tank demonstrators with increasing complexity, to support U.K. transition to the hydrogen economy.
Read MoreRead Next
VIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read MoreAll-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read More














.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)











