SAM XL demonstrates closed-loop digital methodologies via full-size aerocomposite parts development
PeneloPe Project’s modular, zero-defect manufacturing deliverables are being highlighted in an upcoming video that demonstrates the resulting aerospace pilot line’s feasibility.
In this sneak-peek, SAM XL shows how the project pilot line aims at reducing the overhead in programming new product variants in a production setting. Using sensors, the current shape and dimensions of the product are determined and used to generate robot trajectories, enabling the company to customize the production process to different parts and products. Source | SAM XL
Over the last couple of years, manufacturing automation expertise center SAM XL (Delft, Netherlands), alongside 30 other consortium partners, has been developing a closed-loop, zero-defect manufacturing strategy for flexible and modular manufacturing of large components under the PenoloPe Project. Now, SAM XL is in the process of processing the raw video footage of the project, which will be combined into a compilation video highlighting each partner’s achievements in PeneloPe’s resulting aerospace pilot line.
The EU-funded project began in 2020 with the goal of achieving an end-to-end digital manufacturing solution, linking product-centric data management and production planning in a closed-loop digital pipeline. PeneloPe’s partners worked to develop technologies such as simulation models, online control, data analytics and AI, all to achieve new methods of manufacturing that result in:
- A reduction of 15% in production costs
- A 20% decrease in production time
- Better use of raw materials
- A direct reduction of up to 22% of energy consumption.
The final solution will be implemented, benchmarked and demonstrated in industrial pilot lines to indicate its feasibility of developing large-scale, high-precision components in real manufacturing conditions.
PeneloPe’s resulting vision is an end-to-end modular, scalable and networked manufacturing architecture. Source | PeneloPe Project
Manufacturing and repairing large-scale parts, usually one-of-a-kind components, tends to be a complex and challenging process that requires the implementation of an integrated methodology capable of ensuring the manufacturability, quality and high precision of the parts from all stages — i.e., design, simulation/modeling and production planning.
The resulting closed-loop digital pipeline involves online control and quality assurance as its zero-defect manufacturing strategy. An exchange between TU Delft scientists and SAM XL’s software and hardware engineers, together with the 30 European collaboration partners, have been working closely together to incorporate large industrial robots and the company’s gantry robot as automation platforms. The developed demonstrator pilot line, located at SAM XL in the Netherlands, is being used to design, develop and test different manufacturing technologies, though it will initially focus on assembly, inspection and finishing a full-size composite fuselage section and wing section.
The infrastructure at SAM XL will also be used as a didactic factory for workforce training and follow-up innovation. To improve manufacturing techniques on a large scale, the company believes that knowledge sharing is essential; thus creation of a European network of didactic factories will facilitate discussing and sharing.
“The PeneloPe project showcases how state-of-the-art technology and teamwork can transform manufacturing into a sustainable, precise, and modular process,” says Dave Kroezen, lead robotics software engineer. “It’s inspiring to be part of a journey that advances aerospace production capabilities by working on the factory of the future and sharing that knowledge with our partners.”
Related Content
Siemens Gamesa, Airborne develop automatic preforming robot system for offshore wind blades
Danish-funded ALMA project furthers collaboration, adds new functionality, advanced sensor systems and digital twinning for reduced man-hours, waste and cost per blade.
Read MoreAdaptive composite elements for building facades exhibited at JEC World 2023
University of Stuttgart institutes use carbon and glass fiber composites, robotic fabrication, biomimetic design and digial twin/control to demonstrate adaptive facade elements for future buildings.
Read MoreNext-gen composites manufacturing: Combining material, machine and mold cavity data with analytics
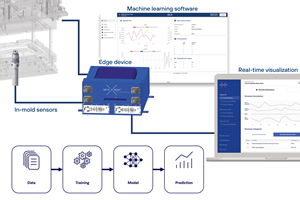
Using a sensor, an edge device and machine learning software, sensXPERT sees into processes and is improving quality and cutting scrap, cycle time and energy use for composites customers like ZF and Carbon Revolution.
Read MoreHow AI is improving composites operations and factory sustainability
Workforce pain points and various logistical challenges are putting operations resilience and flexibility to the test, but Industry 4.0 advancements could be the key to composites manufacturers’ transformation.
Read MoreRead Next
Loop Technology completes installation of composite preformer with long-reach robots
Delivery of 21-meter track, industrial robot arms and new cutting equipment enable the manufacture of large composite aerostructures at the Loop Technology Centre.
Read MoreAddcomposites announces AFP-XS global install base milestone
More than 50 of the production-ready AFP solution for small- to medium-scale composite part manufacturing have been installed and is rapidly growing thanks to its affordability and versatility.
Read MoreRoMaNi 2 project enhances industrial robot flexibility for composites, metals machining
Newly developed milling kinematics on a linear axis enables versatile and efficient machining with up to 0.1-millimeter production tolerance.
Read More













.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)