How AI is improving composites operations and factory sustainability
Workforce pain points and various logistical challenges are putting operations resilience and flexibility to the test, but Industry 4.0 advancements could be the key to composites manufacturers’ transformation.
Share
Read Next

Source (All Images) | Plataine
Manufacturers currently face a distinct set of challenges that are putting the resilience and flexibility of their operations to the test. While technology is evolving quickly and global markets are constantly shifting, businesses are dealing with the need to ramp up production rates, which has become more difficult due to the critical shortage of skilled and experienced workers. Supply chain disruptions have also become common, often resulting in longer material lead times and further complicating manufacturing logistics. On top of this, pressure is increasing to meet higher sustainability standards as stakeholders demand more environmentally responsible practices. Accordingly, companies manufacturing composite parts face a multifaceted puzzle in their efforts to maintain efficiency, profitability and sustainability in a world that is constantly transforming.
The rearview mirror of composites manufacturing
Historically, composites manufacturing has relied heavily on human expertise and traditional methods for short-, mid- and long-term planning and execution of production. These methods — including first-in, first-out (FIFO), Kanban and others — were guided by best practices in the 20th century. Now, they’ve reached a limit in terms of enhancing key performance indicators (KPIs) for production such as throughput and yield, on-time delivery and quality. Such methodologies don’t sufficiently account for the dynamic nature of manufacturing environments, where unforeseen changes on the factory floor can present significant hurdles to efficiency, scalability and growth targets. This static approach used in the past often fell short and affected several critical aspects of operations:
- Manufacturing planning was constrained, not able to fully consider the variability and unpredictability in composites production processes.
- Daily execution was often inefficient, as manual interventions and decision-making couldn’t keep up with the need for real-time adjustments.
- Logistics and supply chain management weren’t very flexible, which led to inefficiencies, disruptions and late deliveries.
- Decision-making was hindered at all levels (management and operational), often based on outdated information or insufficient understanding of the current situation on the factory floor, for example, because the data was coming from a variety of unconnected systems (ERP, MRP, purchasing, shift logs and so on).
To be more specific, material selection processes were often manual, which was not only time-consuming but also led to remnants, scrap and lower yield. Material receiving was also typically manual, and often prone to errors and delays. Planning efforts commonly relied on tools like Excel spreadsheets, which resulted in schedules that were quickly outdated, low overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and subsequent delays in delivery, proving that these methods were just not sufficient to deal with the new, more dynamic nature of the composites industry.
The dawn of digital transformation
Advanced manufacturing is currently going through a major transformation with the arrival of digital technologies, integrating sensors, IIoT and AI. Although still in its early stages, this digital turn promises substantial improvements in workflow, waste reduction and energy use. AI is becoming a key driver, enabling smarter decisions that enhance production efficiency and sustainability. Plataine (High Point, N.C., U.S.) has seen this transformation and has been a part of it for the last decade. We see that by using AI, composites manufacturing is experiencing exceptional advancements in several key areas:
Planning and scheduling: Traditional manual planning tools like Excel are being replaced with AI-driven software to automate and optimize production schedules and keep plans up to date. Software leverages AI algorithms to maximize production throughput and minimize inefficiencies. With AI-based software solutions, this digital change not only improves efficiency but also dynamically adjusts to unexpected changes on the factory floor happening in real time. This guarantees optimal resource utilization and minimal downtime. For example, one of our customers that manufactures composite parts for medical devices, used Plataine software to simulate how the addition of molds will impact their ability to increase volumes. Simulating multiple scenarios enabled them to reach a sweet spot — balancing between the need to increase part volumes versus the cost to purchase additional molds.
Supply chain collaboration: Cloud software enables better communication and collaboration between suppliers and manufacturers. This integration accelerates and simplifies the shipping and receiving processes, reduces delays and improves the overall responsiveness of the supply chain.
Inventory management: AI algorithms are able to analyze trends and predict demand, which then allows material managers and purchasing to maximize inventory efficiency. This approach significantly reduces scrap and waste, which helps these companies to achieve greater sustainability and cost savings.
Equipment and tool management and service: AI-assisted software provides alerts and recommendations to staff responsible for equipment service. This proactive maintenance approach prevents unplanned downtime, extends the life of machinery and ensures that resources are optimally used.
Energy consumption optimization: AI algorithms can play a big part in optimizing energy use, especially in energy-intensive processes like autoclave curing. Plataine is constantly learning from our customers. For example, one recent focus is that autoclave scheduler systems are imperative. We see that AI technology is leading a significant change in autoclave operations management within factories. By optimizing schedules, manufacturers using this technology are substantially reducing the number of autoclave runs, reducing energy consumption.
AI’s role in manufacturing for the future
As we look forward, we see that AI is a tool that is used more and more by factory staff to make their facility’s manufacturing processes easier and more efficient. In the same way that AI has become part of our daily life — with our smart phones, Siri, Alexa and more — AI will take a very significant part in our professional life at the factory.

In manufacturing, we see AI operating as another digital assistant to make our day-to-day work a lot easier. For example, production planners will run simulations of different scenarios and outcomes to reach high efficiency. The future of AI in manufacturing planning will take place across three horizons, each with its own set of possibilities and innovation:
- Short-term planning (up to 2 weeks): AI will enable factories to simulate various scenarios, such as different job assignments to machines or operations, and the allocation of inventory and tools for work orders. These simulations can create detailed schedules for each shift and respond rapidly to unexpected events on the factory floor. By quickly evaluating multiple scenarios, AI-based software can present the most efficient outcome, ensuring high flexibility and responsiveness in short-term weekly planning.
- Mid-term planning (2-4 months): Looking further ahead, AI’s capabilities will extend to simulating scenarios for operational adjustments, such as adding shifts, increasing staff per shift or purchasing additional tools or molds. This mid-term planning will help align tactical decisions with predicted demand and operational capabilities. As a result, resource allocation and productivity can be optimized.
- Long-term planning (1-2 years): Over the long term, AI-assisted software will fast track strategic expansions and investments, such as purchasing new machines or adding production lines and factory space. These simulations will support long-term growth strategies, making sure that investments are worthwhile and aligned with future market demands.
We believe that AI will also play an important part in encouraging collaboration and connectivity between manufacturing facilities and sites, predicting demand peaks and shortages, as part of the connected factory ecosystem. Even further, AI-based software will aid collaboration between suppliers and customers, streamlining communication, creating transparency and shortening processes.
Fostering innovation to stay competitive and grow
The journey through the current evolution in manufacturing — from reliance on traditional methods to the pioneering adoption of AI — involves a truly transformative shift toward efficiency, sustainability and innovation. There is no doubt that the integration of generative AI (GenAI) will further develop this dynamic. While traditional AI focuses on analyzing historical data and using algorithms to make future predictions, GenAI enables digital technologies to produce new outputs, including images, videos, text, sounds and other media.
New GenAI tools will enable natural communication between humans and machines, making complex software more intuitive, friendly and accessible. Such technology can not only help to streamline production processes, but also to get real-time alerts and smart insights and recommendations — which humans in the factory will learn to trust over time (remember Siri, Alexa and Waze?). Plataine, centered around sustainable, customer-focused production, has experienced how embracing AI has helped factories to enhance their OEE, reduce material waste and save operators time as well as operational costs. As composites manufacturers adopt these innovations, they will move toward more responsive and environmentally responsible processes.
About the Author
Amir Ben-Assa
Amir Ben-Assa is responsible for global marketing and product strategy at Plataine (High Point, N.C., U.S.). Over the past 20 years, Ben-Assa directed marketing departments and the development and successful deployment of innovative technologies and solutions for the industrial sector. Prior to joining Plataine, he held various marketing and business development roles at RFKeeper, AeroScout (acquired by Stanley) and Siemens. Ben-Assa holds a B.Sc. in mechanical engineering from the Technion, Israel Institute of Technology and is a graduate of the Executive MBA program at Tel-Aviv University.
Related Content
Reducing accidental separator inclusion in prepreg layup
ST Engineering MRAS discusses the importance of addressing human factors to reduce separator inclusion in bonded structures.
Read MoreComposites opportunities in eVTOLs
As eVTOL OEMs seek to advance program certification, production scale-up and lightweighting, AAM’s penetration into the composites market is moving on an upward trajectory.
Read MoreThe next-generation single-aisle: Implications for the composites industry
While the world continues to wait for new single-aisle program announcements from Airbus and Boeing, it’s clear composites will play a role in their fabrication. But in what ways, and what capacity?
Read MoreThe evolution, transformation of DEA from lab measurements to industrial optimization
Over the years, dielectric analysis (DEA) has evolved from a lab measurement technique to a technology that improves efficiency and quality in composites production on the shop floor.
Read MoreRead Next
Optimizing machining for composites: Tool designs, processes and Industry 4.0 systems
Hufschmied moves beyond optimized milling and drilling tools to develop SonicShark inline quality control system and Cutting Edge World cloud platform for optimized tool use and processes.
Read MoreMeasuring energy use to enable sustainable composites production
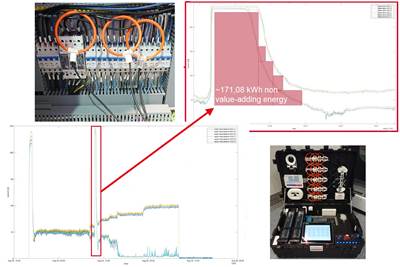
Airbus subsidiary CTC uses new technology to measure energy use in machine components and processes to optimize equipment, production lines and guide decisions for future composites.
Read MoreNext-gen composites manufacturing: Combining material, machine and mold cavity data with analytics
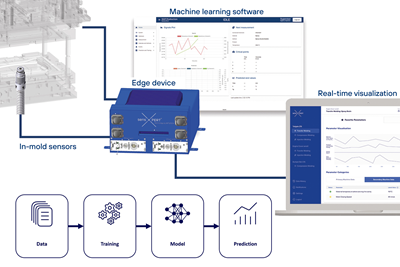
Using a sensor, an edge device and machine learning software, sensXPERT sees into processes and is improving quality and cutting scrap, cycle time and energy use for composites customers like ZF and Carbon Revolution.
Read More