Toray uses carbon nanotube composites for ultra-high frequency communication
Toray says that its ultra-high frequency (UHF) printed radio-frequency identifier (RFID) has potential application in retail and logistics operations.
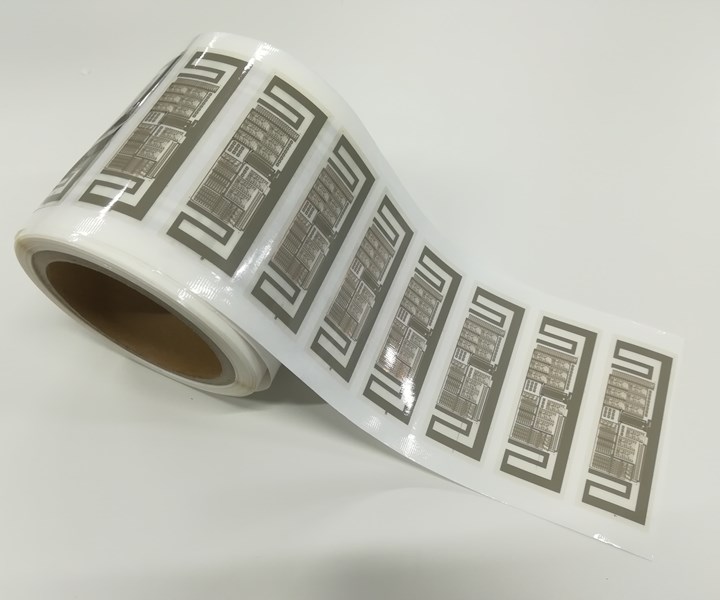

Source | Toray Industries Inc.
Toray Industries Inc. (Tokyo, Japan) announced on Jan. 20 that it has successfully developed a method for wireless communication across ultra-high frequencies (UHF) with a printed radio-frequency identifier (RFID), which employs the use of semi-conductive carbon nanotube composites.
Toray says that its achievement demonstrates the potential for manufacturing UHF RFIDs by low-cost printing processes, with potential application in retail and logistics operations, ranging from automated cash registers to more efficient inventory management. The company plans to accelerate development with the goal of commercializing printed RFIDs.
According to the company, RFIDs offer more efficient long-distance workplace communication and batch reading for retail and logistics operations, but conventional silicon RFID tags are not used widely due to expensive integrated circuit (IC) chips, complex processing methods that require high temperatures and vacuum environments, and the requirement for additional IC chip mounting processes. Efforts to manufacture lower-cost ICs and printed semiconductors that do not require mounting have resulted in mobility of 20 cm2/Vs.
In comparison, Toray says its carbon nanotube composite semiconductor delivers a mobility of 182 cm2/Vs. While thin film transistors (TFTs) are either p-type (positively charged) or n-type (negatively charged), carbon nanotubes are normally p-type. Toray employed proprietary material technology to develop an n-type feature, realizing both p- and n-type TFTs that would be necessary to form power-saving, low-cost ICs.
The company fabricated an RFID prototype incorporating a 24-bit memory with a low-cost printing technology by adopting this new material and proprietary device and process technologies. It was then able to communicate wirelessly with UHF waves across a distance of 20 centimeters, becoming, according to Toray, the first in the world to do so with a printed UHF RFID. Toray’s product goal is to materialize a 60-bit memory.
The company plans to improve communication performance, including communication distance, while developing on-film manufacturing technologies.
Toray’s research in this area was supported in part by the Low Carbon Technology Research and Development Program of Japan’s Ministry of the Environment.
Related Content
-
TU Munich develops cuboidal conformable tanks using carbon fiber composites for increased hydrogen storage
Flat tank enabling standard platform for BEV and FCEV uses thermoplastic and thermoset composites, overwrapped skeleton design in pursuit of 25% more H2 storage.
-
Recycling end-of-life composite parts: New methods, markets
From infrastructure solutions to consumer products, Polish recycler Anmet and Netherlands-based researchers are developing new methods for repurposing wind turbine blades and other composite parts.
-
Infinite Composites: Type V tanks for space, hydrogen, automotive and more
After a decade of proving its linerless, weight-saving composite tanks with NASA and more than 30 aerospace companies, this CryoSphere pioneer is scaling for growth in commercial space and sustainable transportation on Earth.

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)










.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)

