Composites Air Cans Lighten Riser Loads
Low-pressure air cans, designed to add buoyancy to a spar platform’s riser string, are good candidates for composite materials. Up to 12 ft/3.7m in diameter and from 30 to 60 ft/9.2 to 18.5m long, the hollow structures support the riser weight and take load off of the platform’s hull. Typically installed insid
Low-pressure air cans, designed to add buoyancy to a spar platform’s riser string, are good candidates for composite materials. Up to 12 ft/3.7m in diameter and from 30 to 60 ft/9.2 to 18.5m long, the hollow structures support the riser weight and take load off of the platform’s hull. Typically installed inside spar hulls, air cans are usually made from steel. However, the weight of steel cans makes them less efficient in deeper water, and there is a depth below which they cannot cost-effectively support their own weight. While composites have the weight advantage, an all composite can must also be strong enough to withstand the enormous impact side loads caused by wave motion. A thicker composite is one way to handle the loads, but it results in a heavier can.
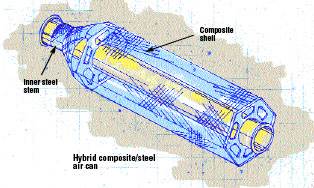
EDO Fiber Science, in cooperation with CSO Aker Maritime Inc. (Houston, Texas, U.S.A., a division of Coflexip Stena Offshore) has developed a hybrid composite/steel air can for use as a buoyancy element on top-tensioned risers. The design incorporates a system of composite air chamber shells installed over an inner steel “stem” that fits over the riser. It allows the riser to move freely up and down through the air can stem. A patented “iron cross” steel frame carries the structural load, while the hollow, airfilled interior provides buoyancy. The design is non-integral, meaning that the air can supports the riser without being rigidly attached to it (as in an integral design).
Because development is still underway, the companies have not released details about how the air can is manufactured. Says EDO’s Jones, “It’s made with a combination of processes that can produce a high fiber content. When all of the modules are assembled in the spar, the buoyancy can is about 200 ft/61.5m long has to be built in sections and shipped to the site for final assembly.” The team is preparing a prototype module for sea testing in 2002.
A major oil producer is underwriting the hybrid buoyancy can development, and a full-diameter, field-capable module was recently completed in Salt Lake City. According to Jones, future applications may include use on tension leg risers, steel catenary risers (SCRs) and offset risers.
Fiberglass Structural Engineering Inc. (FSE, Bellingham, Wash., U.S.A.), another company involved in composite air can development, has patented flotation tube technology. The concept employs hollow filament wound E-glass and vinyl ester fiberglass tubes ganged together within a rigid steel framework and filled with compressed air for necessary buoyancy. The individual tubes are sealed at the top, but open on the bottom, so they don’t experience external hydrostatic loading. This means that the tubes, designed primarily for hoop tension, can be filament wound with a thinner wall. Vinyl ester has been specified for the system because it is less prone to matrix cracking.
FSE project manager Steve Gaber says that the flotation tube technology can be utilized for single riser flotation, with placement of five to seven tubes approximately 4 ft/1.2m in diameter around the riser body. But he adds that it can be scaled up to support an entire platform structure, with 72 or more large diameter (10 ft or 12 ft) tubes needed for an entire spar hull (see Chapter 8).
Related Content
Al Seer Marine, Abu Dhabi Maritime unveil world’s largest 3D-printed boat
Holding the new Guinness World Record at 11.98 meters, the 3D-printed composite water taxi used a CEAD Flexbot to print two hulls in less than 12 days.
Read MoreBioabsorbable and degradable glass fibers, compostable composite parts
ABM Composite offers sustainable options and up to a 60% reduction in carbon footprint for glass fiber-reinforced composites.
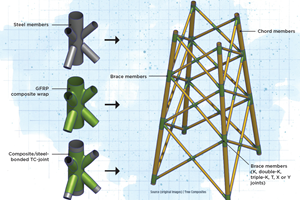
Read MoreNovel composite technology replaces welded joints in tubular structures
The Tree Composites TC-joint replaces traditional welding in jacket foundations for offshore wind turbine generator applications, advancing the world’s quest for fast, sustainable energy deployment.
Read MoreOwens Corning initiates review of strategic alternatives for glass fiber business
Owens Corning considers alternative options like a potential sale or spin-off as part of its transformative move to strengthen its position in building and construction materials.
Read MoreRead Next
Design Issues With Subsea And Downhole Components
For structures below the water line and in the borehole, composites add to their list of benefits the key characteristic of design flexibility, because composite materials can be tailored to meet specific challenges. For example, composites can add buoyancy to low-pressure steel air cans on a spar platform’s r
Read MoreSubsea And Downhole Components
Composite buoyancy elements, riser arch trays, wellhead enclosures and downhole parts meet service challenges.
Read More














.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)