The cost equation
Keynote speakers at CompositesWorld Expo 2009 delivered news both sobering and encouraging to those who are trying to predict what the future holds for composites in the postrecession manufacturing economy.
At the end of September, we here at CT hosted the CompositesWorld Expo 2009 in Schaumburg, Ill. As usual, our conference gurus Scott Stephenson and Ralph Jessie put together a robust keynote speaker lineup that featured, among others, Jim deVries, staff technical specialist and manager of the Manufacturing Research Dept. at the Ford Research Laboratory, and Dr. Habib Dagher, director of the AEWC Advanced Structures and Composites Center at the University of Maine (to see our CW Expo report, click on the link under "Editor's Picks," at right).
DeVries talked about the prospects for increased carbon fiber use in cars. He suggested that the best use of carbon fiber in cars might be via sheet molding compound (SMC), but only if the cost of raw carbon fiber comes down to $5/lb. As it stands, he said, the current cost per pound of weight saved with carbon fiber SMC ($10.60) does not come close to that for aluminum ($1.00) or fiberglass SMC ($3.33). Even if carbon fiber comes down to $5/lb and a fabrication process is developed that can cost-effectively produce 200,000 units or more per year, he doubted that manufacturers of raw carbon fiber would be able to reliably provide enough fiber for the 75 million lb of carbon SMC that the auto industry would consume annually.
This is sobering. If carbon fiber SMC is ever to find a significant home in production vehicles — especially in body panels — it has to buy its way in, and it’s clear that the Fords of the world are watching material price points closely. I wonder, though, if hurdles for carbon fiber are that high: How close is the industry to a high-speed carbon fiber process to produce body panels? Are body panels on vehicles expected to provide structural support to a vehicle, and if not, then how does that change the product development equation? Finally, does it make sense, and is it fair, to simply replace metal parts with similar parts made with carbon composites? With the automotive industry shifting so many paradigms of late, this seems like a good time to reconsider automobile design to optimize components for composites.
In the infrastructure market, the cost equation appears to be shifting in favor of composites, as revealed by Dr. Dagher during his keynote. Dagher helped develop the “bridge in a backpack” composites technology at the Advanced Structures and Composites Center (see "Bridge cost cut with inflatable arches," under "Editor's Picks"). He reported that this technology is now competitive on a first-cost basis with concrete and steel. This is important because for years composites have had to be “sold” into infrastructure applications on the basis of valid, but too-easily-ignored true-cost calculations, derived from lifecycle analysis that factors in the composite’s extended service life and low maintenance. Further evidence of this competitiveness can be found in this issue, as well. Our “Engineering Insights” feature this issue (see "Tough I-beam bridge for tank traffic," under "Editor's Picks") highlights a thermoplastic composite bridge developed to support military vehicles.
As the Ford data show, it might be a little early to declare all composites so competitive, but it’s encouraging to see glass and carbon fiber considered for their durability, strength, light weight and thrift.
Related Content
Swedish parking garage to incorporate decommissioned wind blades
Architect Jonas Lloyd is working with Vattenfall to design the multistory building with a wind blade façade, targeting eco-friendly buildings and creative ways to remove blades from landfills.
Read MoreRecycling end-of-life composite parts: New methods, markets
From infrastructure solutions to consumer products, Polish recycler Anmet and Netherlands-based researchers are developing new methods for repurposing wind turbine blades and other composite parts.
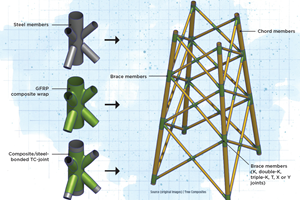
Read MoreNovel composite technology replaces welded joints in tubular structures
The Tree Composites TC-joint replaces traditional welding in jacket foundations for offshore wind turbine generator applications, advancing the world’s quest for fast, sustainable energy deployment.
Read MoreComposites reinvent infrastructure
Celebrating National Composites Week, CW shares ways in which composites continue to evolve the way we approach infrastructure projects.
Read MoreRead Next
Bridge cost cut with inflatable arches
Stay-in-place composite formwork shortens installation, doubles service life of concrete bridge structure.
Read MoreTough I-beam bridge for tank traffic
Immiscible polymer blending combines the strength of HDPE and the stiffness of glass-reinforced PP to create I-beams with specific strength greater than steel.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read More