AMULET project aims to create new value chains for fiber-reinforced polymers and CMCs
R&D demonstration projects targeting current challenges in auto, aero, energy and building will be developed to reach TRL7 with the goal of accelerating industrial use of advanced lightweight materials.
To create a decarbonized and efficient circular economy, it is essential to widely establish lightweight construction as a key technology. However, small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have not yet fully realized the potential of advanced lightweight materials, due to a lack of application knowledge, as well as technical and financial resources.
The trans-European project “Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies united for Lightweight” (AMULET) aims to develop the untapped innovation potential of SMEs in the field of lightweight construction and to help establish new pan-European value chains for advanced lightweight materials. The AMULET consortium is funded by the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (INNOSUP-1). The project launch meeting was held Sept 6, 2021. AMULET will run until Sept 2024.
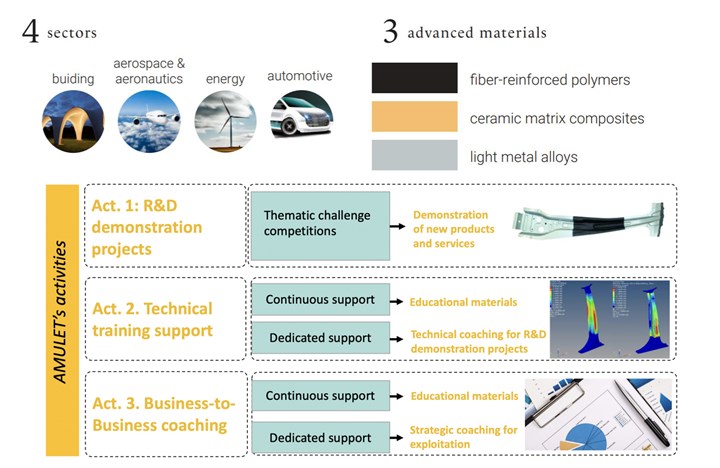
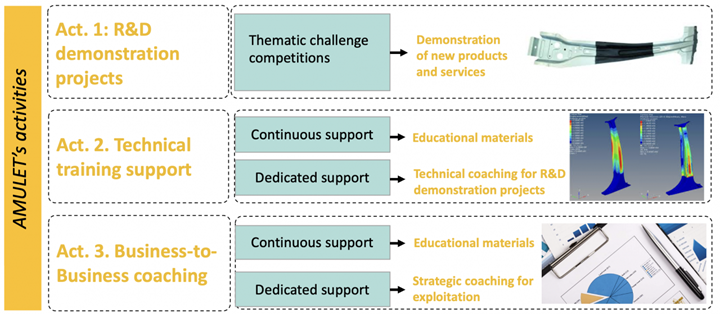
The vision of the AMULET consortium is to make a significant contribution to reducing CO2 emissions in the EU by strengthening innovative, lightweight construction in SMEs. R&D demonstration projects targeting current sectoral challenges will be developed to reach technology readiness level (TRL) 7, following a competitive-based approach. SMEs participating in AMULET will receive technical training support and business-to-business coaching for accelerating the commercialization of their innovative solutions. AMULET will focus on the automotive, aerospace, energy and construction industries and support innovative development and application of three advanced lightweight materials:
- Fiber-reinforced polymers (FRPs)
- Ceramic matrix composites (CMC)
- Light metal alloys
AMULET’s three phases
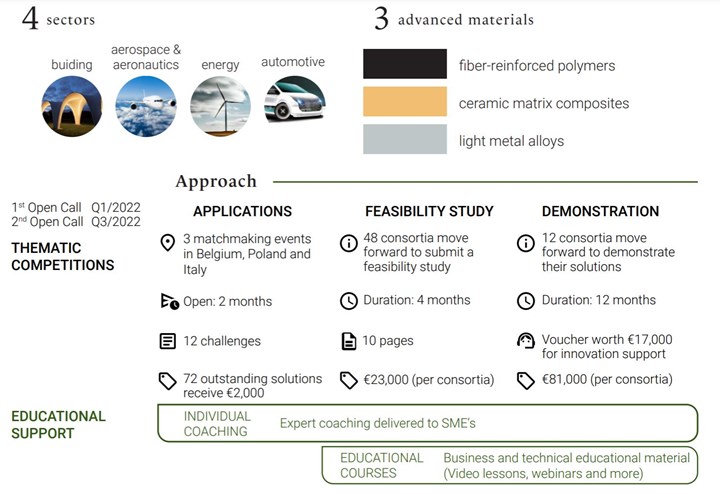
Within AMULET’s first application phase, participants will discuss and evaluate current technical challenges in the use of advanced lightweight materials through expert groups. This will be followed by up to 12 thematic competitions in which the European consortia of SMEs will participate. Matchmaking events on-site in selected partner countries will help form consortia of interested SMEs.
In the second phase, companies that have joined AMULET will complete a feasibility study, and demonstrate their proposed solutions in the third and final phase. Financial and advisory support will be provided and SMEs will be assisted to develop topic-specific technical and business knowledge. A curriculum of at least 12 technical and six business management topics will be developed in the consortium for this purpose and then provided to SMEs via online platforms for the entire duration of the project.
In addition to this learning content, webinars will be offered on each topic area. Individual coaching sessions will also available to exchange personal knowledge. The goal is to make a significant contribution to a more sustainable EU with significantly reduced CO2 emissions.
The AMULET consortium
The AMULET consortium brings together a comprehensive network of more than 1,717 SMEs, 341 large companies and 93 universities and research and innovation institutes.
The AMULET project is coordinated by professors Lothar Kroll and Maximilian Schwarz from the Technical University of Chemnitz (Chemnitz, Germany). Nine ELCA partners are also part of the consortium: Bydgoszcz Industrial Cluster (Poland), Cluster MAV (Spain), Flanders Make (Belgium), Jožef Stefan Institute (Slovenia), IMAST (Italy), Plastipolis (France), Southwest Hungarian Engineering Cluster (Hungary) and Clust-ER MECH (Italy).
For more information, view the AMULET website and download the AMULET project flyer, available in English, German and Polish.

AMULET is supported by the European Lightweight Clusters Alliance (ELCA). The European Green Deal aims to make Europe climate neutral by 2050. Lightweight technologies are key in achieving this goal. Composites provide the highest potential for reducing weight but are encountering bottlenecks for their mass adoption by various sectors, including automotive and construction. The multi-material approach is gaining force, but also presents new challenges in both processing and performance. ELCA is a collaborative initiative that aims to accelerate the adoption of lightweight materials in strategic industries. Mobility is the alliance’s primary focus, but applications in other lightweighting-related sectors are also targeted, including energy, healthcare, defense and construction.
Related Content
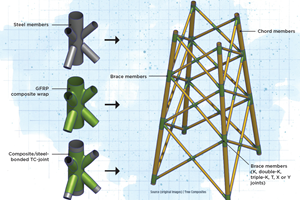
Novel composite technology replaces welded joints in tubular structures
The Tree Composites TC-joint replaces traditional welding in jacket foundations for offshore wind turbine generator applications, advancing the world’s quest for fast, sustainable energy deployment.
Read MoreJEC World 2023 highlights: Recyclable resins, renewable energy solutions, award-winning automotive
CW technical editor Hannah Mason recaps some of the technology on display at JEC World, including natural, bio-based or recyclable materials solutions, innovative automotive and renewable energy components and more.
Read MoreAchieving composites innovation through collaboration
Stephen Heinz, vice president of R&I for Syensqo delivered an inspirational keynote at SAMPE 2024, highlighting the significant role of composite materials in emerging technologies and encouraging broader collaboration within the manufacturing community.
Read MoreHexagon Purus opens new U.S. facility to manufacture composite hydrogen tanks
CW attends the opening of Westminster, Maryland, site and shares the company’s history, vision and leading role in H2 storage systems.
Read MoreRead Next
“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read MoreAll-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read More