Leonardo invests for the future, establishes pilot carbon fiber plant in Italy in collaboration with MAE
Part of government-supported project to innovate composites, pilot line will be operational in 2022 and enable testing of new precursors and process variations.
Photo Credit: MAE corporate video
Leonardo SpA (Rome, Italy) provides services to the aerospace, defense and security sectors including: aerostructures, helicopters, aircraft, airborne and space systems, land and naval defense electronics and defense systems. As part of its mission to “develop and deploy advanced technology in the pursuit of security, progress and value, today and tomorrow,” Leonardo has invested in a new important project together with MAE (Fiorenzuola, Italy).
MAE specializes in the engineering and construction of production lines for polymer fibers. Located outside of Piacenza, the company’s core business has now become construction of pilot- to industrial-scale production lines for carbon fiber PAN (polyacrylonitrile) precursor (see “CSIRO developing higher-quality, higher-strength, lower-cost carbon fibers”). MAE was chosen by Leonardo to build a €17-million pilot carbon fiber plant in Piacenza, as part of a larger research project to innovate composites technologies (see “Leonardo and CETMA disrupting composites for lower cost and environmental impact”).
The new factory is co-financed by the national business development agency Invitalia (Rome, Italy), which supports innovative programs to boost Italy’s production structure. Carbon fiber is a material that is increasingly strategic in terms of production in the aerospace sector and in other fields such as automotive, energy and construction.
“The future is carbon fiber,” says Paola Rovellini, MAE’s chief financial officer, who played a leading role in the agreement with Leonardo for the new pilot plant. "The boom in carbon fiber demonstrates how it is already a strategic product in many industrial sectors internationally. And it will be an increasingly important material to face the ecological transition all over the world, reducing emissions, energy consumption, production costs and improving product quality. Carbon fiber guarantees better results than much heavier materials such as steel.” She cites aerospace, “Let's just think of the fuel savings obtained with much lighter aircraft. And this is true not only from an economic point of view, but also from an environmental point of view.”
“In the field of aeronautics, the history of composite materials began in the 1980s and Leonardo immediately grasped what was already considered a challenge for the future,” recalls Giancarlo Schisano, managing director of Leonardo's aerostructures division. “In recent years, the use of these composite materials has grown and not only in the aeronautical sector. The collaboration with MAE is another step forward for Leonardo in a strategic and competitive sector.”
The Lampo project
The pilot carbon fiber plant is one part of the three-year R&D project called “Lampo” that was conceived in 2019. According to Italian press reports, Leonardo's main objective with the project is the expansion and enhancement of its aerostructures plant in Foggia, where new types of carbon fiber with new properties will be used to improve aircraft performance and cost. This work will also exploit the skills and equipment of the Leonardo materials lab in Grottaglie (Taranto).

Photo Credit: MAE corporate video.
MAE was reportedly chosen because it is one of the few companies in the world with a complete know-how along the carbon fiber supply chain. "MAE is a unique company in designing plants and carrying out research and innovation on carbon fiber and, in general, on monomers and polymers,” explains Vincenzo Colla, councilor for regional economic development in Emilia-Romagna. Other project partners include composites specialist Aviorec (Anagni, Italy) and the National Research Council (CNR, Rome, Italy), which is the largest public research institution in Italy.
The Lampo project is reportedly structured to represent a technological competitive lever for the main sectors of the Italian economy. For example, carbon fiber is used increasingly not only in aerospace, but also in automotive. Less than 100 kilometers from Piacenza, for example, is the Emilian Motor Valley, home to Ferrari, Lamborghini, Maserati and Dallara, all of which make extensive use of carbon fiber.
The Lampo project, thus, is seen as also enabling the creation of ad hoc carbon fibers to improve the performance of automotive products. This fits wells with the Emilia Romagna region’s strategy to make innovation and research one of its distinctive traits. “The evolution of materials is an area that the region also supports,” notes Vincenzo Colla, “with a view to a growing capacity for recycling and reuse, to affirm a circular and environmentally sustainable economy."
Leonardo invests for the future
“We started this partnership to develop, for the first time, carbon fiber production in Italy,” says Stefano Corvaglia, materials engineer, head of R&D and IP manager of Leonardo Aerostructures Division (Grottaglie, Pomigliano, Foggia, Nola production facilities, southern Italy). He notes that Nicola Gallo, lead R&D engineer at Leonardo, did much of the work to establish the Lampo project, its funding and regional/national partnerships.
“This is a big project,” says Gallo. “The new carbon fiber plant is just one part. Our goal is to develop new technologies for large carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) parts, such as the Boeing 787 horizontal stabilizer, which is made at Leonardo’s Foggia plant.” He describes the five key parts of the overall R&D program:
- New tools for monolithic parts to increase reconfigurability and reduce cost
- New automated inspection technologies
- Automated repair technologies
- Automated assembly of large parts
- New materials for future opportunities
Gallo describes MAE as a key partner for this research project. “They are building a big plant that starts from precursor and goes through the whole process, including treatment of the carbon fiber at the end,” he notes. “Roughly half of all newly established carbon fiber precursor spinning plants of the last 10 years were supplied by MAE. Having worked so extensively in the carbon fiber business, they have amassed significant experience. They are also using their knowledge of acrylic production from the textile industry. This type of production is similar to PAN, but with different end-product goals.”
“With MAE,” Gallo continues, “we will develop and try new formulas for different types of carbon fiber as well as new precursors, including different PAN formulations.” He notes the most recent plants MAE has built are not just for precursor but also carbon fiber production. Notably, on its website, MAE notes 50% of its revenue comes from China, but this is expected as China produces more than half of the world’s chemical fibers. A significant portion of its business also comes from carbon fiber manufacturing companies in Europe and the company has a branch in the U.S. “They have an idea which could be the right precursor for high-quality grades of carbon fiber,” says Gallo. “But they also understand formulations that have been tested for textile applications but not used for various reasons. MAE sees some of these as interesting for carbon fiber as well. For sure, we want to have a product comparable to the standard composite materials used in structural applications today. But we will also try to improve that recipe.”
Gallo says there are no plans to test microwave or induction heating for oxidation and carbonization at this time. He points out that 100% of carbon fiber plants in operation today use only electrical resistance or natural gas heating for oxidation and carbonization. “I think we will begin by using standard equipment and getting the line operational,” he explains. “Our initial R&D focus will be on the kind of process parameters that could affect carbon fiber properties and cost. For example, extrusion to increase the number of tows that can pass through the oven. This could provide cheaper fiber for new applications. But we will also look at tailoring properties for specific composites solutions that Leonardo will develop in the future.”
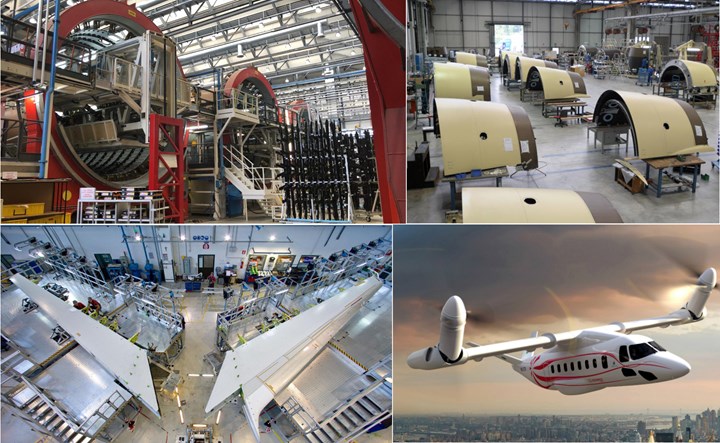
Leonardo is already a leader in composite aerostructures, producing one-piece barrel sections and horizontal stabilizers for the Boeing 787 (top and bottom left) as well as nacelles (top right) and other structures. It also is developing new thermoplastic composite technologies and is project leader for Clean Sky 2’s Next Generation Civil TiltRotor aircraft (bottom right). Photo Credit: Leonardo, Clean Sky 2.
The pilot plant will be completed in 1Q 2022, says Gallo, with a goal to start production by 2Q and having carbon fiber samples ready for testing and other R&D activities by the end of 2022. Production line capacity will be in the range of 120 kilograms/day for PAN precursor and 50 kilograms/day for carbon fiber, which equates to roughly 30 and 12.5 metric tons, respectively, at 250 days/year.
“After that, we will look at how to improve and change parameters and process steps to target certain properties or reduce cost and increase productivity,” he adds. “In Italy, there are no carbon fiber products made currently, and it’s difficult to simulate the entire carbon fiber production process in a lab. You only know real results from this type of complete production line. This is why we are investing in this pilot plant.”
Related Content
US Air Force selects Integris Composites ballistic body armor
Cratus Wave armor is thin, lightweight and reduces heat stress, providing buoyant personal protection for the 582nd Helicopter Group.
Read MoreFrom the CW Archives: Airbus A400M cargo door
The inaugural CW From the Archives revisits Sara Black’s 2007 story on out-of-autoclave infusion used to fabricate the massive composite upper cargo door for the Airbus A400M military airlifter.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read MoreMATECH C/ZrOC composite is deployed in hypersonic aeroshells
Ultra high-temperature insulating CMC targets hypersonics, space heat shields and other demanding applications, tested up to 2760°C under extreme stagnation pressures.
Read MoreRead Next
All-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read More




















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)









