Basaltex reveals basalt fiber milestone for use in rail carriage interiors
Testing and development of basalt fiber, bioresin and rPET combo achieves rigidity, fire resistance and lightweight properties that meet railway application standards.
Share
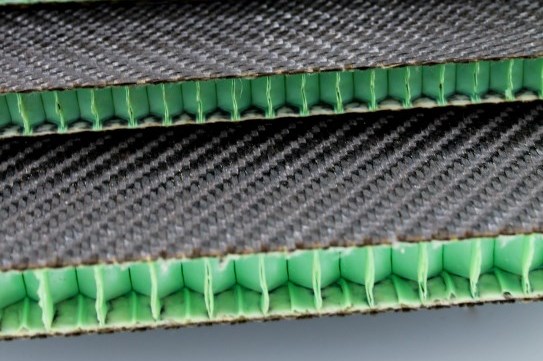
Photo Credit: Basaltex NV
Basalt fibers company Basaltex NV (Wevelgem, Belgium) reports that it has achieved a significant milestone in developing and testing a new composite material solution for railway applications comprising basalt fibers with EconCore’s (Leuven, Belgium) patented honeycomb technology.
Combining basalt fibers (extrudable at a temperature of 1,450ºF), a polyfurfuryl alcohol bioresin — 100% derived from sugarcane waste — and recycled polyethylene terephthalate (rPET), Basaltex says the new material development has greatly improved fire resistance, and is highly rigid. This is in addition to lightweighting properties from the honeycomb, a drastic weight reduction compared to traditional monothilic glass fiber-reinforced polymers (GFRP) used in train interiors, the company notes. This combination also makes the final product sustainable and environmentally friendly, unlike a majority of thermoset solutions in this type of application.
Such sandwich panel could be deployed in applications such as cladding panels, partitions, tables and flooring. The thermoset skin layers provide a fast cure at elevated temperature for short cycle times and potential automated production capabilities. As well as the railway interior application, Basaltex says this new material combination could be used in any application that requires fire performance combined with a low weight.
“Honeycomb and stone? Some combinations don’t automatically come to mind, but this material solution could enable converters to combine fire safety, lightweighting and sustainability in an elegant way,” says Jef Delbroek, project engineer at EconCore. “We look forward to seeing how the railway industry will respond to this novel material combination and hope to arouse interest of other industries as well.”
Related Content
-
LIST opens innovation center focusing on sustainable composite materials
The Sustainable Composite Materials and Manufacturing Innovation Centre (SCMM) will be supported by major players in rail, aerospace, automotive and space to transition sustainable composites research to commercialization.
-
Hexagon Purus opens new U.S. facility to manufacture composite hydrogen tanks
CW attends the opening of Westminster, Maryland, site and shares the company’s history, vision and leading role in H2 storage systems.
-
Composite sidewall cover expands options for fire-safe rail components
R&D project by CG Rail explores use of carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastics and recycled manufacturing scrap to meet fire safety, weight and volume targets.











.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)

