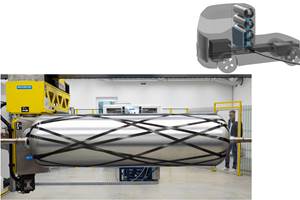
GE starts GE9X certification testing
As the second GE9X engine begins testing at the Peebles Test Operation (PTO) in Ohio, assembly of the third and fourth GE9X engines is well underway at GE Aviation’s headquarters in Evendale, Ohio.
GE Aviation has began GE9X engine certification tests at its Peebles Test Operation (PTO) in Ohio. The GE9X will power Boeing’s new 777X aircraft.
The first round of GE9X certification tests are being conducted on the second GE9X production-configured powerplant built by GE. To prepare for the certification program, trials of the first full engine to test (FETT) GE9X engine commenced in March 2016, generating critical data on the full engine system and aerodynamic performance, mechanical verification and aero thermal system validation. Testing of the FETT engine concluded earlier this year with a series of preliminary natural-icing tests at PTO, where the GE9X ran more than 50 test points, accumulating 168 hours and 162 cycles.
“Completing a full year’s worth of validation efforts on the FETT engine gave us great confidence heading into the certification program with the second GE9X engine,” says Ted Ingling, GE9X general manager at GE Aviation. “By incorporating all the learnings from the FETT engine, we start the GE9X certification program with a stable configuration and position ourselves to meet the schedule and performance expectations of our customers from day one of service entry.”
As the second GE9X engine begins testing at PTO, assembly of the third and fourth GE9X engines is well underway at GE Aviation’s headquarters in Evendale, Ohio. The fourth GE9X engine is slated for installation and flight tests aboard GE’s 747-400 Flying Test Bed flown out of GE’s Mojave Desert facility in Victorville, Calif., before the end of this year.
Maturation testing of the GE9X engine began about six years ago, progressing from component-level all the way through the completed first full engine to test (FETT) validation efforts. FETT brought all the GE9X technologies together to demonstrate their operability as a complete propulsion system.
In October 2016, GE completed the second phase of GE9X CMC (ceramic matrix composite) component testing in a GEnx demonstrator engine, accumulating 1,800 cycles while exposing the engine to harsh environmental conditions of dust and debris. The level of debris exposure was equivalent to about 3,000 take-off and landing operation cycles. For the second round of tests, the GEnx demonstrator engine utilized the same CMC combustor liners, HPT stage 1 shrouds and HPT stage 2 nozzles from the first round of tests run in September 2015 along with the addition of the HPT stage 1 CMC nozzles. (For more about GE’s CMC parts production, check out Plant Tour: GE Aviation, Asheville, NC, US)
With almost 700 GE9X engines on order, the GE9X engine will be in the 100,000 pound thrust class and will have the largest front fan at 134 inches in diameter with a composite fan case and 16 fourth generation carbon fiber composite fan blades. Other key features include; a next-generation 27:1 pressure-ratio 11-stage high-pressure compressor; a third-generation TAPS III combustor for high efficiency and low emissions; and CMC material in the combustor and turbine.
IHI Corp., Safran Aircraft Engines, Safran Aero Boosters and MTU Aero Engines AG are participants in the GE9X engine program.
Check out the video below that shows the GE9X preliminary icing testing.
Related Content
Plant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
Read MoreCombining multifunctional thermoplastic composites, additive manufacturing for next-gen airframe structures
The DOMMINIO project combines AFP with 3D printed gyroid cores, embedded SHM sensors and smart materials for induction-driven disassembly of parts at end of life.
Read MoreThe potential for thermoplastic composite nacelles
Collins Aerospace draws on global team, decades of experience to demonstrate large, curved AFP and welded structures for the next generation of aircraft.
Read MoreCryo-compressed hydrogen, the best solution for storage and refueling stations?
Cryomotive’s CRYOGAS solution claims the highest storage density, lowest refueling cost and widest operating range without H2 losses while using one-fifth the carbon fiber required in compressed gas tanks.
Read MoreRead Next
Developing bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read MoreAll-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read More