Kevlar-based artificial cartilage mimics real tissue
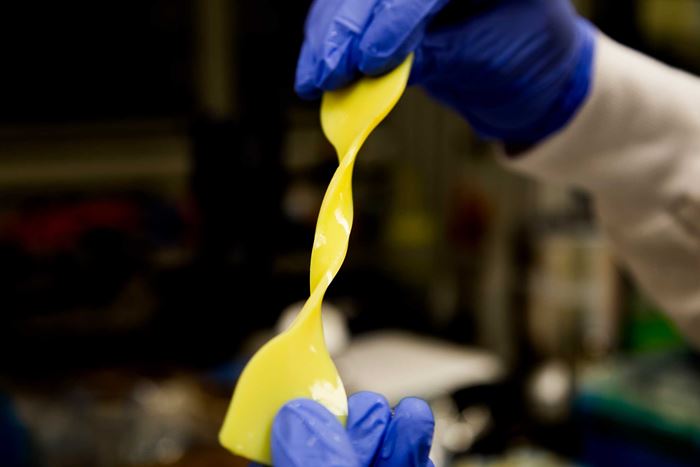
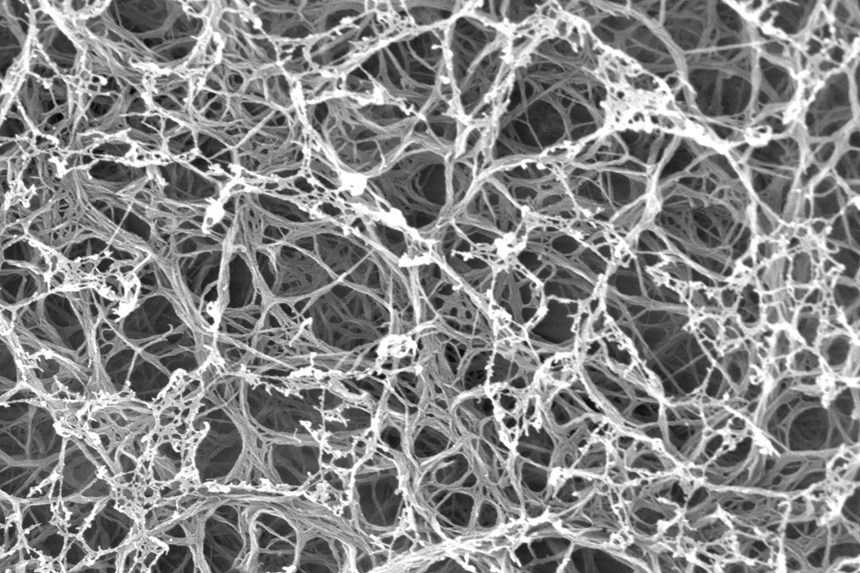
The new Kevlar-based hydrogel recreates the magic of cartilage by combining a network of tough nanofibers from Kevlar with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA).
Researchers at the University of Michigan and Jiangnan University have developed a Kevlar-based synthetic cartilage. The new Kevlar-based hydrogel recreates the magic of cartilage by combining a network of tough nanofibers from Kevlar with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA).
In natural cartilage, the network of proteins and other biomolecules gets its strength by resisting the flow of water among its chambers. The pressure from the water reconfigures the network, enabling it to deform without breaking. Water is released in the process, and the network recovers by absorbing water later.
This mechanism enables high impact joints, such as knees, to stand up to punishing forces. Running repeatedly pounds the cartilage between the bones, forcing water out and making the cartilage more pliable as a result. Then, when the runner rests, the cartilage absorbs water so that it provides strong resistance to compression again.
The synthetic cartilage boasts the same mechanism, releasing water under stress and later recovering by absorbing water like a sponge. The aramid nanofibers build the framework of the material, while the PVA traps water inside the network when the material is exposed to stretching or compression. Even versions of the material that were 92 percent water were comparable in strength to cartilage, with the 70-percent version achieving the resilience of rubber.
As the aramid nanofibers and PVA don't harm adjacent cells, Nicholas Kotov, the Joseph B. and Florence V. Cejka Professor of Engineering at U-M, who led the study, anticipates that this synthetic cartilage may be a suitable implant for some situations, such as the deeper parts of the knee. He also wonders whether chondrocytes might be able to take up residence inside the synthetic network to produce a hybrid cartilage.
But his potential applications are not limited to cartilage. He suspects that similar networks, with different proportions of aramid nanofibers, PVA and water, may be able to stand in for other soft tissues.
"We have a lot of membranes in the body that require the same properties. I would like to evaluate the space," Kotov said. "I will talk to doctors about where the acute need is and where this intersection of the properties will allow us to make best headway and biggest impact."
Kotov is a member of the Biointerfaces Institute, which provides shared space for researchers from U-M's engineering and medical schools. He is also a professor of chemical engineering, materials science and engineering, and macromolecular science and engineering.
The study, recently published in Advanced Materials, is titled "Water-rich biomimetic composites with abiotic self-organizing nanofiber network." It was supported by the National Science Foundation, with additional funding from the Department of Defense. The university is seeking patent protection and partners to bring the technology to market.
Related Content
-
Universal Matter acquires main operating business of Applied Graphene Materials
UMI aims to combine its graphene capabilities with AGM’s dispersion technologies to accelerate the growth of graphene-based solutions.
-
Viritech and Haydale pursue new functionalized materials for Type V composite vessels for hydrogen storage
Goal is considerable weight savings via lightweight, impermeable pressure vessels without a liner, further advance in Graph-Pro structural storage tanks with integrated fixation.
-
JEC World 2023 highlights: Recyclable resins, renewable energy solutions, award-winning automotive
CW technical editor Hannah Mason recaps some of the technology on display at JEC World, including natural, bio-based or recyclable materials solutions, innovative automotive and renewable energy components and more.