Mikrosam to supply ATP machine for UD-CCM research
Initial University of Delaware studies conducted with the automated tape placement (ATP) machine will evaluate placement of thin ply materials to support current projects with NASA.
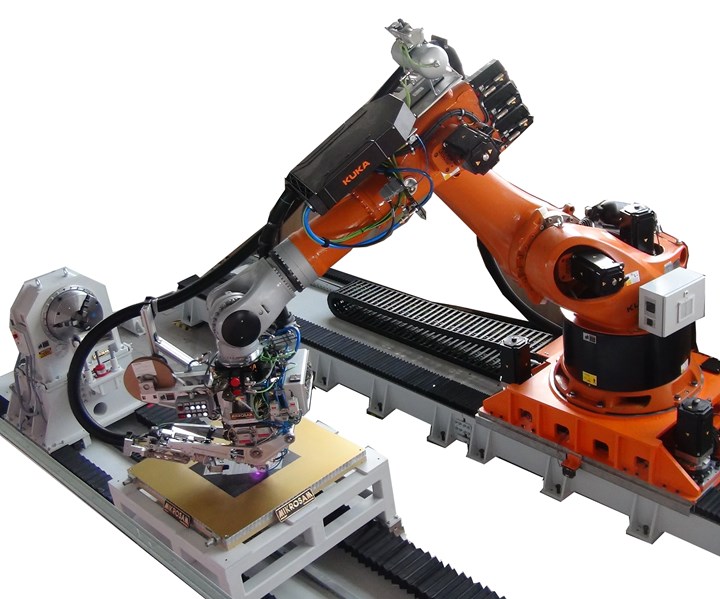
Source | Mikrosam
The University of Delaware's Center for Composite Materials (UD-CCM, Newark, Del., U.S.) has selected Mikrosam (Prilep, Macedonia) and its U.S. representative Composite Automation LLC (Cape Coral, Fla., U.S.) to deliver an integrated automated tape placement (ATP) machine for automatic placement of dry, thermoset and thermoplastic tapes.
Equipment specifications for the UD-CCM machine include placement of thin to standard ply thickness tape (up to 1 inch in width), laser and infrared (IR) heating with in-situ temperature control and thermal camera feedback, and horizontal axes enabling manufacturing of full-scale prototypes of up to 10 feet in length.
The system at UD-CCM will become available in summer 2020 for prototyping, material and process evaluation.
According to Mikrosam, the new equipment will enable UD-CCM to research and develop primary structures at rate production, and initial studies will evaluate placement of thin ply materials to support current projects with NASA.
For example, UD-CCM’s Tailorable Universal Feedstock for Forming (TuFF) material — developed under a four-year Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) program and introduced at JEC World 2019 — is designed as a steerable tape option with low areal weight, enabling variability in stiffness for weight-critical applications, and tailored blank formation for forming of aerospace and automotive parts, as well as increasing productivity.
“We are looking forward to collaborating with Mikrosam and other industry and government partners on next-generation ATP materials and processes,” says Dirk Heider, UD-CCM assistant director for technology.
Mikrosam has designated UD-CCM as its primary academic partner in the U.S. In addition to providing the ATP machine, Mikrosam is also providing open software and hardware access for R&D targeted at development of new material solutions, in-situ process control and path/placement optimization.
UD-CCM was a pioneer investigating laser-based thermoplastic ATP in the 1980s. UD-CCM’s long history of composites manufacturing research includes thermoset and thermoplastic filament winding and tape placement, infusion of dry preforms, and development of process models, sensors and control systems.
Designed as an integrated, modular and upgradeable ATP work-cell, Mikrosam’s 8-axis robotic automated fiber placement (AFP) machine is capable of automated and precise placement of dry/thermoset and thermoplastic tape.
“The market for automated layup of thermoplastic and thermoset composites demands flexible equipment to ensure maximum utilization in exploring new techniques and applications,” says Dimitar Bogdanoski, sales manager at Mikrosam.
Composite Automation LLC enters its fourth year as the exclusive partner of Mikrosam and is now fully represented throughout the North American marketplace for composites representing ten diverse technologies for the manufacture of advanced composite structures.
Related Content
-
ASCEND program update: Designing next-gen, high-rate auto and aerospace composites
GKN Aerospace, McLaren Automotive and U.K.-based partners share goals and progress aiming at high-rate, Industry 4.0-enabled, sustainable materials and processes.
-
The lessons behind OceanGate
Carbon fiber composites faced much criticism in the wake of the OceanGate submersible accident. CW’s publisher Jeff Sloan explains that it’s not that simple.
-
TU Munich develops cuboidal conformable tanks using carbon fiber composites for increased hydrogen storage
Flat tank enabling standard platform for BEV and FCEV uses thermoplastic and thermoset composites, overwrapped skeleton design in pursuit of 25% more H2 storage.

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)














