Smart, self-powering composite from DITF uses a "textile power plant" concept
Multilayer fabric-based piezoelectric elements and pyroelectric energy harvesters reinforce the FRP structure, generating electrical energy using vibration, oscillation and temperature fluctuation.
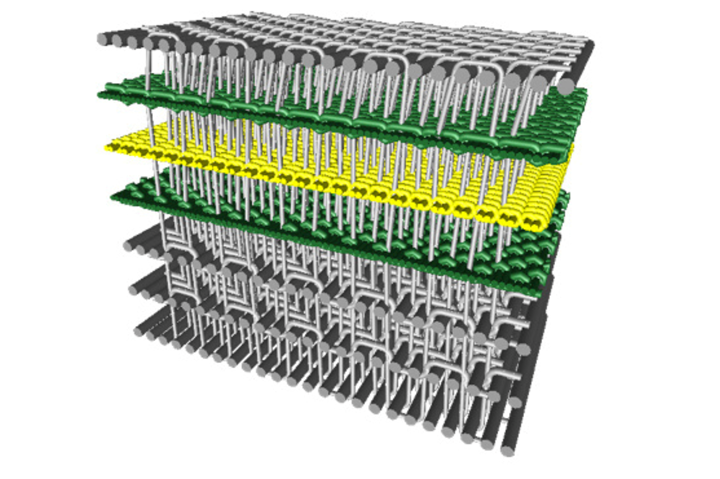
Schematic representation of the multilayer woven textile structure of the textile power plant. Photo Credit: DITF
According to the German Institutes of Textile and Fiber Research (DITF, Denkendorf), which offers expertise in fiber optic and piezoelectric sensors (see “DITF develops textile sensors for composites”), smart fiber-reinforced plastics (FRP) have much to offer. Alongside this opportunity, DITF says there is also a need to consider how integrated arrays of sensors and actuators can actually be powered. With this in mind, DITF has developed a multilayer textile, an in-built “textile power plant” that can generate electrical energy using vibration, oscillation and temperature fluctuation. This would reportedly allow the smart composite used in an electric vehicle (EV), for instance, to harness power from its own motion. In general, the significance of the research project will add further capability to the composite, making it lightweight and smart, in addition to acting as its own power plant.
According to Dr. Marie O’Mahony, an industry consultant, visiting professor at the Royal College of Art (RCA, London, U.K.) and author of several books on advanced and smart textiles, piezoelectric and pyroelectric principles are employed. The textile reinforcement structure for the FRP provides for the generation of electrical energy using the piezoelectric effect to harness vibration, while the pyroelectric effect generates electrical energy from waste heat. Since polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) has both piezoelectric and pyroelectric properties and is available as a yarn, it is possible to create “textile generators” based on multilayer fabrics to be developed for both principles.
The functional principle is demonstrated in this project with a smart, self-powering composite. Vibration occurs through moving parts and friction, while waste heat is generated in EVs, for example, at the battery — or, in the case of vehicles with conventional combustion engines, through the combustion of the fuel. The technology is expected to be used both in conventional cars with combustion engines, as well as EVs, O’Mahony mentions.
There are two specific areas of development in the project. The first is a piezoelectric energy harvesting system based on a multilayer fabric structure designed to harness vibration as an energy source. The second is a woven pyroelectric generator for the use of waste heat as an energy source.
First, multilayer fabric-based piezoelectric elements were developed and characterized as a reinforcement structure for FRP. This structure is intended to be used in high-vibration areas of the vehicle to generate electrical energy. The tests carried out at the DITF show that even the slightest vibrations can lead to a significant charge displacement in the material and thus generate electrical energy.
Based on this technology, pyroelectric energy harvesters have been developed. These are analogous to the pyroelectric energy harvesters and have been constructed from the multilayer fabric structures and characterized in terms of their recuperation properties. Because the vehicle is equipped with large-surface components that are exposed to vibrations, deformations and temperature fluctuations, through these smart composite materials, previously unused waste energy can be made usable.
Related Content
Mold 3D printing helps automate composite bathtub, shower production
As part of its efforts to automate as much of its production process as it can, Lyons Industries acquired a Massivit 10000 additive manufacturing system to quickly produce high-performance molds and support fixtures.
Read MoreHow AI is improving composites operations and factory sustainability
Workforce pain points and various logistical challenges are putting operations resilience and flexibility to the test, but Industry 4.0 advancements could be the key to composites manufacturers’ transformation.
Read MoreASCEND program update: Designing next-gen, high-rate auto and aerospace composites
GKN Aerospace, McLaren Automotive and U.K.-based partners share goals and progress aiming at high-rate, Industry 4.0-enabled, sustainable materials and processes.
Read MoreAirborne delivers composite upper stage tank for EU ENVOL project
Nine-member consortium targets development of low-cost, green vertical orbital launcher with manufacture of an ultra-lightweight composite tank design in an automated manufacturing environment.
Read MoreRead Next
VIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read More













.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)









