Cevotec upgrades SAMBA Fiber Patch Placement cells for production of large aerostructures
New features enable increased efficiency for curved structures using biaxial and quasi-isotropic laminates.
Cevotec (Unterharching, Germany) has already widely expanded the range of components that can be produced with its Fiber Patch Placement (FPP) technology by scaling the patch size 50X. This development, aimed primarily at aerospace requirements, has now also resulted in a new “Rolling Motion” deposition behavior for FPP’s form-flexible patch gripper. A second new feature is the Draped-Curve function, which enables replicating traditional biaxial or quasi-isotropic laminates using the ARTIST STUDIO software for FPP. Also helping to meet the requirements of large aerostructures production, this feature achieves biaxial and QI laminates while eliminating the issues of waste, expensive automation and low-efficiency that have characterized traditional composites processes.
New Rolling Motion function
One of the core features of the Fiber Patch Placement (FPP) technology is use of a form-flexible gripper to apply patches of different materials on almost any shaped surface. The gripper can currently apply patches sized up to DIN A4 (192 by 272 millimeters) to even highly curved large surfaces, such as those typically used in aircraft and aerospace applications.
However, in certain convex areas the process is limited by the height of the gripper body. When the size of the gripper is too large in relation to the limiting surface features of the part, its base plate would touch the surface before the edges of the patch could come into contact. Up to now, an in-process gripper exchange system enabled processing of such areas with smaller grippers and patches. Now, however, Cevotec’s newly developed Rolling Motion function is an added option
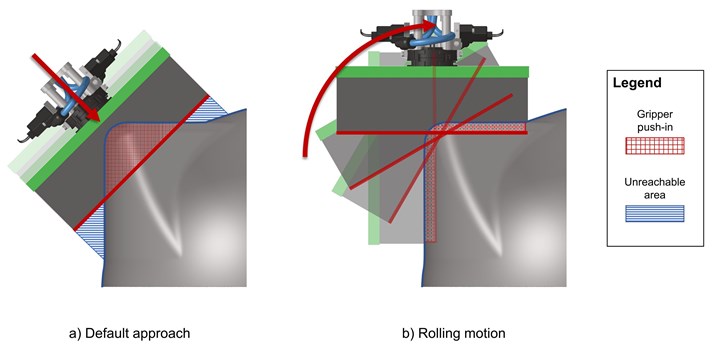
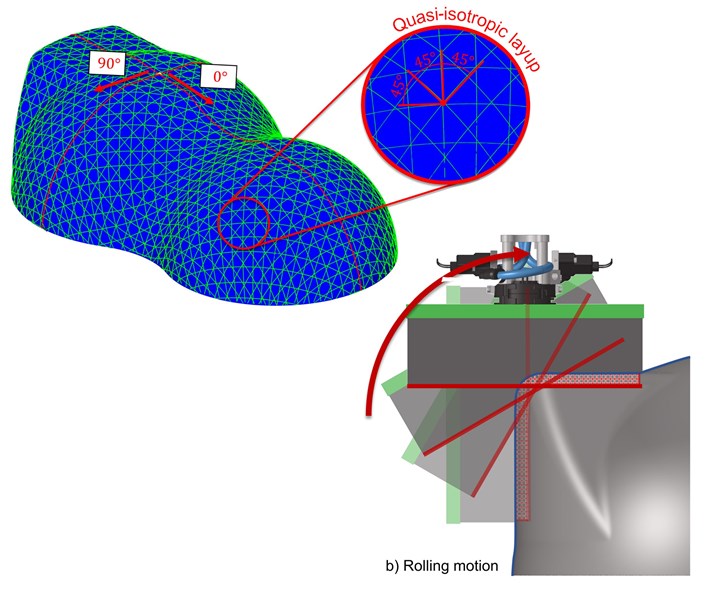
Instead of applying the patch along a single normal, the contact point rolls along a curve with a different normal for each point of the curve. This behavior is inspired by the rolling movement of a wheel. Since the gripper needs to fulfill complex movements, Cevotec’s SAMBA Scale and Multi cells feature six-axis-robots as gripper manipulators. Based on the curvature of the patch, the best contact curve is automatically calculated by the FPP-specific ARTIST STUDIO software, which makes it easy for engineers to use this new feature.
New Draped Curve function
ARTIST STUDIO has additionally been enhanced with another important function: Draped Curve. One of ARTIST STUDIO’s strengths has always been the creation of custom patch patterns, especially for local reinforcements along curvilinear load paths. With the new Draped Curve function, ARTIST STUDIO can also support the creation of more traditional laminates like biaxial ([0°, 90°]) or quasi-isotropic (QI, e.g. [0°, 90°, +45°, -45°]). In ARTIST STUDIO 1.3, Cevotec introduces the new kinematic draping features, enabling users to predict the shape of applied patches with increased accuracy.
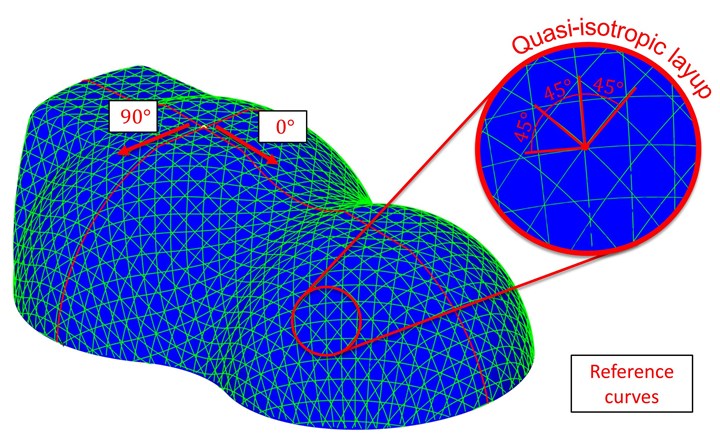
With the new Draped Curve function, it’s possible to create FPP laminates with fiber orientations similar to traditional woven fabrics that feature a 90° angle between warp and weft direction, together with the ability to drape this pattern over complex shapes. But it is also possible to add additional +/- 45° layers that follow the same principle. So parts fabricators are only a few clicks away from a QI laminate for the whole part — while maintaining FPP’s flexibility to pick any arbitrarily curved line as the 0° reference, and enabling more sophisticated patch patterns than ever before.
The new Rolling Motion and the Draped Curve features are key developments to further increase the productivity and flexibility of SAMBA production cells. Cevotec’s objective is to provide the most powerful systems for the industrial production of complex composites.
About Cevotec:
Munich-based automation specialist Cevotec enables manufacturers to build complex composites in high volume and quality. With Fiber Patch Placement based SAMBA systems, Cevotec offers customized, fully automated fiber layup systems with integrated process control for manufacturing complex 3D geometries and multi-material laminates. ARTIST STUDIO is the technology-specific CAD-CAM software for generating patch-based fiber laminates and automated robot programming. Cost and time reductions of 20-60% can be realized when switching from manual layup to Cevotec’s SAMBA systems. Manufacturers also benefit from a comprehensive service portfolio, including application-specific customizations and FE-based component development.
Related Content
Co-molding SMC with braided glass fiber demonstrates truck bed potential
Prepreg co-molding compound by IDI Composites International and A&P Technology enables new geometries and levels of strength and resiliency for automotive, mobility.
Read MoreASCEND program update: Designing next-gen, high-rate auto and aerospace composites
GKN Aerospace, McLaren Automotive and U.K.-based partners share goals and progress aiming at high-rate, Industry 4.0-enabled, sustainable materials and processes.
Read MorePlant tour: Albany Engineered Composites, Rochester, N.H., U.S.
Efficient, high-quality, well-controlled composites manufacturing at volume is the mantra for this 3D weaving specialist.
Read MoreBio-inspired EV underbody panel developed by TPI Composites, Helicoid Industries
Composite underbody panel for battery pack protection, made of stacked multiaxial noncrimp fabric, will serve high-volume commercial and automotive markets.
Read MoreRead Next
Plant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read MoreDeveloping bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read More


























