EuCIA announces addition of new carbon fiber data to Eco Impact Calculator
The European Composites Industry Association’s Eco Impact Calculator is a free life cycle assessment tool to calculate a composite part’s ecological footprint.
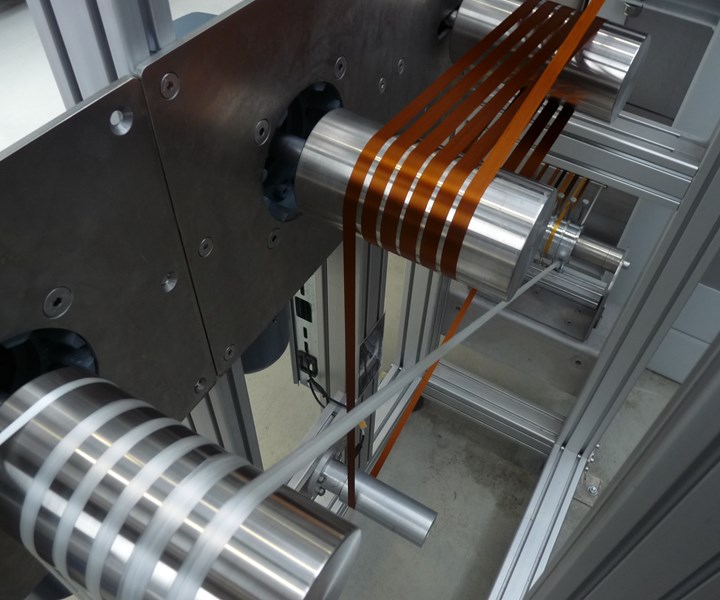
Stabilization of carbon fiber at the Institut für Textiltechnik (ITA) of RWTH Aachen University. Source | ITA-RWTH
The European Composites Industry Association (EuCIA, Brussels, Belgium) has announced the addition of new carbon fiber data to its Eco Impact Calculator, an online tool that enables composites companies to calculate the environmental impact associated with the production of their products.
The Eco Impact Calculator is available free of charge at http://ecocalculator.eucia.eu, and is a life cycle assessment (LCA) tool that is regularly updated to incorporate materials and process advances. The inclusion of this new carbon fiber data follows the addition of data on core materials and thermoplastic conversion processes last year.
EuCIA was prompted to develop an LCA for carbon fiber following a survey of industry, academia and other stakeholders. This LCA for industrial-grade carbon fiber, released in late 2018, was based on an in-depth study of available literature and data for polyacrylonitrile (PAN) available in the ecoinvent 3.1 database. This work was carried out in cooperation with EY Climate Change and Sustainability Services in the Netherlands (EY CCaSS). In a recent cooperation, experiment-based data produced by the Institut für Textiltechnik (ITA) of RWTH Aachen University, Germany, and EuCIA’s study were thoroughly reviewed and EuCIA’s initial LCA data adjusted to reflect actual experience of the PAN to carbon fiber conversion efficiency. Both data sets, initial and new, are now available to Eco Calculator users.
EuCIA’s Eco Calculator calculates the eco footprint of composites parts using a transparent and uniform sector methodology for processes following ISO 14.040/044. The Eco Calculator calculates the environmental impact of products from cradle to gate, including the raw materials, transport, processing and waste generation up to the point of sale. The calculation of consecutive manufacturing processes is possible as well as modified materials. Users do not need any in-depth knowledge of LCA techniques to use the tool and the data can be exported in the form of an Eco Report to allow full life cycle LCA calculations.
The Eco Calculator incorporates a pre-defined set of materials and processes, based on data EuCIA has collected over the past four years. Users are also able to enter their own data to generate a more precise result for their individual products and processes. The materials and processes included in the tool are under continuous review for quality and consistency, and new data is regularly added to extend and improve its scope and accuracy.
“Carbon fiber-reinforced composites have attracted a lot of attention as a lightweight material for replacing heavier parts in the transport sector,” says Tim Röding, group leader of Carbon Fibre Research Group, Institut für Textiltechnik (ITA) of the RWTH Aachen University. “Making airplanes and vehicles lighter is a very important step that can contribute to reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. However, the production of carbon fibers involves very energy-intensive processes. To fully understand the energy-saving effect of carbon fibers and their composites, reliable life cycle assessment data for the entire process chain are indispensable.”
“EuCIA believes that sustainability will be a key driver in the future development of the composites industry worldwide,” says Roberto Frassine, president of EuCIA. “We would like to thank ITA-RWTH for their help in developing this new carbon fiber data for the Eco Calculator and we welcome the industry’s feedback. We invite organizations wishing to contribute to the further development of the Eco Calculator to contact EuCIA.”
EuCIA’s sustainability experts will be available to discuss this new data in more detail at JEC World 2020 in Paris on 3-5 March.
Related Content
Plant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
Read MoreRecycling end-of-life composite parts: New methods, markets
From infrastructure solutions to consumer products, Polish recycler Anmet and Netherlands-based researchers are developing new methods for repurposing wind turbine blades and other composite parts.
Read MoreCryo-compressed hydrogen, the best solution for storage and refueling stations?
Cryomotive’s CRYOGAS solution claims the highest storage density, lowest refueling cost and widest operating range without H2 losses while using one-fifth the carbon fiber required in compressed gas tanks.
Read MoreManufacturing the MFFD thermoplastic composite fuselage
Demonstrator’s upper, lower shells and assembly prove materials and new processes for lighter, cheaper and more sustainable high-rate future aircraft.
Read MoreRead Next
“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read MoreDeveloping bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)












.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)