Mouldbox rebrands as Plyable, uses AI to automate composite tooling
By uploading CAD data into the Plyable app, businesses access a pre-qualified manufacturing network offering superior quality, plus time and cost savings.
Share
“Following substantial growth and development in the past year, we are realizing our ambition of actively disrupting the traditional composite manufacturing supply chain,” said Plyable CEO Martin Oughton. “We wanted to celebrate this success with a name change that showcases the simplicity, capability and flexibility of our composite tooling innovations and which also signals our growth and commitment to helping our clients, which is central to our mission.”
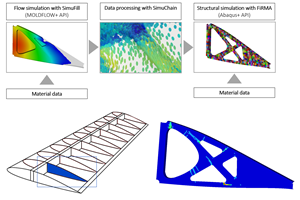
Plyable harnesses the latest AI and machine learning technology to create a proprietary software that automates the design and manufacture of composite tooling. By simply uploading component CAD data into the Plyable app, businesses can take advantage of a pre-qualified, distributed manufacturing network and enjoy superior results as well as significant time and cost savings.
Harnessing AI and machine learning
“Our unique technology can determine the moldability of a customer component in seconds,” explains Plyable CTO Adam Lofts. “Deep learning models can provide insights that trained engineers know ‘at a glance’ but which are hard to automate using traditional methods. The similarity of one geometry to another and feature identification are areas where convolutional neural networks show excellent results.”
A convolutional neural network is a deep learning algorithm which can take an input image, assign importance to various aspects/objects in the image and then differentiate these aspects/objects from each other. “These techniques support our moldability and manufacturability analysis,” says Lofts, “which then feeds results into our pricing model.” Plyable's machine learning pricing model then calculates the price of tooling, based on the component geometry. “The model has priced thousands of parts, and gets better over time,” Lofts continues. “It can also adapt to market conditions and seasonality.”
The Plyable app works with metal tooling, composite tooling and 3D printed tools. “We offer tools from polyurethane board to steel and everything in between,” notes Oughton. “Because we don’t own our own machines, we can be agnostic to material and process, as well as scale and location.” In other words, even small customers around the world can be customers who gain a benefit.
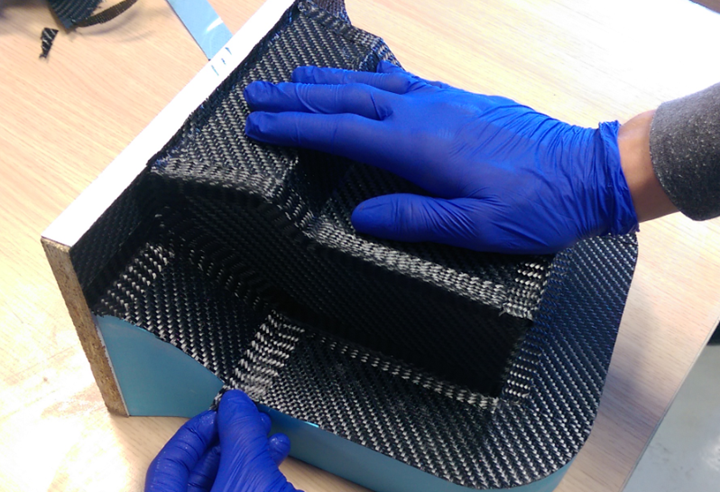

Delivering a manufacturing network via one app
The tools delivered through Plyable are actually made by a large network of manufacturing partners. “There are more machine shops in the U.K. and the U.S. than there are Starbucks,” notes Oughton. “We go outbound to add to our supplier network, sourcing only the best quality. Many are accredited, which is required by some of our customers; however, we also find small businesses that are extremely good at what they do. We help to make them more efficient, by becoming a key revenue stream for them, while supplying our customers with the highest-quality molding tools.”
How is quality assured? “Every single element is digitally inspected with a CMM (component measuring machine) to ensure our tolerance targets are achieved,” Oughton explains. “At every step of the process, the customer is updated in real time on the platform. Once complete, inspection reports are available for download on the platform as well. Quality is a top priority, because we know that you only get good parts with good tools.”
Plyable has also recently announced that it is ISO 9001:2015 certified, a globally-recognized quality management standard, which demonstrates its ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements. "Gaining our ISO certification is a major achievement for our team,” notes Plyable COO Adam England. “It demonstrates the robust quality processes that we have in place and gives our strategic partners and customers the confidence that we deliver composite molds to the very highest standard in design and manufacturing."
Future development
“Our tech team is hard at work,” says Lofts, “so expect to see significant changes in 2020. Moldability and mold automation will be upgraded so that our users can see an instant preview of the tooling. This new tech will allow our design engineers to work more quickly and consistently, ensuring that our customers always get the best quality tools. Also, our distributed manufacturing network will move more online, meaning better scheduling and faster lead times. Finally, our manufacturablity feedback will be supercharged with a number of DFM (design for manufacturing) modules, such as thin wall analysis, curvature analysis and visibility analysis.”
Visit www.plyable.com to learn more.
Related Content
Composite sidewall cover expands options for fire-safe rail components
R&D project by CG Rail explores use of carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastics and recycled manufacturing scrap to meet fire safety, weight and volume targets.
Read MoreJeep all-composite roof receivers achieve steel performance at low mass
Ultrashort carbon fiber/PPA replaces steel on rooftop brackets to hold Jeep soft tops, hardtops.
Read MoreNine factors to consider when designing composites cure tooling
Gary Bond discusses the common pitfalls and compromises when designing good cure tooling and their holistic significance for a robust composite production process.
Read MoreImproving carbon fiber SMC simulation for aerospace parts
Simutence and Engenuity demonstrate a virtual process chain enabling evaluation of process-induced fiber orientations for improved structural simulation and failure load prediction of a composite wing rib.
Read MoreRead Next
VIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read MoreAll-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read More















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)