Bally Ribbon Mill develops advanced woven textile products
The company offers its woven E-Webbings and TPCM thermoplastic materials to increase part functionality and utility for a variety of industries.
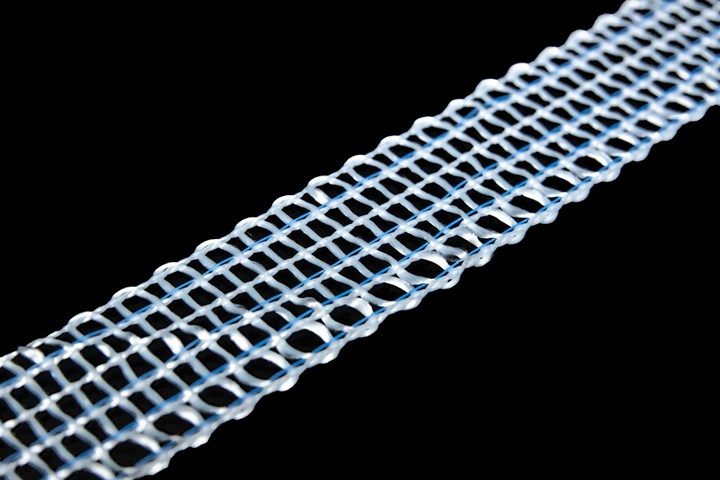
Photo Credit: Bally Ribbon Mills
Bally Ribbon Mills (BRM, Bally, Penn., U.S.) a company that designs, develops and manufactures engineered woven fabrics, announces its new line of advanced textile products, E-Webbings and TPCM thermoplastic materials, to increase part functionality and utility. Both products offer lighter weight, specific strength, durability, stability, abrasion resistance and sustainability. According to the company, these materials are suitable for use as a preform in a “variety of composites manufacturing processes.”
E-Webbings are narrow fabrics that are conductive, enabling the electronic transmission of data sensations (light, noise, vibrations, heat), and power that can be stored or used to actuate/transform objects. The conductive fibers can be woven in conjunction with other fibers and can be used in embedded sensors in both wearable and integral technology, including the Internet of Things (IoT).
TPCM thermoplastic composite materials are 2D- or 3D-woven thermoplastic structures for incorporation into composite parts produced within varied, continually-evolving molding processes. The woven structural shapes are used in hybrid composite structures used in numerous industries, including aerospace, automotive, defense, infrastructure, marine and sports/recreation.
BRM is in accordance with safety standards, specifications and certifications, including ISO9001, AS9100, ISO13485, ISO14000, NFPA, ASTM, ANSI, *UL, and CSA.
Related Content
-
TU Munich develops cuboidal conformable tanks using carbon fiber composites for increased hydrogen storage
Flat tank enabling standard platform for BEV and FCEV uses thermoplastic and thermoset composites, overwrapped skeleton design in pursuit of 25% more H2 storage.
-
Plant tour: Teijin Carbon America Inc., Greenwood, S.C., U.S.
In 2018, Teijin broke ground on a facility that is reportedly the largest capacity carbon fiber line currently in existence. The line has been fully functional for nearly two years and has plenty of room for expansion.
-
Natural fiber composites: Growing to fit sustainability needs
Led by global and industry-wide sustainability goals, commercial interest in flax and hemp fiber-reinforced composites grows into higher-performance, higher-volume applications.













