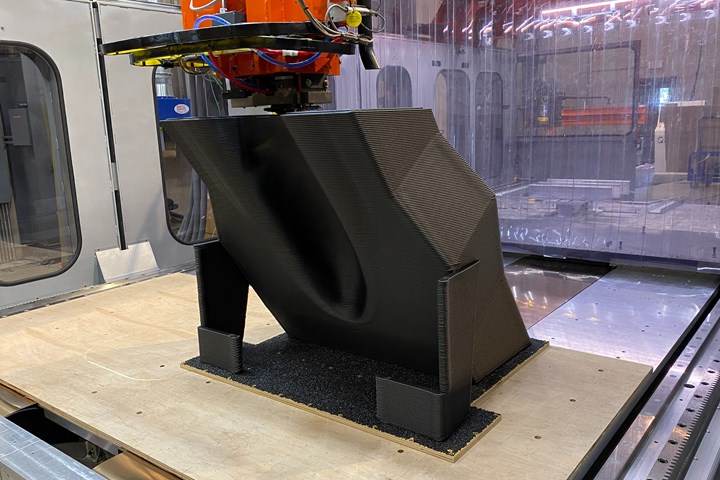
Thermwood’s LSAM 1020 machine printed a large-scale, autoclave-curable carbon fiber composite tool in seven hours and 26 minutes. Printing and trimming were accomplished using one machine center. Photo Credit, all images: Thermwood
The Boeing Research and Technology laboratory (Ladson, S.C., U.S.) and its partners recently completed a Navy ManTech-funded program to validate large-format additive manufacturing (LFAM) as a method for producing autoclave-capable composite tooling as a lower-cost, time-saving alternative to traditional tooling production methods.
The program was managed by Advanced Technology International (ATI) for the Office of Naval Research (ONR) with funding provided by the Naval Air Systems Command (NAVAIR) Aircraft Equipment Reliability and Maintainability Improvement Program (AERMIP).
Neil Graf of the Office of Naval Research (ONR), notes, “Composites manufacturing is a strategic technology for future platforms, and development of more cost-effective tooling solutions would significantly benefit the implementation.”
According to project partner Thermwood (Dale, Ind., U.S.), requirements for the composite tool, including vacuum integrity and dimensional stability, targets both in and out of the autoclave. The tool also needed to be durable enough to withstand multiple autoclave cure cycles at 355°F and 85 psi.
After several early attempts at additively manufacturing tooling, Thermwood’s large-scale additive manufacturing (LSAM) machine was ultimately selected for the project. Techmer PM PESU CF 1810 was chosen as the print material.
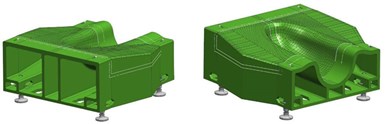
Challenges in the tool’s complex shape and potential issues with build angle limits and excessive material buildup were solved through CAD modeling.
The U.S. Navy’s Fleet Readiness Center East (FRCE) in Maryland provided a high contour mold line surface to Boeing for generating the composite cure tool. According to Thermwood, the mold line shape was very aggressive and would stretch the LFAM technology process capability. The spherically shaped portion of the mold line offered the largest challenge, because the machine’s limits only allow it to print at a build angle of 45° unsupported. To overcome this, Boeing rotated the 3D print plane 35°, which eased the build angle for the printer and allowed for printing without added support material Final tool dimensions were 16.3 inches tall x 43.1 inches wide x 41.2 inches long.
According to Thermwood, the complex build angle and high-temperature print material also tested the limits of the LSAM 1020 machine. Two interim support features were added to compensate for the center of gravity shift during the print. Overall, the tool was printed in seven hours and 26 minutes using 610 pounds of material. The composite cure tool was machined in 53 hours using the LSAM gantry router machine, which is combined with the LSAM printer on a single platform. The composite cure tool mold line part surface achieved a surface profile tolerance of 0.020 inch (± 0.010 inch).
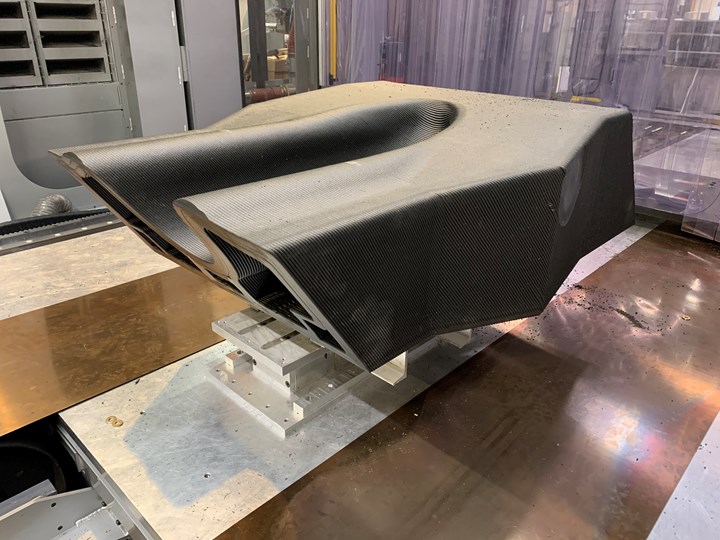

The finished tool was tested for vacuum integrity, dimensional stability, temperature performance and durability through multiple autoclave cure cycles at the Boeing Research and Technology laboratory.
After printing, the Boeing laboratory performed functional testing on the composite cure tool to ensure vacuum integrity and dimensional stability requirements were reached. According to Thermwood, the tool performed as expected and achieved all requirements.
Three composite demonstrator parts were fabricated from the tool as well. Nondestructive inspection (NDI) on the composite parts did not indicate any porosity, and C-scan and X-ray results revealed no delamination or defects.

Three test parts were molded on the finished 3D-printed tool and evaluated via NDI testing.
According to Thermwood, the technology cost savings was estimated at 50% compared to traditional tool fabrication methods, and reduced tool fabrication lead-time by 65%. “The program provided significant results in validating additive manufacturing as a viable method of producing lower-cost, capable tooling with substantial time savings over traditional methods,” says Michael Matlack, Boeing associate technical fellow.
Thermwood CEO Ken Susnjara notes that the program benefited from the collaboration of multiple partners. “Collaborations such as this help expand the scope of capabilities of emerging large-scale additive technology by addressing real-world challenges that would be difficult for any single entity to define and address by itself.”
Related Content
3D-printed CFRP tools for serial production of composite landing flaps
GKN Aerospace Munich and CEAD develop printed tooling with short and continuous fiber that reduces cost and increases sustainability for composites production.
Read MoreCorebon induction heating
This sidebar to CW’s August 2024 feature article reviews this technology for more efficient composites manufacturing and why it aligns with Koridion active core molding.
Read MoreTPI, UMaine, ORNL to leverage world’s largest polymer 3D printer for wind turbine tooling
Ingersoll Masterprint LFAM printer will be used to produce and demonstrate 100% recyclable tooling that could cut large composite blade development cycles and tooling costs by as much as 50%.
Read MoreMold 3D printing helps automate composite bathtub, shower production
As part of its efforts to automate as much of its production process as it can, Lyons Industries acquired a Massivit 10000 additive manufacturing system to quickly produce high-performance molds and support fixtures.
Read MoreRead Next
Thermwood releases “A Manager's Guide to Large Scale Additive Manufacturing"
Written by Thermwood founder, chairman and CEO Ken Susnjara, the 315-page book covers the basics behind new large-scale additive manufacturing (LSAM) technology.
Read MoreQ&A: Importance of reliability in large-scale additive manufacturing
Thermwood Corp. CEO Ken Susnjara shares an LSAM supplier’s perspective on enabling reliable, continuous manufacturing performance.
Read MoreAll-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)





















