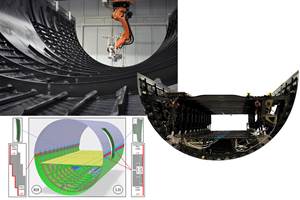
Corebon equipped a metal mold with a custom inductor coil used with its CorePower inverter to provide fast, uniform heat and shorten the molding cycle for Alia Mentis’ carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) car hood demonstrator. Source (All Images) | Corebon
Corebon (Malmo, Sweden) provides production solutions for manufacturing and assembly of fiber-reinforced composites using thermoset and thermoplastic polymers, including high-end aerospace materials. “Our solutions are based on proprietary induction technology that uses highly efficient noncontact heating,” says Kenneth Frogner, head of R&I at Corebon. “This provides unique opportunities for molding composite parts.”
Induction can be used to heat all types of electrically conductive materials, he explains, including steel, Invar, aluminum and carbon fiber. “Induction has been used for about a century to heat small metal objects, but large parts and complex geometries have, with some exceptions, been a challenge until recently,” explains Frogner. “By providing very uniform heating and cooling, Corebon can help reduce the mass of the molds to a minimum, limited only by the structural requirements and to resist pressure during molding. This enables fast and efficient temperature cycling of metal molds.”
Infrared images showing uniform heating across induction heated molds for CFRP hood demonstrator using Koridion core molding.
“While traditional induction heating suffers from size and geometrical limitations,” he continues, “with significant losses in the coils, Corebon uses flexible wires and modern materials, resulting in superior energy efficiency versus other heating methods. For example, 90-95% of the power in the wall outlet is transformed into heat within the mold. We can typically reduce energy use by 50-80% compared to traditional composites processes. However, the largest energy savings come from the reduction in the mold’s thermal mass.”
Demonstration of molding thermoplastic comosite violin cases with induction heated shell tool at JEC 2023.
Corebon provides different types of tooling solutions, including metal shell tools with or without support structure (see CW’s reporting on “Tooling for composites,” Weber’s NVD tools and a nickel shell tool at Dowty Propellers). “We can also accommodate tools with a significant thickness variation,” says Frogner. “Shell tools are the most efficient, with possible heating and cooling rates of more than 100°C/minute, and they are the best suited for volume production. Similar to how each part needs a custom-made tool, each induction-heated shell tool needs a customized inductor and cooling configuration. Cooling uses air, water or a mixture, depending on the application requirements.”
For tools with a flat back side, Corebon offers more generic solutions that can be used with different tool geometries. These CorePlates are available in three formats depending on the heating and cooling technology used:
- All-in-one is a thermally cycled plate, typically mounted in a press, where heating and cooling are transferred to the mold through the lightweight press platens.
- Adapt plates enable the molds to be directly heated by induction with two different options for cooling: within the mold or through conduction from a cooling structure.
- Tailor is a combination of the other two, tailored for a certain geometry, where faster heating and cooling rates can be achieved. This approach is used when a high level of optimization and high production rates are needed, for applications with only minor geometrical variations.
Alia Mentis used a CorePlate Adapt tool, modified to its design, for the CFRP car hood to demonstrate its Koridion active core molding process (see “Active core molding: A new way to make composite parts.”).
The heart of Corebon’s induction technology is its frequency inverter, says Frogner, which powers the heating and enables sophisticated process control. “Our inverters have been developed specifically for use with composites,” he explains. “They are easy to operate and offer a wide range of functionality, making them versatile. For example, our systems can be used for induction welding or easily integrated into autoclaves or press systems.”
Multi-piece induction heated mold for Alia Mentis’ CFRP hood demonstrator (bottom left) using Koridion active core molding. Protector plates are used on top and bottom of bolted mold assembly for insertion into press.
The CorePower inverters are modular and can be stacked for larger production setups. They can also supply power to multiple zones to maintain very uniform temperature across changes in thickness and geometry. “We also have features that enable real-time analysis of process data for improved process control,” says Frogner.
He notes that Corebon is also working with direct heating of carbon fiber structures. “Induction welding of carbon fiber thermoplastics is one example, but we are also providing in-situ heating for preforming of prepreg and dry layups.”
“Our goal is to remove the limits that hold composites manufacturing back,” says Frogner. “So, we are very aligned with Alia Mentis and their Koridion technology. Corebon as a partner offers very fast, accurate heating and cooling, resulting in shorter cycles using less energy.”
Related Content
TU Munich develops cuboidal conformable tanks using carbon fiber composites for increased hydrogen storage
Flat tank enabling standard platform for BEV and FCEV uses thermoplastic and thermoset composites, overwrapped skeleton design in pursuit of 25% more H2 storage.
Read MoreLarge-format 3D printing enables toolless, rapid production for AUVs
Dive Technologies started by 3D printing prototypes of its composite autonomous underwater vehicles, but AM became the solution for customizable, toolless production.
Read MoreManufacturing the MFFD thermoplastic composite fuselage
Demonstrator’s upper, lower shells and assembly prove materials and new processes for lighter, cheaper and more sustainable high-rate future aircraft.
Read MoreJeep all-composite roof receivers achieve steel performance at low mass
Ultrashort carbon fiber/PPA replaces steel on rooftop brackets to hold Jeep soft tops, hardtops.
Read MoreRead Next
KVE INDUCT: Welding a torsion box demonstrator
To meet sustainability targets and market demands, the aerospace industry is searching for alternative joining methods. Automated assembly of thermoplastic composite structures by induction welding offers a solution. (Sponsored)
Read MoreVIDEO: Corebon Demos Induction Heating Systems at JEC World 2023
Kenneth Frogner, Head of Research at Corebon, demos their different induction heating systems on the show floor at JEC World 2023.
Read MoreDeveloping bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read More