No-oven, No-autoclave (NONA)
Room-temperature cure epoxy composites with a 400°F Tg, comparable properties vs. commercial systems without external heat or post-cure, and offering reduced cost and cycle time. Really?

Slightly curved composite tool for Space Launch System (SLS) test panels.
SOURCE: NONA Composites, LLC
No-oven, No-autoclave (NONA) composites technology was developed by Cornerstone Research Group (CRG, Dayton, Ohio) through a 2010 SBIR in conjunction with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Glenn Research Center (Cleveland, Ohio, USA) and is now being commercialized by CRG’s spinoff, NONA Composites LLC (Dayton, Ohio). The original goal was more cost-effective processing of large composite structures and tooling without the large capital expense of autoclaves, ovens or heated tools for cure.
NONA is largely based on what the company terms “commercial off-the-shelf” (COTS) technology. The NONA-001 two-part epoxy resin uses readily available COTS components, combined in its own proprietary formulation. It is processed using conventional resin infusion and low-cost machined foam tooling (i.e., COTS polymeric tooling board). The innovative part is controlling the resin’s exothermic reaction and capturing its heat to achieve full cure and high temperature properties. NONA Composites LLC claim laminates with a glass transition temperature (Tg) of 400°F/204°C achieved via a two-hour cure and six-hour cool-down cycle, enabling service temperatures up to 350°F/177°C.
Welcome! You’ve unlocked premium content.
Recent developments were reviewed in the SAMPE Tech 2013 (Oct 21-24, Wichita, Kan., USA) paper, “No-oven, no-autoclave processing for NASA composite structures”, including construction of a 127cm by 66cm (50-inch by 26-inch) carbon fiber skin/aluminum honeycomb sandwich part and a 117cm by 107cm (46-inch by 42-inch) curved carbon tool as preparation for building a 1:10 scale payload fairing section (including upper barrel and ogive) tool for the NASA Space Launch System (SLS) heavy-lift launch vehicle. The SLS tooling project is now underway and currently scheduled for completion by late Spring 2014. This is one of many out of autoclave (OOA) composite technologies NASA is exploring (see “Tooling up for larger launch vehicles” in September 2013 CT).
NONA composites have also been tested using National Institution for Aviation Research (NIAR, Wichita, Kan.) specifications, in order to provide a comparison with a currently used matrix system — Cycom 5215 OOA epoxy resin from Cytec (Tempe, Ariz., USA), which has an extensive properties listing in the National Center for Advanced Materials Performance (NCAMP) database. The SAMPE paper cited similar performance in seven-day boil, open hole tension (OHT), open hole compression (OHC), and compression after impact (CAI) testing. Compression and tensile properties are still being completed, but the damage tolerance an shear properties have been released (see below). The total number of specimens tested so far is still relatively small, but the initial results look promising. Fiber volumes have ranged from 62 to 67 percent by weight with void content consistently below 1 percent.
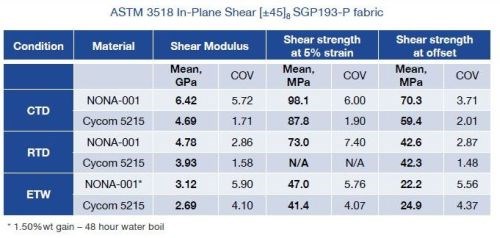
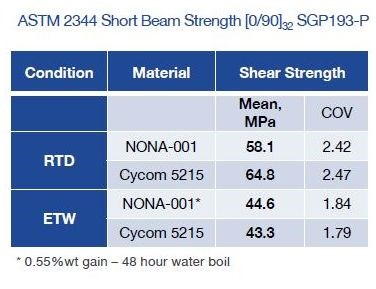
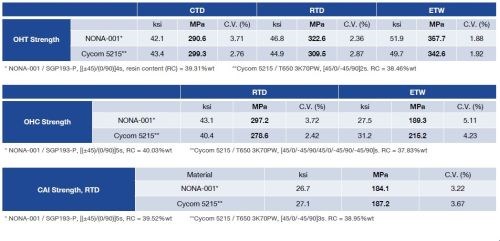

Comparison of NONA process thermal and mechanical performance
to conventional OOA system. SOURCE: NONA Composites, LLC
“We are now working with composite tooling and structures manufacturers,” says Ben Dietsch, NONA Composites LLC chief operating officer, “and have an inventory of resin available to support the increased interest we have received.” He explains companies are seeking reduced cycle time and the ability to make high performance tools from low-cost master models using foam, which machines faster and reduces tooling weight vs. higher density epoxy tooling board. According to Dietsch, though savings are greatest with larger tools, time and cost reductions can be achieved with tools as small as a couple of square feet. “We compare favorably versus LTM tooling prepreg, for example, and we’re also demonstrating advantages beyond tooling, in secondary and tertiary structures.” NONA Composites is also looking forward to primary-type structures, investigating how the NONA resin and curing technology can be combined with toughened prepreg to enable processing benefits for systems already qualified with desired fiber volume and damage tolerance properties.
NONA Composites will exhibit their latest developments at the Wasatch Front Materials Expo (March 5, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA) and CAMX (Oct 13-16, Orlando, Fla., USA).
Related Content
Plant tour: Spirit AeroSystems, Belfast, Northern Ireland, U.K.
Purpose-built facility employs resin transfer infusion (RTI) and assembly technology to manufacture today’s composite A220 wings, and prepares for future new programs and production ramp-ups.
Read MorePEEK vs. PEKK vs. PAEK and continuous compression molding
Suppliers of thermoplastics and carbon fiber chime in regarding PEEK vs. PEKK, and now PAEK, as well as in-situ consolidation — the supply chain for thermoplastic tape composites continues to evolve.
Read MorePlant tour: Albany Engineered Composites, Rochester, N.H., U.S.
Efficient, high-quality, well-controlled composites manufacturing at volume is the mantra for this 3D weaving specialist.
Read MoreTU Munich develops cuboidal conformable tanks using carbon fiber composites for increased hydrogen storage
Flat tank enabling standard platform for BEV and FCEV uses thermoplastic and thermoset composites, overwrapped skeleton design in pursuit of 25% more H2 storage.
Read MoreRead Next
Plant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read MoreDeveloping bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read More




















