Effman installs AFP-XS as part of project to enable AFP for SMEs
uCOMP project with Addcomposites and Quebec partners demonstrates new woven tape and high-permeability preforms for resin infusion in <2 minutes.
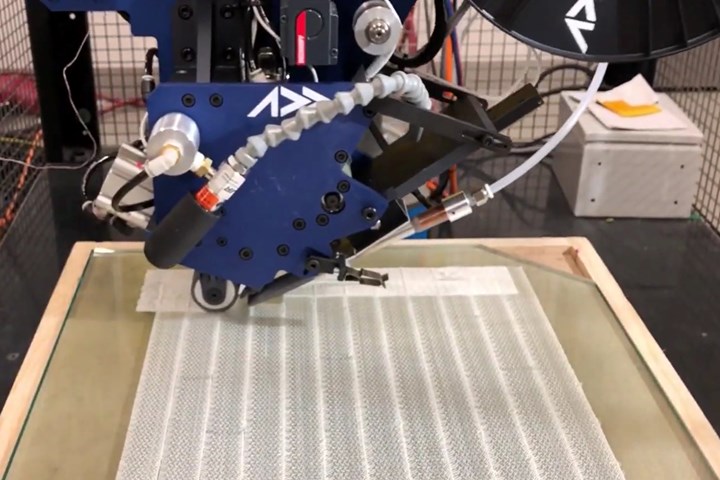
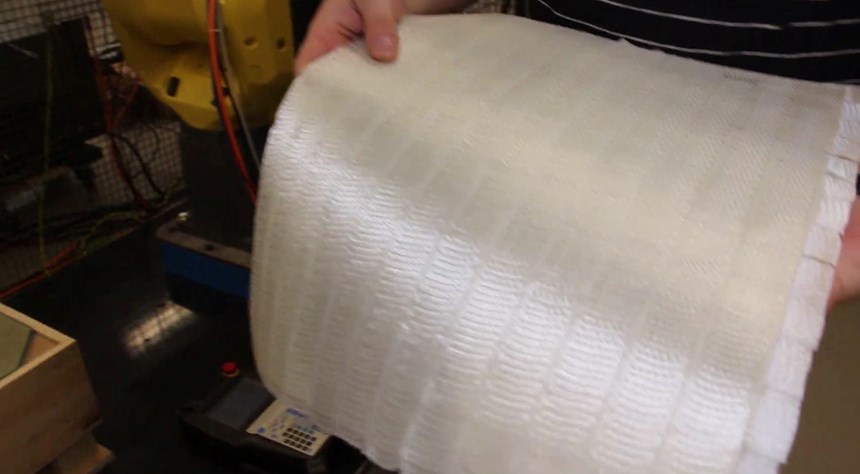
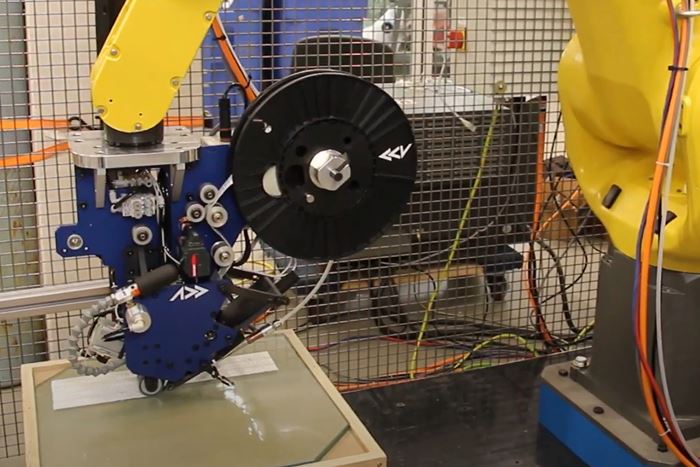
Effman installs Addcomposites AFP-XS onto FANUC robot. Photo Credit: Effman.
Effman (Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada) has integrated and tested the first AFP cell in North America formed by plugging an Addcomposites (Espoo, Finland) AFP head into a FANUC robot. “Until now, AFP has been reserved for major players in the aerospace industries because of the complexity and cost of equipment,” says Yoann Bonnefon, president of Effman. Specializing in the development of automation for composites manufacturing, Effman is now collaborating with Addcomposites to make AFP robotic cells accessible to small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
“The uCOMP project started with the idea of bringing more automation to composites processes,” says Bonnefon. “We see that small companies especially are still relying on manual methods. We want to help them be prepared for the type of industrialization needed in today’s supply chains.” One goal is the ability to produce preforms for processes like vacuum infusion, resin transfer molding (RTM) and Light RTM. “We can improve the process and economics for such preforms,” says Bonnefon.
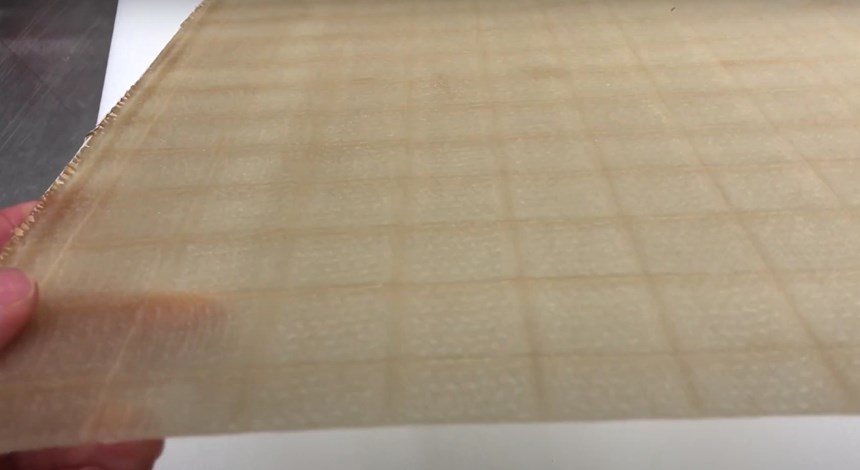
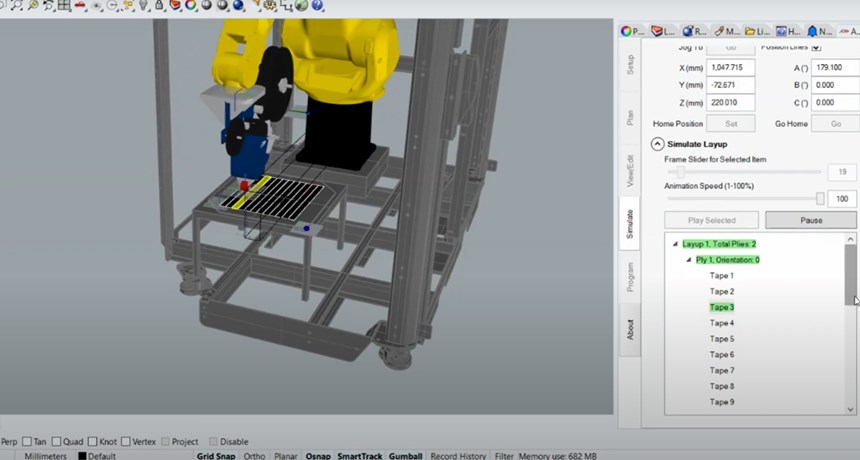
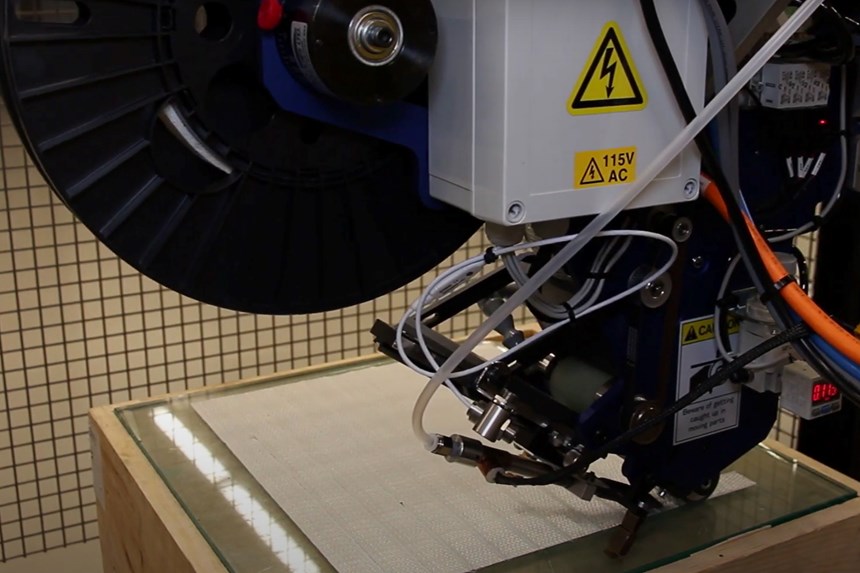
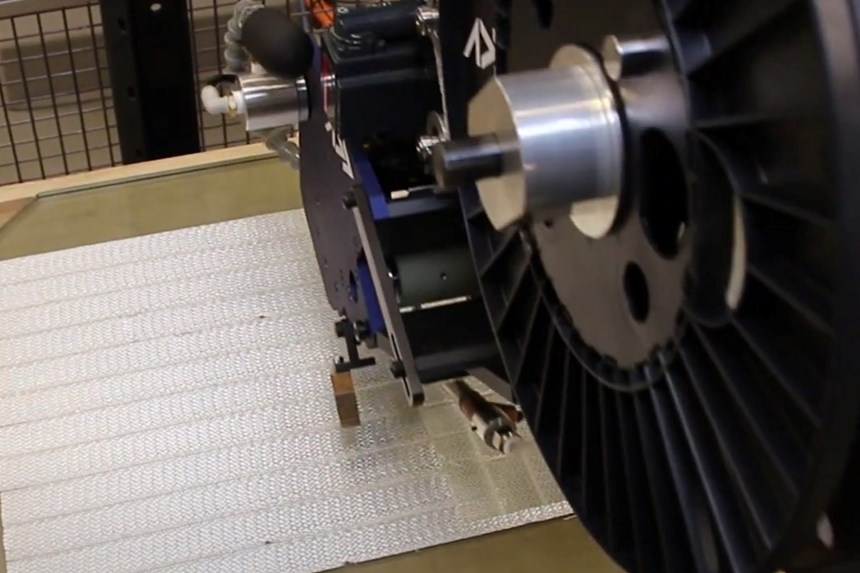
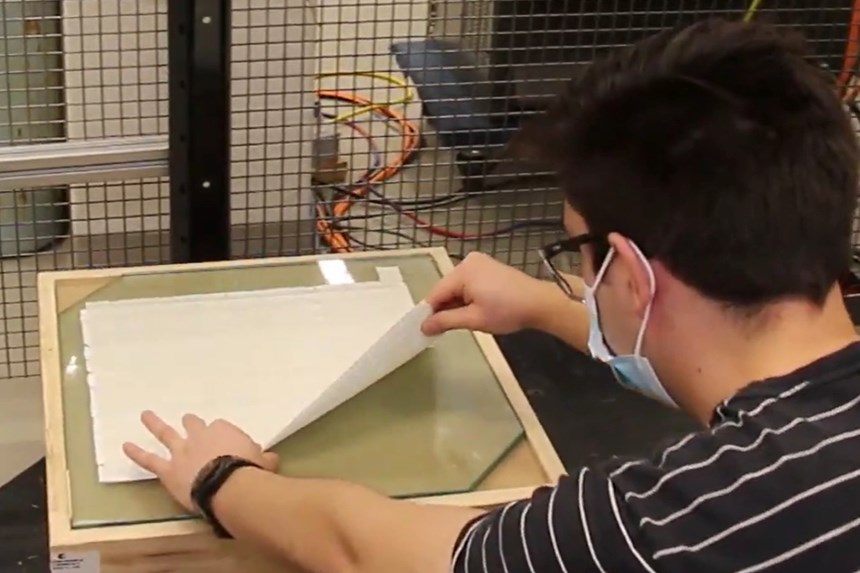
The AFP-XS provides the key for a light and compact robotic equipment solution that is affordable for small companies with limited financial resources. “This solution also needs to be simple,” adds Bonnefon, “able to be quickly installed and in operation without a lot of expense and training. The AFP-XS has met these needs, weighing less than 20 kilograms and fitting easily within a standard robotic cell. Without any experience with either the AFP-XS head or the ADD PATH software, we were able to complete the installation and, within a few weeks, complete the AFP simulation for parts using a new tape that we developed with a partner in Quebec. This woven glass fiber tape had never before been tested on an AFP-XS head, and yet we were able to use it and make preforms in less than two minutes that were easily processed using resin infusion.”
manufacturing and infusion of preforms
The uCOMP project aims to help SMEs use AFP. This technological advance is being achieved with Effman’s network of Quebec-based partners: CTT Group, Centre de développement des composites du Québec (CDCQ), FANUC America Corp., Armtex Fibres Inc. and Robox. “Our aim is to democratize the use of AFP and composites to make high-performance, affordable small- and medium-size parts,” says Bonnefon.
In addition to thermoset and thermoplastic tapes already used with the AFP-XS, Effman and its partners have developed dry-weave tapes (glass or carbon fiber) allowing the realization of preforms optimized for infusion and injection processes. Effman is now exploring projects with research organizations, to create new structures and new knowledge, but also sees opportunities in the supply chains for sporting goods, as well as automotive and aerospace, as the trends in electrification and new mobility advance. “This equipment is much cheaper than what currently exists in the market, yet enables precise fiber placement to make structural parts,” says Bonnefon. “We see many applications and look forward to working with companies across North America.”
Interested companies can contact Yoann Bonnefon and James Kuligoski for more details on part and equipment trials.
Related Content
Plant tour: BeSpline/Addcomp, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada
Composites automation specialist increases access to next-gen technologies, including novel AFP systems and unique 3D parts using adaptive molds.
Read MoreCombining multifunctional thermoplastic composites, additive manufacturing for next-gen airframe structures
The DOMMINIO project combines AFP with 3D printed gyroid cores, embedded SHM sensors and smart materials for induction-driven disassembly of parts at end of life.
Read MoreManufacturing the MFFD thermoplastic composite fuselage
Demonstrator’s upper, lower shells and assembly prove materials and new processes for lighter, cheaper and more sustainable high-rate future aircraft.
Read MoreATLAM combines composite tape laying, large-scale thermoplastic 3D printing in one printhead
CEAD, GKN Aerospace Deutschland and TU Munich enable additive manufacturing of large composite tools and parts with low CTE and high mechanical properties.
Read MoreRead Next
Addcomposites and Effman partner to provide AFP cells for SMEs
Aim is affordable, enclosed composites manufacturing cells for many different processes (AFP, grinding, buffing, sanding, drilling) in North American market.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read MoreAll-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read More