UBC engineers successfully develop carbon fiber from bitumen
Through a distinctive spinning process, the university team has enabled the production of carbon fiber for less than $12/kilogram, targeting high-volume industries like automotive.
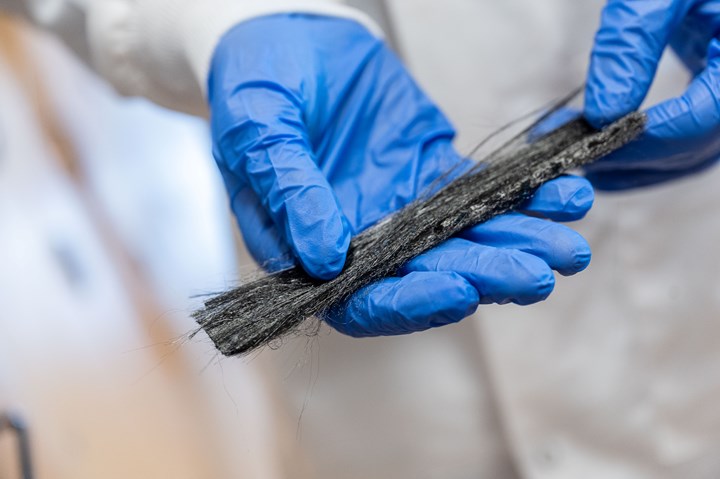
Finished carbon fibers derived from bitumen. Photo Credit, all images: UBC Applied Science/Paul Joseph
A new process developed at the University of British Columbia (UBC, Canada) has the potential to turn the ability to make lightweight composite electric vehicles (EVs) into reality. At her lab in the Faculty of Applied Science, UBC materials engineering assistant professor Dr. Yasmine Abdin and her collaborators, Dr. Frank Ko and Dr. Scott Renneckar, have successfully transformed bitumen into carbon fiber — spinning the black, sticky substance from Alberta’s oil sands into a crucial product for the energy transition.
Compared to gasoline-powered cars, battery electric vehicles (BEVs) can be hundreds to thousands of pounds heavier due to the weight of their batteries. “Building a car’s chassis or body with lightweight carbon fibers not only helps to compensate for a heavy EV battery pack, the carbon fibers also enhance a battery’s ability to stay cool, improves passenger safety and extends driving range,” Dr. Abdin, the project lead and an expert on polymer-based composite materials, explains.
However, producing carbon fiber is notoriously expensive, with about half of the cost attributed to the raw material, polyacrylonitrile (PAN). By switching to bitumen, researchers contend that costs can be significantly reduced while also mitigating the environmental impact associated with bitumen, which releases carbon dioxide when burned.
The team’s process is said to enable the production of carbon fiber for less than $12 per kilogram, in contrast to the typical commercial rate of $33 per kilogram.
“We are repurposing what is essentially a low-value product that can cause environmental damage, to produce materials that will enable clean tech,” Dr. Renneckar, a professor in the department of wood science at UBC and the Canada Research Chair in Advanced Renewable Materials, points out.
The process developed by Dr. Abdin and her colleagues was one of the winning solutions during the first two phases of the Carbon Fibre Grand Challenge, a competition launched by Alberta Innovates (Canada) to recover valuable products from oil sands.
At the core of the successful UBC formula lies a process that is not radically different from how carbon fibers are currently made, but in a distinctive method of spinning finer fibers while maintaining the fibers’ structural integrity. Additionally, the UBC team has developed two distinct fiber sizes — regular micro-diameter fibers, and nano-fiber structures, both derived from bitumen. The team’s process is said to enable the production of carbon fiber for less than $12 per kilogram, in contrast to the typical commercial rate of $33 per kilogram.
“With a price point of $12 per kilogram, high-volume industries like automakers will have the opportunity to use more carbon fiber,” Dr. Abdin says. “Currently, composite materials like carbon fibers comprise only about 15% of a car’s composition. Affordable carbon fibers can potentially double this figure, which could be a game changer.”
Dr. Abdin and her team plan to apply for the third phase of the Carbon Fibre Grand Challenge competition, which will involve testing of the fibers on a larger scale, ultimately leading to commercial-scale production. The additional funding in the third round will facilitate scaling up fiber production and the manufacturing of composite products.
Twelve teams were funded in phase two, but only five or six teams will be funded for the final phase. With $4 million in funding at stake, Dr. Abdin is gearing up for the future.
“Automakers aren’t the only industry we’re targeting with the cost and performance benefits of our fibers,” she adds. “We’re also exploring wider applications in wind turbines, structural batteries, supercapacitors, pipelines and even hockey sticks!”
Also read, “UCalgary researchers turn Alberta oilsands bitumen into high-value carbon fibers.”
Related Content
Infinite Composites: Type V tanks for space, hydrogen, automotive and more
After a decade of proving its linerless, weight-saving composite tanks with NASA and more than 30 aerospace companies, this CryoSphere pioneer is scaling for growth in commercial space and sustainable transportation on Earth.
Read MoreThe lessons behind OceanGate
Carbon fiber composites faced much criticism in the wake of the OceanGate submersible accident. CW’s publisher Jeff Sloan explains that it’s not that simple.
Read MoreCryo-compressed hydrogen, the best solution for storage and refueling stations?
Cryomotive’s CRYOGAS solution claims the highest storage density, lowest refueling cost and widest operating range without H2 losses while using one-fifth the carbon fiber required in compressed gas tanks.
Read MoreSulapac introduces Sulapac Flow 1.7 to replace PLA, ABS and PP in FDM, FGF
Available as filament and granules for extrusion, new wood composite matches properties yet is compostable, eliminates microplastics and reduces carbon footprint.
Read MoreRead Next
DITF develops water-spun lignin fibers as PAN precursor alternative
Lignin fibers produced via an aqueous solution and dry spinning process result in homogeneous, smooth-surfaced fibers that are more environmentally friendly and cost-saving.
Read MoreBio-based acrylonitrile for carbon fiber manufacture
The quest for a sustainable source of acrylonitrile for carbon fiber manufacture has made the leap from the lab to the market.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read More