Noncontact digital gage enables precise materials, structural testing
CAMX 2024: Trilion Quality Systems is showcasing the Aramis optical strain gage, a material-independent measurement device with 3D-DIC capabilities.
Share
Trilion Quality Systems (King of Prussia, Pa., U.S.) exhibits its Aramis optical strain gage, a noncontact and material-independent measuring system that can provide critical data such as full-field optical strain, 3D displacement and vibration analysis with ease. Aramis is designed to be a cost-effective alternative for foil gages and extensometers. It can operate with 50 times less labor/time and provide 100 times more data, according to the company. With applications from finite element analysis (FEA) validation, material/structural testing, structural health monitoring and high-speed measurements, the Aramis optical strain gage can be used for a wide range of industries from automotive, aerospace, biomechanics and more.
At Aramis’ core is 3D digital image correlation (3D-DIC), a noncontact measuring technique based on advanced image processing, which can provide accuracy comparable to a mechanical gage. DIC is capable of mapping 3D coordinates and evaluating displacement and strain maps on the surface of measured samples. DIC uses a stochastic pattern and/or point markers to track the surface of the materials with subpixel accuracy or microns of motion.
In addition to its testing system, Trilion can perform its services on-site at customer facilities to provide flexibility and quick implementation or deployment of technologies.
Related Content
-
Plant tour: BeSpline/Addcomp, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada
Composites automation specialist increases access to next-gen technologies, including novel AFP systems and unique 3D parts using adaptive molds.
-
3D-printed CFRP tools for serial production of composite landing flaps
GKN Aerospace Munich and CEAD develop printed tooling with short and continuous fiber that reduces cost and increases sustainability for composites production.
-
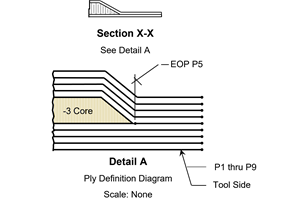
The basics of composite drawing interpretation
Knowing the fundamentals for reading drawings — including master ply tables, ply definition diagrams and more — lays a foundation for proper composite design evaluation.
Related Content
Plant tour: BeSpline/Addcomp, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada
Composites automation specialist increases access to next-gen technologies, including novel AFP systems and unique 3D parts using adaptive molds.
Read More3D-printed CFRP tools for serial production of composite landing flaps
GKN Aerospace Munich and CEAD develop printed tooling with short and continuous fiber that reduces cost and increases sustainability for composites production.
Read MoreThe basics of composite drawing interpretation
Knowing the fundamentals for reading drawings — including master ply tables, ply definition diagrams and more — lays a foundation for proper composite design evaluation.
Read MoreBladder-assisted compression molding derivative produces complex, autoclave-quality automotive parts
HP Composites’ AirPower technology enables high-rate CFRP roof production with 50% energy savings for the Maserati MC20.
Read MoreRead Next
Automated robotic NDT enhances capabilities for composites
Kineco Kaman Composites India uses a bespoke Fill Accubot ultrasonic testing system to boost inspection efficiency and productivity.
Read MoreReinforcing hollow, 3D printed parts with continuous fiber composites
Spanish startup Reinforce3D’s continuous fiber injection process (CFIP) involves injection of fibers and liquid resin into hollow parts made from any material. Potential applications include sporting goods, aerospace and automotive components, and more.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read More