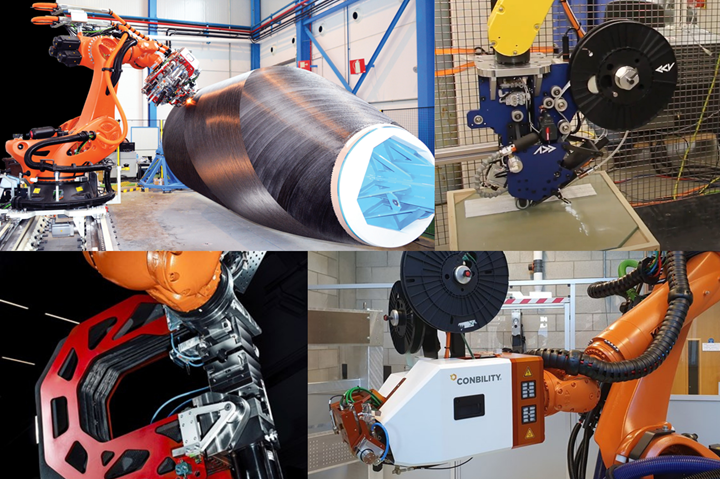
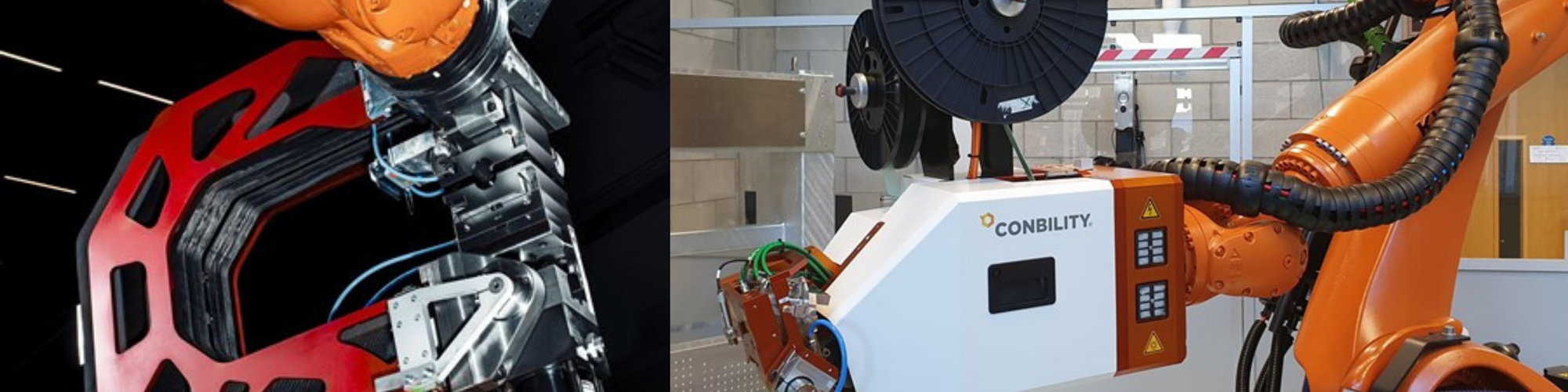
Photo Credit: MTorres (top left), Effman (top right), Anybrid (bottom left) and Bilsing Automation (bottom right).
CW received a press release in April titled, “TRB Lightweight Structures manufactures prepreg material to streamline part production.” Bringing materials manufacture in-house isn’t new. I remember touring Diamond Aircraft’s (Wiener Neustadt, Austria) composite aircraft manufacturing facility in London, Ontario, Canada in the 1990s and seeing European resin impregnation machines that allowed the company to produce its own “wet” prepreg materials on-demand, which were immediately used to build aircraft structures using hand layup (see “Plant tour: Diamond Aircraft”). The goal was to control materials production and quality to enable the production flexibility and cost-control needed by the small aircraft manufacturer.
What is different now is that, thanks to new robotic and digital technologies, everything from fiber placement to computed tomography (CT) to injection molding is being automated in increasingly smaller equipment that is more flexible and cost-effective. This not only gives small companies the capability for high-quality, high-performance composite parts production at potentially high volumes — a capability traditionally affordable only to large, Tier 1 aerospace suppliers — but it also expands the market for such composite parts beyond the traditionally high-value, high-margin realm of aerospace.
Both goals were noted in my 2018 blog, “The democratization of composites” about Covestro’s (Leverkusen, Germany) launch of Maezio continuous carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic tapes. Covestro asserted that Maezio was fulfilling a desire for democratization by innovative companies (e.g., Haier air conditioners and Bmai running shoes) to provide the design and performance advantages of composites without a Lamborghini price tag.
An increasing number of advanced manufacturing capabilities can now be brought in-house, including not just prepregging, but production of dry braids (e.g., Herzog) and dry fiber tapes (e.g., MTorres), automated tape laying (e.g., Addcomposites, Effman, Conbility, etc.), robotic inspection (e.g., Radalytica, Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence, CIKONI, etc.) and robotic injection overmolding (Anybrid). Couple this with all of the sensors now available, and the ability to outsource traditional jobs such as tooling to online portals (e.g., Plyable, ExOne) — at lower lead time and cost than previously possible — and you have a totally new supply chain beginning to form.
Let’s go back to TRB Lightweight Structures (Huntingdon, U.K.) as one example of this trend. The company was founded as a honeycomb core sandwich structures manufacturer and then acquired by composites investor Jonathan McQueen in 2007. In 2018, it announced a new biocomposite prepreg and foam core door for passenger railcars. In 2019, it was named among the U.K.’s Fast Track 100 companies and as a supplier to Airbus, and then announced a new, 40,000-square-foot manufacturing center in the U.S. — a joint venture with Toyota Tsusho America (New York, N.Y., U.S.) — for high-volume production of carbon fiber composite electric vehicle components using its advanced robotics-based press-forming process that allows price parity with aluminum parts.
This commingled advance in equipment, processes and materials is another trademark of the democratization trend. As composites automation specialist Effman (Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada) adapted a plug-and-produce AFP head by Addcomposites (Espoo, Finland) into an automated cell aimed at small and medium enterprises (SMEs), it also developed a novel dry glass fiber tape to facilitate flexible and cost-effective dry preform production. MTorres’ dry fiber tape lines were developed for production of wind blades and automotive parts while also enabling affordable runs of new materials — something not available from most current tape suppliers. Another interesting characteristic of companies embracing this advance in composites affordability and new markets is that they are often also pushing boundaries in worker training and sustainability. All of this is worth noting for future supply chains.
What we at CW are seeing is that traditional hand-laid prepreg will give way to automated, digital manufacturing, and the skills/personnel required will change accordingly. Though manual labor jobs will decrease, there will be an increased need for new imagination and creativity in how to exploit these new technologies and also for workers skilled in Composites 4.0/digital tools, sensors and data science, robotics, mechatronics, industrial integration and human/robot collaboration. Sustainability is also key. Already a powerful tool for composites startups in fundraising, the reality is that sustainability is an existential issue. Emerging composites supply chains will be led by companies with C-suite execs and technical personnel that investigate and implement not only recycling at end of life, but also raw materials that exploit increased bio and recycled content and renewable energy, as well as reduced water use, emissions and toxicity throughout manufacture, use and re-use.
The composites industry has always been dynamic — change has been constant and, I have no doubt, will continue to be so. But the pace has increased, and noticeably. It will be interesting to see which companies embrace this democratization and which resist — and the latter, I believe, will find themselves no longer key players in the fast-developing supply chains of the future.
Related Content
Watch: A practical view of sustainability in composites product development
Markus Beer of Forward Engineering addresses definitions of sustainability, how to approach sustainability goals, the role of life cycle analysis (LCA) and social, environmental and governmental driving forces. Watch his “CW Tech Days: Sustainability” presentation.
Read MoreJEC World 2023 highlights: Recyclable resins, renewable energy solutions, award-winning automotive
CW technical editor Hannah Mason recaps some of the technology on display at JEC World, including natural, bio-based or recyclable materials solutions, innovative automotive and renewable energy components and more.
Read MoreNovel composite technology replaces welded joints in tubular structures
The Tree Composites TC-joint replaces traditional welding in jacket foundations for offshore wind turbine generator applications, advancing the world’s quest for fast, sustainable energy deployment.
Read MoreNatural fiber composites: Growing to fit sustainability needs
Led by global and industry-wide sustainability goals, commercial interest in flax and hemp fiber-reinforced composites grows into higher-performance, higher-volume applications.
Read MoreRead Next
Composites 4.0: Digital transformation, adaptive production, new paradigms
An evolving landscape of automation, sensors and AI software is not an end, but a means to achieve the cost, quality, efficiency and agility required for future manufacturing.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read MoreDeveloping bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read More