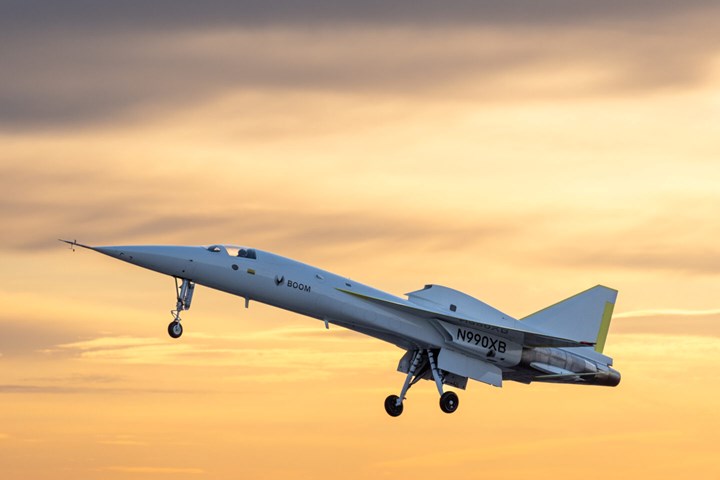
Boom Supersonic achieves first XB-1 demonstrator flight
Supersonic demonstrator met all test objectives, aided by use of carbon fiber materials, advanced avionics, digitally optimized aerodynamics and a supersonic propulsion system.
On March 22, Boom Supersonic’s (Denver, Colo., U.S.) XB-1 supersonic aircraft demonstrator achieved its first successful flight in Mojave, California. Like Overture, XB-1 leverages technologies that will enable efficient supersonic flight including carbon fiber composites, advanced avionics, digitally optimized aerodynamics and an advanced supersonic propulsion system.
Flown by chief test pilot Bill “Doc” Shoemaker, XB-1 took off from the Mojave Air & Space Port and flew in the same airspace that hosted many historic first flights, including the flights of the Bell X-1, the North American X-15 and the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird. Test pilot Tristan “Geppetto” Brandenburg flew the T-38 chase aircraft which monitored XB-1 in the air. Chase planes accompany new aircraft on their maiden flights to observe how the test plane is handling and verify things like altitude, airspeed and airworthiness during flight.
Importantly, XB-1 met all of its test objectives, including safely and achieving an altitude of 7,120 feet and speeds up to 238 knots (273 miles per hour). While XB-1 was in the air, the team performed an initial assessment of the aircraft’s handling qualities, including airspeed checks with the T-38 chase aircraft, and assessing the aircraft’s stability in the landing attitude (at a high angle of attack).
The XB-1 program provides the foundation for Overture’s design and development, while establishing a safety-first culture in engineering and manufacturing. XB-1 validates key technologies and Boom’s own innovations, including:
- Augmented reality vision system: Two nose-mounted cameras, digitally augmented with attitude and flight path indications, feed a high-resolution pilot display for runway visibility. This system enables improved aerodynamic efficiency without the weight and complexity of a movable nose.
- Digitally-optimized aerodynamics: Engineers used computational fluid dynamics simulations to explore thousands of designs for XB-1. The result is an optimized design that combines safe and stable operation at takeoff and landing with efficiency at supersonic speeds.
- Carbon fiber composites: XB-1 is almost entirely made from composite materials, enabling it to realize an aerodynamic design in a strong, lightweight structure.
- Supersonic intakes: XB-1’s engine intakes slow supersonic air to subsonic speeds, efficiently converting kinetic energy into pressure energy, allowing conventional jet engines to power XB-1 from takeoff through supersonic flight.
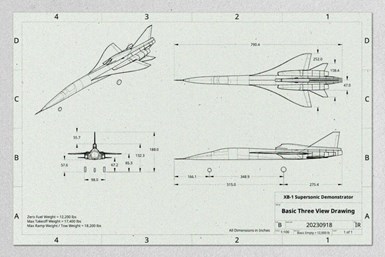
XB-1 is 62.6 feet long with a wingspan of 21 feet and is powered by three GE J85-15 engines with a combined max thrust of 12,300 pounds of force (lbf).
“Boom Supersonic is the first civil business entity to create its own X-plane, a supersonic demonstrator,” claims Ric Parker, chair of Singapore Aerospace Program, former Rolls-Royce CTO and Boom advisory council member. “This milestone is on the critical path to deliver Overture, the first supersonic transport aircraft to enter service in over half a century. It is an exciting time to be involved!”
Now that XB-1 has successfully completed its first flight, the team will systematically expand the flight envelope to confirm its performance and handling qualities through and beyond Mach 1. When XB-1 is ready for its first supersonic flight, Brandenberg will be at the controls.
Overture is expected to carry 64-80 passengers at Mach 1.7, about twice the speed of today’s subsonic airliners. Optimized for speed, safety and sustainability, Overture is designed to run on up to 100% sustainable aviation fuel (SAF).
Related Content
The potential for thermoplastic composite nacelles
Collins Aerospace draws on global team, decades of experience to demonstrate large, curved AFP and welded structures for the next generation of aircraft.
Read MorePEEK vs. PEKK vs. PAEK and continuous compression molding
Suppliers of thermoplastics and carbon fiber chime in regarding PEEK vs. PEKK, and now PAEK, as well as in-situ consolidation — the supply chain for thermoplastic tape composites continues to evolve.
Read MoreWelding is not bonding
Discussion of the issues in our understanding of thermoplastic composite welded structures and certification of the latest materials and welding technologies for future airframes.
Read MoreA new era for ceramic matrix composites
CMC is expanding, with new fiber production in Europe, faster processes and higher temperature materials enabling applications for industry, hypersonics and New Space.
Read MoreRead Next
Boom Supersonic announces aircraft, engine and investment milestones
New strategic investment from NEOM comes as XB-1, Symphony and Overture achieve important program turning points.
Read MoreStratolaunch celebrates first powered flight of TA-1 test vehicle
Reusable hypersonic test aircraft met primary flight objectives and approached Mach 5 speed, gathering data for concurrent TA-2 and TA-3 test beds.
Read MoreLockheed Martin rolls out X-59 supersonic X-Plane
The composites-intensive aircraft demonstrator was highlighted at a rollout ceremony at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works, and will soon undergo extensive testing prior to first flight later this year.
Read More