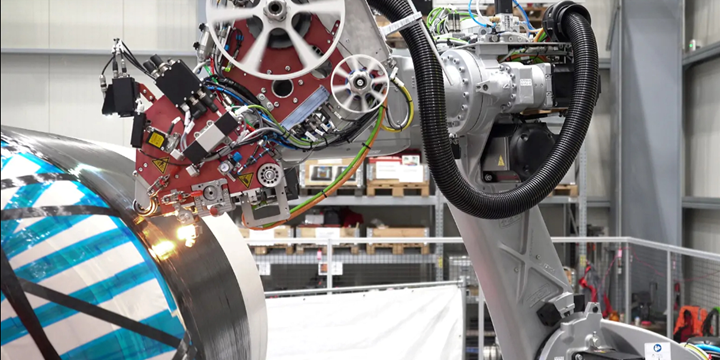
Broetje-Automation demonstrates rCF placement via AFP
Through the ScrapSeRO project, the system integrator and machine builder successfully processed recycled composites, in addition to more traditional materials, via its highly flexible Staxx One system.
In April 2023, Broetje-Automation (Rastede, Germany) laid the foundation for more sustainability in composites production with the successful demonstration of recycled carbon fiber processing using the company’s Staxx One automated fiber placement (AFP) system.
As a system integrator and special machine builder, Broetje-Automation GmbH has assembled and machined large parts for more than 40 years. In the field of composites manufacturing automation, Broetje-Automation says it has also built a wealth of experience and a broad product family through the successful handling of numerous R&D and customer projects. Together, with end users from various industries, Broetje-Automation is constantly developing innovative, tailor-made automation solutions for use in series production.
In particular, the processing of recycled carbon fiber (rCF) materials was investigated in the completed “ScrapSeRO” project together with the Fraunhofer Institute for Casting, Composite and Processing Technology (IGCV, Augsburg, Germany) and several partners from industry and research. As a result, a novel AFP system called Staxx One was developed, which consists of a highly flexible AFP end effector on a robot and an associated rotary table. The configuration was presented for the first time at JEC 2022 and is located today at the Composite Technology Center (CTC) in Stade, Germany.
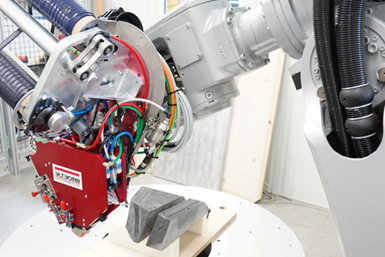
The Staxx One rounds off the Staxx AFP product family with a small, cost- efficient and highly flexible robotic solution. Particularly noteworthy is its high flexibility — the Staxx One is completely material independent, i.e., it can process all material types from dry fiber to prepreg to thermoplastic. On the other hand, different end effector configurations can be realized within a few simple steps, depending on whether 1/4-, ½, 1- or 2-inch-wide materials are to be processed and whether these are provided on film coils or as bobbins. For this purpose, various heating sources are offered, such as infrared heaters, lasers or others. The Staxx One is characterized by a quick setup as well as an easy and fast cleaning of the layup end effector.
These activities for processing resource-efficient recycling materials expand the marketability of Broetje-Automation and provide industry with core technologies for the production of sustainable, lightweight structures. In addition to rCF, glass and carbon fibers can also be precisely processed, such as dry fiber, thermoset and thermoplastic tows.
Thanks to the high degree of standardization of the Broetje-Automation layup head concept, numerous technology solutions are available for the entire Staxx product family. This covers a wide range of components and the corresponding implementation of automated component series production.
In addition to ScrapeSeRO, Broetje-Automation notes successful composites-related projects such as the layup of entire wing shells with a dry fiber placement (DFP) process, as well as the layup of novel hydrogen tank structures, such as those used for future passenger aircraft and other applications in the mobility sector. Here, Broetje-Automation is collaborating closely with leading aircraft manufacturers and the German Aerospace Center (DLR).
For DLR, Broetje-Automation has already developed and supplied the multi-robot AFP system GroFi, on which production trials for the technologies of tomorrow are developed.
Related Content
-
The potential for thermoplastic composite nacelles
Collins Aerospace draws on global team, decades of experience to demonstrate large, curved AFP and welded structures for the next generation of aircraft.
-
Recycling end-of-life composite parts: New methods, markets
From infrastructure solutions to consumer products, Polish recycler Anmet and Netherlands-based researchers are developing new methods for repurposing wind turbine blades and other composite parts.
-
The lessons behind OceanGate
Carbon fiber composites faced much criticism in the wake of the OceanGate submersible accident. CW’s publisher Jeff Sloan explains that it’s not that simple.