MIT develops new CNT film that can heat and cure composites
Researches believe the carbon nanotube film could improve the quality and efficiency of the fabrication processes for large composites, such as wings on commercial aircraft.
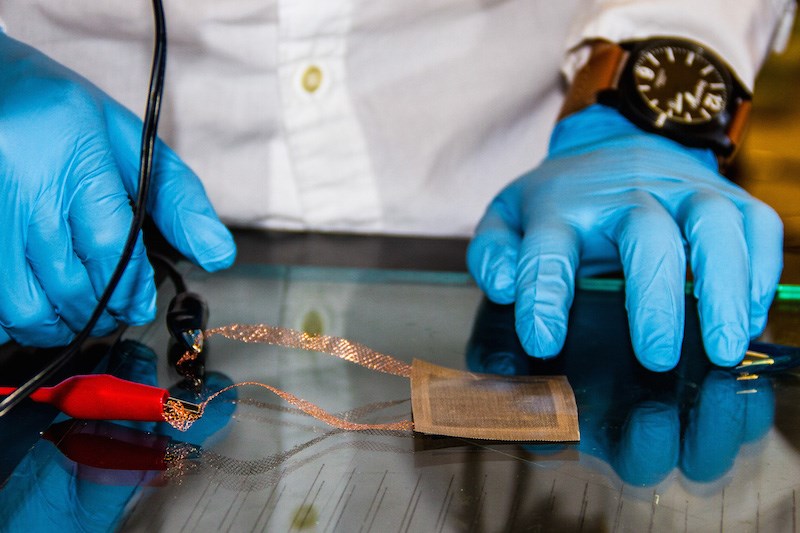
A new technique looks to take aircraft manufacturing out of the oven. Literally. Aerospace engineers at MIT (Cambridge, MA) have developed a carbon nanotube (CNT) film that can heat and solidify a composite without the need for ovens, according to a news release. When connected to an electrical power source, and wrapped over a multilayer polymer composite, the heated film stimulates the polymer to solidify.
The group tested the film on a common carbon fiber material used in aircraft components, and reportedly found that the film created a composite as strong as that manufactured in conventional ovens, but used only one percent of the energy. The researchers say that the carbon nanotube film is also lightweight. After it has fused the underlying polymer layers, the film itself meshes with the composite, which is said to add negligible weight.
Brian Wardle, an associate professor of aeronautics and astronautics at MIT, believes this approach is a more direct, energy-saving method for manufacturing essentially any industrial composite.
“Typically, if you’re going to cook a fuselage for an Airbus A350 or Boeing 787, you’ve got about a four-story oven that’s tens of millions of dollars in infrastructure that you don’t need,” Wardle said. “Our technique puts the heat where it is needed, in direct contact with the part being assembled. Think of it as a self-heating pizza. Instead of an oven, you just plug the pizza into the wall and it cooks itself.”
In initial experiments, the researchers investigated the film’s potential to fuse two types of aerospace-grade composite typically used in aircraft wings and fuselages. Normally the material, composed of about 16 layers, is solidified, or cross-linked, in a high-temperature industrial oven.
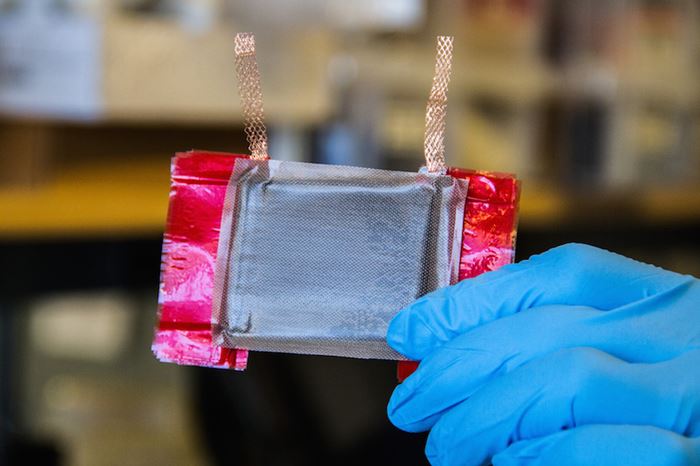
The researchers manufactured a CNT film about the size of a Post-It note, and placed the film over a square of Cycom 5320-1. They connected electrodes to the film, then applied a current to heat both the film and the underlying polymer in the Cycom composite layers.
The team measured the energy required to solidify, or cross-link, the polymer and carbon fiber layers, finding that the CNT film used one-hundredth the electricity required for traditional oven-based methods to cure the composite. Both methods generated composites with similar properties, such as cross-linking density.
As different composites require different temperatures in order to fuse, the researchers looked to see whether the CNT film could take the heat. To do this, the group tested the film’s ability to generate higher and higher temperatures, and found it topped out at over 1,000 F.
“We can process at those temperatures, which means there’s no composite we can’t process,” Wardle said. “This really opens up all polymeric materials to this technology.”
The team is working with industrial partners to find ways to scale up the technology to manufacture composites large enough to make airplane fuselages and wings.
The team, including MIT graduate students Jeonyoon Lee and Itai Stein and Seth Kessler of the Metis Design Corp., has published its results in the journal, ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces. This research was funded in part by Airbus Group, Boeing, Embraer, Lockheed Martin, Saab AB, TohoTenax, ANSYS Inc., the Air Force Research Laboratory at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base and the U.S. Army Research Office.
Related Content
Plant tour: Spirit AeroSystems, Belfast, Northern Ireland, U.K.
Purpose-built facility employs resin transfer infusion (RTI) and assembly technology to manufacture today’s composite A220 wings, and prepares for future new programs and production ramp-ups.
Read MorePultrusion: The basics
A primer describing what pultrusion is, its advantages and disadvantages, and typical applications.
Read MoreActive core molding: A new way to make composite parts
Koridion expandable material is combined with induction-heated molds to make high-quality, complex-shaped parts in minutes with 40% less material and 90% less energy, unlocking new possibilities in design and production.
Read MoreSulapac introduces Sulapac Flow 1.7 to replace PLA, ABS and PP in FDM, FGF
Available as filament and granules for extrusion, new wood composite matches properties yet is compostable, eliminates microplastics and reduces carbon footprint.
Read MoreRead Next
Plant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read MoreAll-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read More