Mitsui Chemical, Microwave Chemical complete microwave-based carbon fiber demo facility
Completed in December 2023, the pilot production line at Mitsui Chemicals Nagoya Works began trials in January and will supply carbon fiber samples within fiscal 2024.
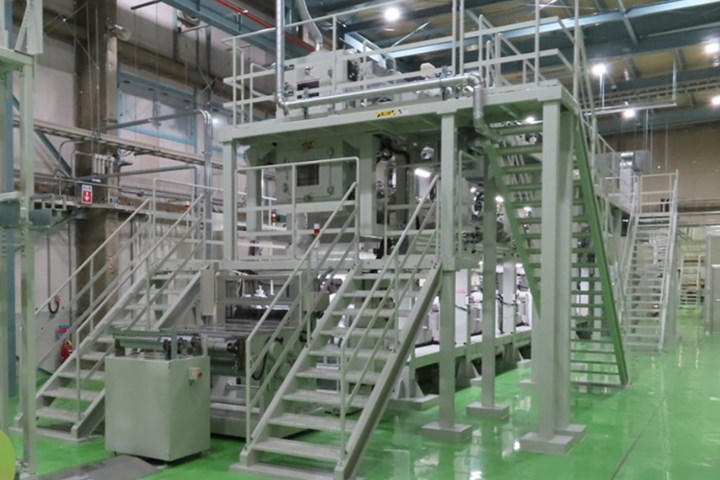
Mitsui Chemicals Inc. (Tokyo, Japan) and Microwave Chemical Co. Ltd. (Osaka, Japan) have completed construction of a demonstration facility for microwave-based production of innovative, eco-friendly carbon fiber at Mitsui Chemicals Nagoya Works. The production line was completed in December 2023.
The facility began a trial run in January 2024. The companies continue to look at establishing mass production technology and intend to begin supplying carbon fiber samples from the facility within fiscal 2024.
Microwave Chemical has collaborated with Mitsui Chemicals to integrate its Carbon-MX technology to carbon fiber production, offering up to 50% less energy use and, with renewable energy, >90% less CO2 emissions. Source | Microwave Chemical
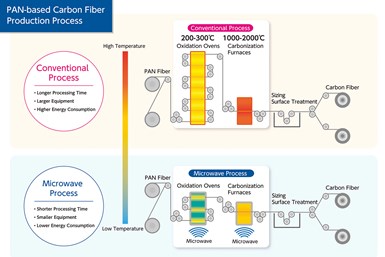
As was announced on Nov. 16, 2022, Microwave Chemical has contributed to the installation of the demonstration facility by supplying Mitsui Chemicals with all of the necessary equipment for a microwave-based heating line that uses its Carbon-MX technology. This technology performs the oxidation and carbonization processes within the carbon fiber production line. Mitsui Chemicals has set up the entire process, integrating the Carbon-MX technology elements.
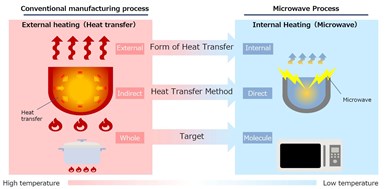
Carbon-MX technology leverages the ability of microwaves to heat a target substance from the inside, enabling processes that minimize unnecessary heat generation. When compared to existing methods, this is reported t significantly reduces the time spent on heat treatment, resulting in a shorter heating process line and thus more compact facilities. (See “Microwave heating for more sustainable carbon fiber”.)
Microwave heating is a direct versus indirect process — instead of heating the reaction vessel, the material molecules are heated. This process is much faster than conventional heating and production line equipment remains much cooler, which is safer. Source | Microwave Chemical
Further, since the equipment itself does not reach high temperatures, the technology is expected to provide benefits with regard to equipment costs, energy costs and safety. Mitsui Chemicals and Microwave Chemical have projected that this approach will cut energy consumption by 50%. If the power used to generate the microwaves is switched to renewable energy, then CO2 emissions are expected to be reduced by over 90%.
Going forward, both Mitsui Chemicals and Microwave Chemical will employ lifecycle assessments (LCA) as the companies look to minimize CO2 emissions throughout their value chains. In this demonstration production line, the companies endeavor to meet the rising need for carbon neutrality in industries where carbon fiber is slated for use, including mobility.
Related Content
-
Recycling end-of-life composite parts: New methods, markets
From infrastructure solutions to consumer products, Polish recycler Anmet and Netherlands-based researchers are developing new methods for repurposing wind turbine blades and other composite parts.
-
PEEK vs. PEKK vs. PAEK and continuous compression molding
Suppliers of thermoplastics and carbon fiber chime in regarding PEEK vs. PEKK, and now PAEK, as well as in-situ consolidation — the supply chain for thermoplastic tape composites continues to evolve.
-
TU Munich develops cuboidal conformable tanks using carbon fiber composites for increased hydrogen storage
Flat tank enabling standard platform for BEV and FCEV uses thermoplastic and thermoset composites, overwrapped skeleton design in pursuit of 25% more H2 storage.