Multifunctional composites could help achieve structural supercapacitors for EVs
In a recent study, functionalized graphene/nanofiber electrodes showed 2X modulus, strength and 5-10X multifunctional efficiency.
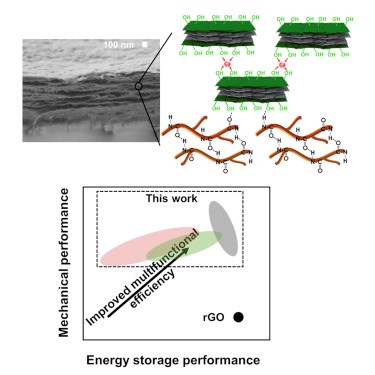
Structural batteries and structural supercapacitors offer a potential solution for electric vehicles (EVs) because they can not only handle structural loads but also store energy and/or produce power. For future ground and air mobility, this offers reduced weight and volume for structures and batteries, as well as more miles between recharging. However, current electrodes for batteries and supercapacitors suffer from poor mechanical performance because they are typically made from brittle materials.
A team led by Texas A&M University (College Station, Tex. U.S.) chemical engineer, Jodie Lutkenhaus, has produced structural supercapacitor electrodes using reduced graphene oxide (rGO), innovative chemistry and aramid nanofibers to mimic the natural material nacre, achieving Young’s modulus and ultimate tensile strength that are 220% and 255%, respectively, higher versus pure rGO electrodes, as well as multifunctional efficiency values of 5–13.6 compared to current electrodes at <1.
Nacre-like multifunctional composite
In an article published in the journal Matter, Lutkenhaus and her team describe using dopamine to functionalize (chemically bond to) rGO and then combine this material with aramid nanofibers to form a composite. The paper explains, “We hypothesized that nature-inspired materials could transform the poor mechanical properties of supercapacitor electrodes into those mimicking nacre, bone, or wood to realize exceptionally high values of multifunctional efficiency.”
Nacre (mother-of-pearl) consists of 95 vol % aragonite (calcium carbonate), chitin, and proteins yet exhibits toughness three orders of magnitude higher than aragonite alone. Its superior mechanical performance results from its hierarchical composite structure: its constituent particles and matrix are organized differently at each geometric scale or level (e.g., nano-, micro-, meso-, macro-) and combine with efficient interfaces between these levels to achieve high modulus and strength while mitigating crack propagation (see the blog “Magnetic 3D printing the next generation of tailored composites”).
The Lutkenhaus team knew that graphene-based nacre-mimicking electrodes have been shown to perform very well electrically. The challenge was to improve their mechanical properties. The team sought to use the hormone and neurotransmitter dopamine to functionalize rGO. Dopamine also self-polymerizes into the highly adhesive polymer polydopamine (PDA). Dopamine mimics the structure of adhesive proteins in nacre-lined mussels, while PDA has been utilized in Li-ion batteries and supercapacitors as an electrode material, separator modifier and binder. However, only a handful of studies have focused on incorporating PDA in rGO composites.
As explained in the Matter technical paper, “We sought to combine for the first time the excellent mechanical properties of PDA-modified rGO with high-modulus, high-tensile-strength Kevlar aramid nanofiber to improve the multifunctional efficiency.” Aramid nanofibers have also been used in a variety of applications including energy storage.
Good structural properties
Nacre-mimicking structural supercapacitor electrodes based on branched aramid nanofibers and dopamine-functionalized rGO sheets were fabricated using vacuum filtration and their performance was evaluated. The excellent mechanical properties exhibited are reported to result from increased hydrogen bonding caused by the dopamine functionalization and chelation caused by Ca2+ ions.
The Lutkenhaus team reports that this approach is applicable to other nacre-mimicking structures which should lead to a new stronger multifunctional family of nature-inspired materials. “Future work should focus on improving the electrochemical performance, either by adding porosity to improve the ionic mobility or by adding a pseudocapacitive material to enhance energy density. To the best of our knowledge, the obtained Young's modulus and multifunctional efficiency is the highest among the electrically conductive composites with low aramid nanofiber content. This leads to strong structural supercapacitor electrodes with high electrochemical performance.”
Related Content
Film adhesive enables high-temperature bonding
CAMX 2024: Aeroadhere FAE-350-1, Park Aerospace’s curing modified epoxy, offers high toughness with elevated temperature performance when used in primary and secondary aerospace structures.
Read MorePittsburgh engineers receive $259K DARPA award for mussel-inspired underwater adhesion
The proposed META GLUE takes inspiration from hydrogels, liquid crystal elastomers and mussels’ natural bioadhesives to develop highly architected synthetic systems.
Read MorePro-Set named official materials supplier for New York Yacht Club American Magic
Competitive sailing team prepares for the 37th America’s Cup beginning in August 2024 with adhesives, resins and laminate testing services for its AC75 monohull construction.
Read MoreHenkel releases digital tool for end-to-end product transparency
Quick and comprehensive carbon footprint reporting for about 58,000 of Henkel’s adhesives, sealants and functional coatings has been certified by TÜV Rheinland.
Read MoreRead Next
Developing bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read MoreAll-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read More


























