National Composites Centre purchases Coriolis C5 robotic gantry AFP
Developed for rate production of large, complex composite structures, C5 will be part of world’s most advanced, flexible dry-fiber deposition cell.

Source | Coriolis Composites
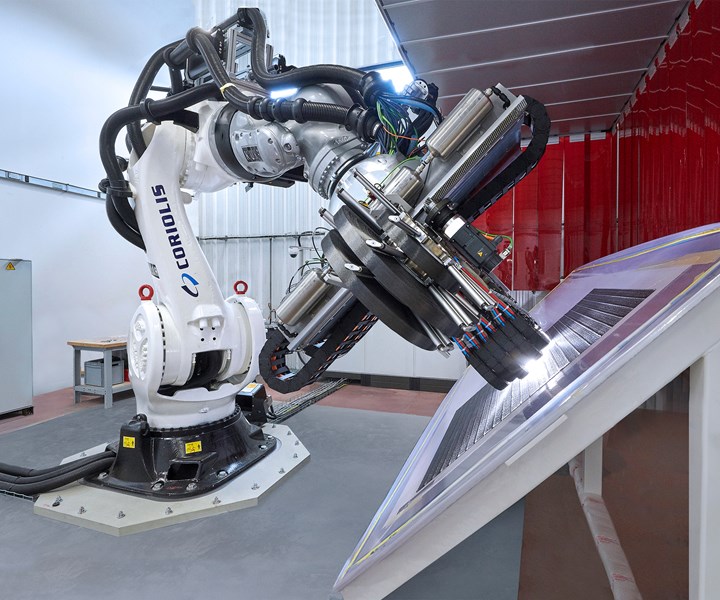
Coriolis Composites (Queven, France) has announced that the National Composites Centre (Bristol, U.K.) is the first customer to purchase the company’s new C5 automated fiber placement (AFP) robotic gantry solution. A long-standing partner of the NCC, Coriolis Composites provided the center’s original AFP solution, and its C5 joins the C1 NCC purchased in 2018.
The C5 reflects an effort by Coriolis Composites to break into the large aerospace structure market where very high lay-up rates, high levels of design optimization and low material wastes are essential. Coriolis Composites’ fiber placement solution is said to enable the manufacture of highly complex parts tailored for industrial applications while remaining in the reach of research organizations. Its adaptable lay-up head ensures precision and repeatability essential to the aerospace industry. Combining the C5 with other industry technologies is said to enable the flexibility needed for the lay-up of large, complex industrial parts.
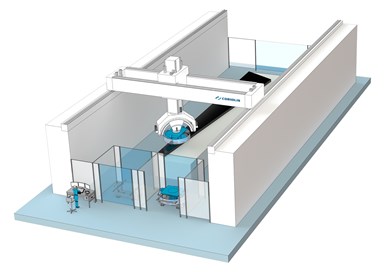
Coriolis Composites has adapted its C5 technology to a newly installed NCC gantry provided by the Loop-Coriolis Composites-Güdel consortium, as part of the NCC’s iCAP program. iCAP is a £36.7 million investment in 10 digital manufacturing technologies tailor-made to the NCC’s specifications, in order to speed the development of all forms of composite manufacturing. The iCAP program is funded by ATI, Local Enterprise Partnership and the High Value Manufacturing Catapult.
“The C5 will be one of five technologies we are combining in what will be the most advanced and flexible dry-fiber deposition cell in the world,” says Enrique J. Garcia, CTO of the NCC.
The modular design of the C5 fiber placement head means that each fiber can be individually cut and restarted, providing high-speed gantry layup for large double-curved parts. The head has 1.5 inches (38.1-millimeters) wide thermoset, thermoplastic and dry-fiber manufacturing solutions, with the latter used by the NCC. The NCC’s dry fiber placement (DFP) head has six motorized spools with sensors that control the activation of individual spools and detection of fiber tension. In addition, the head is exchangeable using an integrated docking station.The gantry is driven by a Siemens (Waltham, Mass., U.S.) 840D controller.
Source | Coriolis Composites
The requirement from the NCC was a machine that can deliver high lay-up rates using dry fiber tapes for large structures, such as wing skins. In combination with the other deposition technologies included in the NCC’s prototype manufacturing cell, Coriolis says that the incorporation of the C5 AFP enables optimal layup with minimal material waste for full-scale aerostructure demonstration.
The C5’s multi-material capability also enables AFP technology to be used for large structures such as wind turbines, marine applications and civil engineering applications. Coriolis Composites has also developed the C3 as part of the gantry layup family.
Related Content
-
Composites end markets: Pressure vessels (2024)
The market for pressure vessels used to store zero-emission fuels is rapidly growing, with ongoing developments and commercialization of Type 3, 4 and 5 tanks.
-
Hexagon Purus opens new U.S. facility to manufacture composite hydrogen tanks
CW attends the opening of Westminster, Maryland, site and shares the company’s history, vision and leading role in H2 storage systems.
-
NCC reaches milestone in composite cryogenic hydrogen program
The National Composites Centre is testing composite cryogenic storage tank demonstrators with increasing complexity, to support U.K. transition to the hydrogen economy.

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)













