University of Southampton develops miniaturized optical fiber condition monitoring technology
A more compact, affordable strain interrogator, currently developed for FBG monitoring, may enable more widespread adoption of optical fiber sensing used in composite materials.
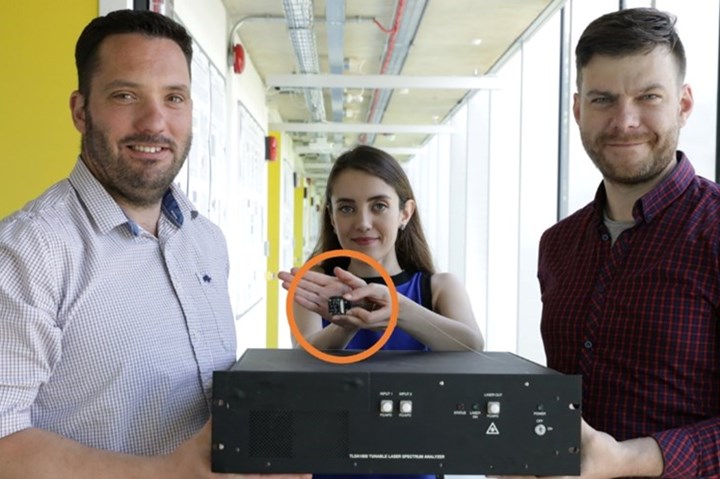

Dr. Shahrzad Zahertar (center) holds the developed miniaturized optical interrogator alongside a more traditional optical interrogator unit (foreground). Photo Credit: University of Southampton.
Recent innovation at the University of Southampton’s (U.K.) Optoelectronics Research Centre have developed an alternative approach for optical signal analysis when using sensors to monitor composite material conditions. The research, “Compact high-resolution FBG strain interrogator based on laser-written 3D scattering structure in flat optical fiber,” published in Scientific Reports 2023, demonstrates a fiber Bragg grating (FBG) strain interrogator — an optoelectronic instrument that enables the reading of optical FBG sensors in static and dynamic monitoring applications.
Optical fiber sensing in composite materials is a mature technology, understood to offer advantages in condition-based monitoring. The optical fiber itself is said to have distinct benefits of immunity to electromagnetic interference and exhibits a small, lightweight footprint (the thickness of a human hair) and inherent multiplexing.
Despite maturity, however, one of the main bottlenecks limiting wider deployment of optical fiber-based condition monitoring has been the cost of the interrogation. Optical interrogators are highly expensive and are often heavy, with a large footprint.
The University of Southamption research team has been working in composites for the past several years, including developing new types of optical fiber to enhance through-thickness sensing. “Over the past several years we have been pioneering new optical fiber for enhanced composite monitoring,” explains Christopher Holmes, Royal Society Industry Fellow. “A big pain I continually heard was the cost of sensing, driven by the optical interrogator. Using expertise we have at the Optoelectronics Research Centre, University of Southampton, we set out on a mission to try and solve this pain and hopefully enable greater usability of a very useful sensing platform, optical fiber sensing.”
Unlike conventional optical signal analysis systems available on the market, the interrogator unit technology developed by this research team offloads the complexity of the hardware design into a machine learning space, resulting in an ultra-compact, lightweight and affordable solution.
The interrogator unit — the system that reads the optical fiber sensor — has currently been developed for FBG monitoring, but it is said to work equally well on other optical fiber-based sensors that are based upon interferometry, (e.g., Fabry Perot, Mach Zehnder interferometer, etc.).
Dr. Shahrzad Zahertar connecting optical fiber sensors to composite panel for cure monitoring. Photo Credit: Michael Godfrey
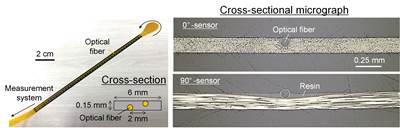
The system uses a special type of optical fiber, developed in the University of Southampton optical fiber drawing towers, called “flat fiber.” Flat optical fiber does not have a circular cross-section, but is instead letterbox-shaped (typically 100 micrometers × 1 millimeter) in cross-section. Combining this new fiber with femtosecond laser processing, a speckle pattern can be projected out from the fiber and captured. This speckle pattern is dependent upon the state of the FBGs, and through machine learning, the pattern can be mapped to strain/temperature changes and more.
Compared to alternative interrogator systems, which typically use wafer-scale processing in a cleanroom, thus making them expensive, the innovation here uses inexpensive fiber (£20/meter) and lower cost industrial laser processing. Furthermore, because it is all fiberized and does not use any free-space optics, it shows excellent stability (discussed further in the publication linked above).
The research team has been looking at autoclave and microwave cure monitoring, though Holmes, believes that enabling digital twins with through-life monitoring is where the big win is. “A more affordable, smaller and lighter weight technology permits wider spread use for more composite structures that need such metrics,” Holmes notes, “such as cargo drones, footbridges and wind turbines.”
The research team is looking to commercialize this innovation, in particular explore new opportunities in composite monitoring. They are part of an Innovate UK program, ICURe, looking into market exploration and fit.
For further information and to provide your thoughts, contact the team Asterium (asterium.co.uk).
Learn more about sensors for composites processing.
Related Content
Technology Marketing Inc. to distribute VacPuc digital sensors
VacPuc is expanding its range of global distributors to deliver its vacuum pressure measurement solution to the composites market.
Read MoreGill highlights custom sensors expertise with industry flexibility
Product offering encompasses specialist level sensing, condition monitoring, position sensors and engine control products for composites-based applications.
Read MoreTemperChip machining temperature sensor for composites
Patented device provides real-time machining data to monitor and accurately predict tool life, opening up the horizons to measure a variety of parameters between cutting tool and material.
Read MoreNext-gen composites manufacturing: Combining material, machine and mold cavity data with analytics
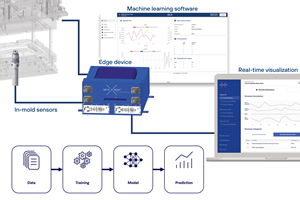
Using a sensor, an edge device and machine learning software, sensXPERT sees into processes and is improving quality and cutting scrap, cycle time and energy use for composites customers like ZF and Carbon Revolution.
Read MoreRead Next
Measuring ply-wise deformation during consolidation using embedded sensors
Strip-type shape sensor method claims real-time measurement of ply-wise deformation.
Read MorePatent-pending Purdue process embeds sensor particles, functionalizes 3D-printed structures
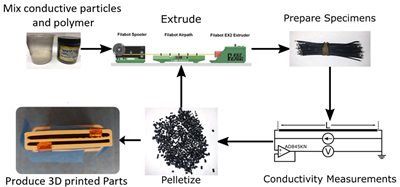
Purdue University researchers have developed a novel wet-mixing method to add sensor particles to 3D printer filaments, which will enable manufacturers to create functional printed parts.
Read MoreModeling and characterization of crushable composite structures
How the predictive tool “CZone” is applied to simulate the axial crushing response of composites, providing valuable insights into their use for motorsport applications.
Read More








.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)