Toray develops heat-dissipating CFRP material for flexible thermal management design
Internal graphite sheets and a porous, heat-conductive layer CFRP support attains a thermal conductivity above that of metals without compromising quality, properties.
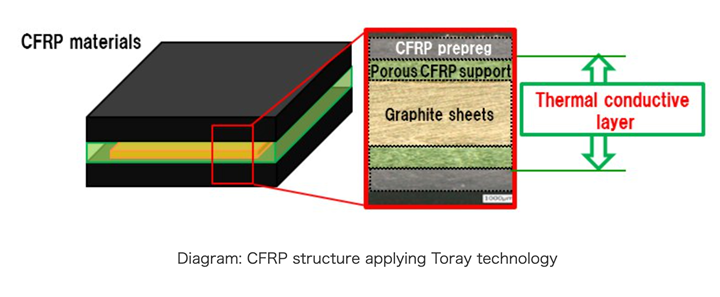
Photo Credit: Toray Industries Inc.
Toray Industries Inc. (Tokyo, Japan) has developed a high thermal conductivity technology that lifts the heat-dissipating properties of carbon fiber-reinforced plastic (CFRP) to that of metals. Toray notes that applying this technology to CFRP dissipates heat effectively through thermal conduction paths inside that material, and, for example, can help suppress battery degradation in mobility applications while boosting performance in electronic device applications.
Efforts to enhance CFRP’s heat dissipation by employing external or internal graphite sheets led to excellent thermal conductivity, heat dissipation and diffusion. However, Toray notes, these sheets were easy to fracture, scatter and damage, compromising the performance of the CFRP material.
Over the years, Toray says it has used proprietary technology to develop and apply highly rigid porous CFRP-forming three-dimensional networks with short carbon fibers. On this occasion, Toray created a heat-conductive layer employing a porous CFRP support that safeguards the graphite sheets. Laminating CFRP prepreg on this thermally conductive layer reportedly enabled Toray to attain a thermal conductivity above that of metals, without compromising the mechanical properties and quality of that material.
Further, Toray says it made it possible to determine the thickness and lamination positions of graphite sheets forming thermal conduction paths. This enabled a flexible thermal management design, which controls the paths to release or use heat for CFRP cooling efficiency and heat diffusion paths.
Related Content
-
Carbon fiber, bionic design achieve peak performance in race-ready production vehicle
Porsche worked with Action Composites to design and manufacture an innovative carbon fiber safety cage option to lightweight one of its series race vehicles, built in a one-shot compression molding process.
-
Plant tour: Joby Aviation, Marina, Calif., U.S.
As the advanced air mobility market begins to take shape, market leader Joby Aviation works to industrialize composites manufacturing for its first-generation, composites-intensive, all-electric air taxi.
-
McLaren celebrates 10 years of the McLaren P1 hybrid hypercar
Lightweight carbon fiber construction, Formula 1-inspired aerodynamics and high-performance hybrid powertrain technologies hallmark this hybrid vehicle, serve as a springboard for new race cars.













