Automated preforming: Intelligent automation in pick-and-place systems
Layups go industrial with hand-like grippers that can fold fabric or prepreg into corners and robot-mounted cameras that inspect from fabric to cut plies to fiber gaps in final preforms.
This is #6 in my series on Automated Preforming. The first five can be found here:
- Automated Preforming: The numbers and landscape
- Automated Preforming: Glide Forming
- Automated Preforming: Quilted Stratum Process (QSP)
- Automated drapability testing
- Automated Preforming: Drapability simulation and a Holistic Quality Optimization
There is also a print article on automated preforming, split into two parts:
This blog comes from my discussions with Composite Alliance Corp. (CAC, Dallas, TX, US). I interviewed CAC for the two-part print article above, but was not able to include most of the information due to lack of space. So I”m finally sharing it here.
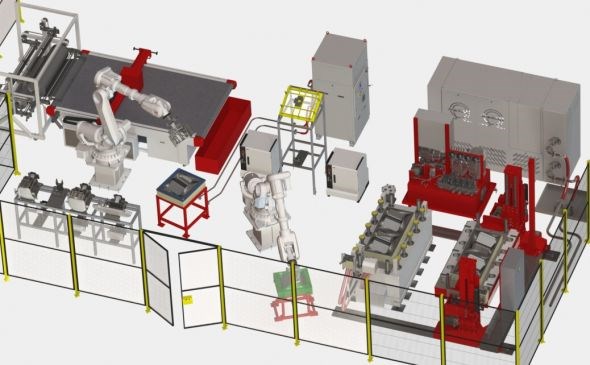
CAC and Techni-Modul Engineering work with partners to design, test and install automated composites production lines, as well as individual components and smaller fabrication cells.
The line shown here was developed in collaboration with Israel Aerospace Industires (IAI, Tel Aviv, Israel). SOURCE: CAC and Techni-Modul Engineering.
CAC provides turnkey automated production lines for composites, but also single components, including systems for injection and dispensing, preforming and handling, as well as presses and tooling.
CAC draws from decades of experience from four major partners:
- Techni-Modul Engineering – turnkey systems, automation
- Isojet Equipments – injection and dispensing systems
- Shikibo – reinforcements including 3D preforms and also resin research
- Corima Technologies – electroformed nickel and composites tooling
“We are not tied to a specific technology,” says CAC sales director Marc-Ruddy Thimon, “so we can work with any technique the customer is interested in.” He notes that compared to many other players in preform technology, “our approach is more general, based on the wide scope of skills we have. We can include several technologies, but our decision is based on what the parts require.”
Thimon says CAC and Techni-Modul Engineering (TME) can supply automation based on prepreg, dry fiber, unidirectional (UD) tape or woven fabrics, with the main target being aerospace but it also supplies systems into automotive. “However,” he acknowledges, “these markets are quite different, and thus, the solutions are as well.”
CAC won the 2016 ACE award at CAMX (Sep 26-29, Anaheim, CA, US) in the Manufacturing Equipment and Tooling category for "Innovative Robotized Preform Cell Providing 3D Stacking and Control".
This ACE award-winning automated cell produces 3D preforms for aerospace I-beams using specially developed grippers and software. The robot lifts the first of two formed C-sections (photo on left) which are placed and compacted to form an I-beam (far left of photo on right).
SOURCE: Composite Alliance Corp. and Techni-Modul Engineering
“We combine pick and place robots with preforming and quality inspection,” Thimon continues. “We develop many of our end effectors in-house and this is one of our areas of strength.” He describes CAC’s development of specialized end effectors that operate like hands, allowing 2D materials to be folded into complex shapes made using resin transfer molding (RTM).
The automated systems that CAC develops start from unrolling the fabric. “We can work with existing equipment at the customer or we can provide a complete cell,” Thimon explains. “We then look at the cutting system required and communication with the cutting station automation. If it’s prepreg, we can integrate removing the backing film during unrolling.” He notes that CAC is receiving more requests for prepreg now and there are many ways to remove the backing film, both before or after cutting.
The next station is automated layup, using one or more pick and place robots and laying into the preforming tool. “We also include debulking for prepreg or compaction for bindered dry fabric, where we apply heat and pressure,” Thimon adds. “Next, there is contour cutting/trimming for molding of net shape parts. And finally, insertion into a curing tool and molding, followed by demolding.” He points out that all transfers are automated depending on the type of part and process requirements. Some systems use all robotics, while others use a combination of robotics and automated static machinery.
|
|
Robotic 3D contour cutting after vacuum compaction of a preform (left) and
“Intelligent Automation” camera inspection system using specially-developed software.
SOURCE: Composite Alliance Corp. and Techni-Modul Engineering
Big Data and “Intelligent Automation”
“We integrate control for all parts of the process and connect to a central control unit,” Thimon explains, “so the operator has all of the data, such as temperatures and pressures, all controlled from a central system.” He claims this “Intelligent Automation” is one of the main features of CAC and TME systems.
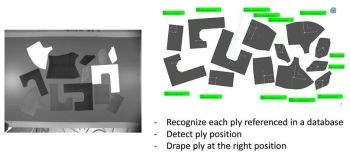
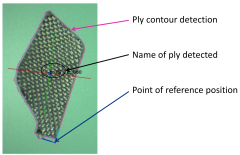
“We integrate a camera into either the robotic arms or stationary equipment for continuous vision inspection throughout preforming operations,” says Thimon. “When you unroll the material, it will check the fiber orientations. On the cutting table, one of our newer features is that the system can recognize each cut ply in a reference database. It uses the camera vision system to register and compare the shape and fiber orientation, but also looks at its sequence from the cutting program and data from the digital part design file. This is useful for minimizing errors in direct work flows from cutting table to tool and also for preforming with stored kits of cut plies.”
 |
|
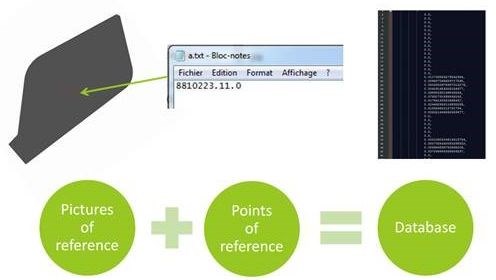
CAC and TME automated preforming cells feature “Intelligent Automation” which integrates inspection via camera vision systems that can detect and track each ply in a reference database using pictures, points of reference and marked labels
to ensure proper layup and positioning on the preforming tool.
SOURCE: Composite Alliance Corp. and Techni-Modul Engineering
For working with kits, Thimon says the system will track the pieces per kit to ensure proper layup and also detect the end of a ply for new ply placement. “This system too is integrated into central control, so it logs each step as part of the whole assembly,” he adds. “The system puts a reference around the entire preform and the edges of the tool to ensure proper positioning of the preform on the preforming and curing tools. However, it also compares the contour of each ply vs. the preform to inspect fine positioning during pick and place layup.” It also detects proper placement of cuts and darts in 2D preform plies as well as unacceptable gaps between fibers after ply placement.
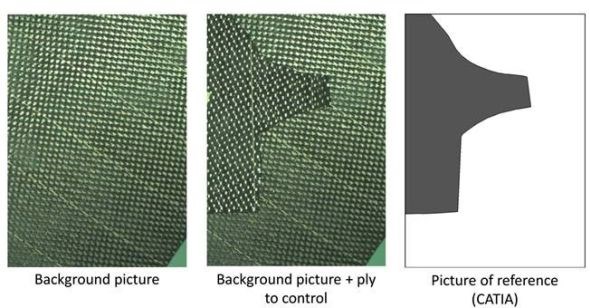
SOURCE: Composite Alliance Corp. and Techni-Modul Engineering
Another important use is to detect foreign object and debris (FOD) at different points in the preforming process. Even the best automation can still be susceptible to human introduction of error. This is why another new feature has been developed to compare points of reference in the production cell. The system basically performs a type of calibration at the beginning of a production cycle — or on demand, for example, to troubleshoot a detected ply placement error — to make sure that different pieces of equipment and other targets, such as a preforming tool with a hole or cutout, are all aligned properly. “The goal of these latest features is to add more flexibility and ways to work in these automated cells.”
CAC is currently working with 3-4 major aerospace OEMs and well-known Tier 1 suppliers to develop automated composite preforming and molding cells/production lines. Most of these will use prepreg. More details on CAC and TME “Intelligent Automation” systems will be presented by Thimon and project engineering director Stephane Besson at the Carbon Fiber 2017 conference Nov. 28-30 (Charleston, SC, US).
Related Content
Infinite Composites: Type V tanks for space, hydrogen, automotive and more
After a decade of proving its linerless, weight-saving composite tanks with NASA and more than 30 aerospace companies, this CryoSphere pioneer is scaling for growth in commercial space and sustainable transportation on Earth.
Read MoreCo-molding SMC with braided glass fiber demonstrates truck bed potential
Prepreg co-molding compound by IDI Composites International and A&P Technology enables new geometries and levels of strength and resiliency for automotive, mobility.
Read MoreCarbon fiber, bionic design achieve peak performance in race-ready production vehicle
Porsche worked with Action Composites to design and manufacture an innovative carbon fiber safety cage option to lightweight one of its series race vehicles, built in a one-shot compression molding process.
Read MoreComposites end markets: Automotive (2024)
Recent trends in automotive composites include new materials and developments for battery electric vehicles, hydrogen fuel cell technologies, and recycled and bio-based materials.
Read MoreRead Next
Plant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read MoreDeveloping bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read More