Getting real: Thermoplastic resin transfer molding
KraussMaffei is launching this fall thermoplastic resin transfer molding (T-RTM), through which caprolactam is injected into a preform and then in-mold polymerized to create polyamide 6.
Share
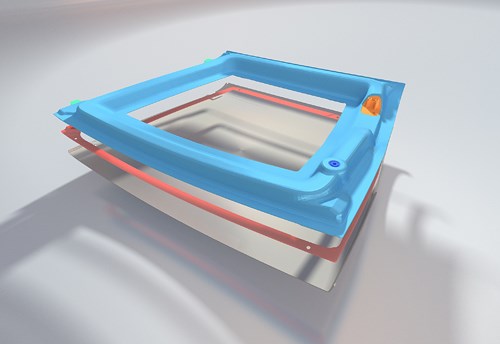
This frame for the roof shell of the Roding Roadster R1 sports car will be molded at K 2016 using KraussMaffei's new thermoplastic resin transfer molding (T-RTM) process, through which caprolactam is injected into a preform and then in-mold polymerized to create polyamide 6.
KraussMaffei Technologies GmbH (Munich, Germany) reports that it will introduce this fall at K 2016, in Düsseldorf, Germany, T-RTM, a thermoplastic resin transfer molding process that uses in-mold polymerization of caprolactam to produce near-net shape fiber-reinforced polyamide 6 parts.
At K 2016, KraussMaffei will demonstrate the production of a 500-mm-by-600-mm automotive structural component with metal inlays under series production conditions. Frames for the roof shell of the Roding Roadster R1 sports car will be created in the exhibition booth several times a day to demonstrate the technology.
The T-RTM process begins in a press mold, where a continuous fiber preform (glass and carbon, 60% fiber volume fraction) is infiltrated with caprolactam. The caprolactam, as it is injected, is mixed with an activator/catalyst, which triggers the polymerization that transforms the caprolactam to polyamide 6.
"The production process on the KraussMaffei K 2016 exhibition booth will last about 2 minutes. The system is intended for high-volume projects and is designed for multiple-shift operations," says Erich Fries, head of the Composites/Surfaces business unit at KraussMaffei.
KraussMaffei says the low viscosity of caprolactam – similar to water – allows the matrix material to penetrate the fiber layers even at low internal mold pressures. For the application demonstrated at the exhibition, a clamping force of approximately 350 MT will be used. In addition, the high flow capacity allows the minimum wall thickness to be reduced and the fiber volume content to be increased to about 60%.

Top view, Roading Roadster R1.
The Roding part being molded at K 2106 features a thermoplastic tear-off edge that is reportedly easily removed post-mold. KraussMaffei adds that the multi-preform concept minimizes fiber waste and allows a tailored fiber architecture.
CW will be at K 2016 and will report again with additional information about this process.
Besides KraussMaffei, the following development partners were also involved in producing the Roding Roadster R1 technology demonstrator: Forward Engineering (component design, hybrid concept), Alpex Technologies GmbH (T-RTM mold), Dieffenbacher (production of preforms/handling), Saertex (fiber layers), Henkel (bonding), Handtmann (aluminum inlays), TUM/LCC (fiber selection) and Keller (extraction technology).
Related Content
-
PEEK vs. PEKK vs. PAEK and continuous compression molding
Suppliers of thermoplastics and carbon fiber chime in regarding PEEK vs. PEKK, and now PAEK, as well as in-situ consolidation — the supply chain for thermoplastic tape composites continues to evolve.
-
Jeep all-composite roof receivers achieve steel performance at low mass
Ultrashort carbon fiber/PPA replaces steel on rooftop brackets to hold Jeep soft tops, hardtops.
-
MFFD thermoplastic floor beams — OOA consolidation for next-gen TPC aerostructures
GKN Fokker and Mikrosam develop AFP for the Multifunctional Fuselage Demonstrator’s floor beams and OOA consolidation of 6-meter spars for TPC rudders, elevators and tails.
















