JEC Composites 2009 showcase
Despite the doleful state of the global economy, the turnout in Paris — exhibitors and visitors — proved surprisingly strong.
The consensus on the show floor at the 2009 edition of the JEC Composites Show was that although attendance this year did not equal 2008 levels, the turnout was greater than expected. Postshow statistics released by show organizers tended to support that contention. By JEC’s count, 1,065 exhibitors (75 percent from outside France) and 25,500 visitors from France (35 percent) and 95 other countries. Some observers credited the attendance levels at the show, held March 24-26 at the Paris Expo in Porte de Versailles, Paris, France, to the fact that JEC highlighted neighboring Germany as its featured guest country and selected an “Automation” theme, which attracted new European exhibitors that offer automated solutions. According to JEC, visitor traffic was actually up significantly this year in four market sectors: wind energy, 35 percent; aerospace, 28 percent; building and construction, 18 percent; and — very surprising, given plummeting new car sales — automotive, 16 percent. JEC says the unexpected statistics owe much to an increase in traffic from composite component end-users.
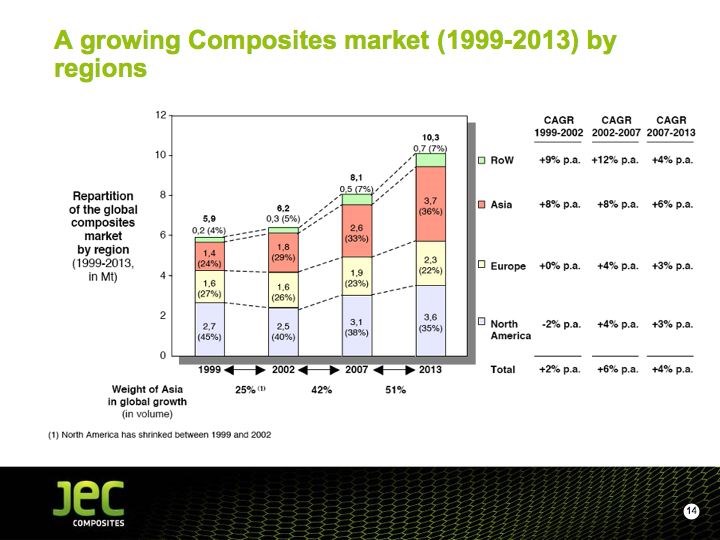
At a show press conference, JEC Group president/CEO Frédérique Mutel added an upbeat note to the gathering with a presentation of JEC’s latest composite market study figures, which puts the worldwide market value of the composites industry at €62 billion ($82.4 billion USD) with a total volume of 8.6 million tonnes (18.9 billion lb). Despite the recessionary climate, her take is that the compound annual growth rate through 2013 will be at 4 percent, with the largest growth occurring in Asia (see the JEC 2009-2013 Growth Forecast at right). The growth rate should be faster than the gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate, says JEC, with building and construction and wind energy the fastest-growing market segments.
In other show-related news, SAMPE Europe, JEC and the organizers of the AUTOMATICA conference signed a joint agreement to collaborate at the next AUTOMATICA gathering in 2010. A dedicated “Composites Pavilion” organized by JEC Composites and a two-day trade conference organized by SAMPE Europe will help advance automation methods in the composites industry, say the three groups. The conference portion of the collaboration, to be entitled "Advanced Composites for Automatization,” is being organized by Dr. Klaus Drechsler of the Technical University of Munich.
On the show floor, exhibitors showed little evidence that they’ll lay low and ride out the recession on last year’s product line. The CT staff found the following noteworthy products, technology developments and expanding services.
RTM method for pressure vessels
A&P Technology Inc. (Cincinnati, Ohio) was recognized by this year’s JEC Innovation Awards jury, along with composite parts manufacturer Profile Composites Inc. (Sidney, British Columbia, Canada), the National Center for Manufacturing Sciences (NCMS, Ann Arbor, Mich.) and Toyota Engineering (Toyko, Japan) and supplier/partners MAG Cincinnati (Hebron, Ky.) and Bayer MaterialScience LLC (Pittsburgh, Pa.). Unlike many pressure vessels, which are produced via filament winding, this pressure vessel was made by placing an A&P carbon fiber braid over an aluminum liner, followed by injection of resin via resin transfer molding. The cycle time for the manufacturing process is only 20 minutes. One of the goals of the project, funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, was to develop a high-volume manufacturing process for pressure vessels designed for alternative-fuel vehicles.
ATL system for thermoplastics
In its first stint as a JEC show exhibitor, Advanced Fibre Placement Technology BV (AFPT, Sprang-Capelle, The Netherlands and Dörth, Germany) showed its automated tape laying (ATL) system, which features a single thermoplastic tape-laying head mounted on a robotic arm. The head uses a laser to heat the tape prior to consolidation rather than a hot gas torch or other conventional technology. The company offers several tape placement systems for industrial applications or R&D activities. ATL-compatible software tools are available to AFPT through its partnership with CGTech (Irvine, Calif.).
New low-loss glass fiber for PCBs
AGY (Aiken, S.C.) announced its purchase of a 70 percent share in Shanghai Grace Technology Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China), an E-glass yarn producer to the electronics industry, with a production capacity of 18,000 metric tonnes (39.7 million lb) per year. AGY intends to purchase the remaining shares in the near future. The acquisition will expand AGY’s yarn manufacturing footprint, says the company, and enable it to service its growing Asia-Pacific customer base. The company also has introduced a new very low-loss glass fiber yarn, trademarked L-Glass, for the printed circuit board (PCB) industry. With its low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor, the product reportedly will enable manufacturers to make smaller devices with greater high-speed functionality while preventing signal loss.
Self-releasing, multilayer bagging film
Airtech International (Huntington Beach, Calif.) attracted crowds at its stand with frequent demonstrations of vacuum infusion, using the company’s line of bagging material and components. The company emphasized its Dahlar Release Bag 520, a self-releasing, multilayer vacuum-bagging film designed for direct contact with prepreg when fabricating hollow parts. The film reportedly maintains vacuum at temperatures as high as 220°C/428°F and can be used with lay-flat tubing and gusset-folded tubing for internal bagging of hollow parts. Also featured was the ultrawide (12m/39.4 ft) Securlon L500 bagging film and Airseal 1 and Airseal 2 bag sealant tapes. The company also announced that its online catalog (www.airtech.lu) is now available in English, French, German, Italian, Spanish and Russian.
Carbon fiber line moves toward startup
AKSA (Akrilic Kimya Sanayii AS, Istanbul, Turkey) continues to advance its new carbon fiber manufacturing program, with the announcement that its full-scale production line in Turkey, capable of producing 1,500 metric tonnes (3.3 million lb) of carbon fiber per annum, is nearing completion and scheduled for startup in mid-2009. AKSA operates the largest acrylic fiber facility in the world, representing 12 percent of worldwide capacity, and is currently using its acrylic material to create carbon fiber precursor in a pilot production line. The company also announced on Feb. 27 that it has formed an exclusive marketing relationship with DeLong and Associates LLC (Atlanta, Ga.). The latter will represent AKSA’s new AKSACA carbon fiber in the Americas.
Distributorship agreement expands customer reach
Building on an established distribution partnership in Germany and France, Amber Composites Ltd. (Langley Mill, U.K.) and Axson Technologies (Cergy, France) announced that Axson/Amber tooling materials and tooling and component prepreg now will be available in three additional European countries. Axson customers in Italy, Spain and Portugal now will have access to the complete package of products previously available only to aerospace, automotive and marine customers in Germany and France.
Reactivity-control additive for thermosets
Arkema Inc. (Philadelphia, Pa.) introduced BlocBuilder RC-50, a new reactivity controller for thermoset resin curing targeted to sheet molding compound (SMC) and bulk molding compound (BMC) manufacturing processes using unsaturated polyester and vinyl ester resins. BlocBuilder RC-50 gives greater resin stability and more control over premature cure. Also announced was the company’s acquisition of Oxford Performance Materials (Enfield, Conn.), which markets polyetherketoneketone (PEKK) under the trade name OXPEKK. Arkema will now offer the PEKK polymer for high-performance applications.
Vinyl ester resin line expanded
Ashland Performance Materials (Dublin, Ohio) expanded its Derakane Momentum epoxy vinyl ester resin line with the addition of Derakane 451-400 and Derakane 515-400, both of which are derived from Ashland’s Hetron corrosion-resistant resins. The expansion, says Ashland, ensures global availability of products for the entire Derakane line. “With the globalization of business, our customers need to have the ability to source our Derakane epoxy vinyl ester resins in all corners of the world. This enhanced export product line supports that need and assures our customers that the resin can be shipped to where it is needed,” said Andy Beer, director, product management – vinyl esters.
New machinery expands 3-D weaving capability
BITEAM AB (Stockholm, Sweden) shared a stand with Oxeon AB (Borås, Sweden), its innovation partner. BITEAM introduced its industrial 3-D weaving machine, jointly developed with the Department of Lightweight Structures, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH, Stockholm, Sweden), under the “MOJO” European 6th Framework Project. The 3-D weaving machine, based on technology invented by company cofounder Dr. Nandan Khokar, can produce complex profiles including tubular, flanged cruciform and other shapes in any type of fiber or fiber combinations. A sample of a double-flanged box beam produced by the machine was on display, together with Oxeon’s TeXtreme and TeXero spread tow woven textiles used in many applications, including Formula 1 racing.
New size formulation for glass fiber
Celanese Emulsion Polymers (Dallas, Texas) highlighted JetSize, a new line of natural polymer starches designed to optimize production of glass fiber yarns. The material has a low ash content, giving it low conductivity, and is said to be easy to process. It’s offered for pressure cooking and atmospheric cooking processes and is designed for use in electronic circuit boards or as a size in fabrics used to reinforce concrete work in construction and infrastructure applications.
Nonhalogenated, intumescent fire retardant
Clariant (Muttenz, Switzerland) featured the Exolit line of additives for fire protection. Exolit AP is a flame retardant system based on ammonium polyphosphate (AP) with a foaming (intumescent) effect when exposed to fire. Because this nonhalogenated flame retardant is not based on aluminum trihydrate, filler content can be reduced by 40 to 50 percent, Clariant reports. An alternative, Exolit RP, describes several flame retardants based on red phosphorus that have established themselves in Europe for the fire protection of fiberglass-reinforced polyamides and casting compounds. They’re available as concentrates in different carrier materials and, when used as an additive at only 6 percent, the fire protection classification UL 94 V-0 can be reached, reportedly without affecting the mechanical or electrical properties of the material.
Hot-melt adhesives with high heat resistance
Collano Adhesives (Sempach-Station, Switzerland) demonstrated its range of specialty adhesives for a range of demanding applications, including noise abatement and vibration damping. The company offers a broad range of hot-melt adhesive films that exhibit high heat resistance. Designed for the transport industry, for use in trucks and other ground vehicles, aircraft, railcars, vessels and interior fittings, the products can be applied with precision, using automated techniques, and quickly processed. Multilayer films also are available. The company’s reactive hybrid adhesives, based on silanes and epoxy resins, address requirements in load-bearing vehicle, ship and container fabrication processes.
Crush-simulation software for composites
Dassault Systèmes (Paris, France and Providence, R.I.) emphasized its recently released CZone for Abaqus, from the DS SIMULIA brand. A new add-on product for Abaqus finite element analysis (FEA) software, the program simulates crushing of composite materials, enabling engineers to accelerate the design and evaluation of energy-absorbing composite components and assemblies. Based on technology from Engenuity Ltd. (West Sussex, U.K.), the new product provides the ability to study the crashworthiness of composite structures in automobiles, helicopters, aircraft, railcars and other vehicles to protect occupants and cargo from shock or injury during severe impact.
Award-winning cored-panel system
DIAB International AB (Laholm, Sweden) received attention for its role in a JEC Innovation award-winning application. Together with composite part manufacturer Skandinaviska Glassystem (SG, Göteborg, Sweden), the company designed a lightweight architectural cladding panel concept for a six-story office building in Copenhagen, Denmark. The geometrically complex panels, cored with DIAB’s Divinycell P structural foam core and faced with glass and travertine marble, appear to be all glass when viewed from one angle and all marble when viewed from the opposite angle. DIAB engineered the shaped fiberglass panels, which were resin infused by SG. When the marble and glass panels were bonded and mechanically joined, the resulting panels were one-quarter the weight of a comparable panel built with a conventional steel-braced approach, says the company.
Joint ventures create new distribution networks
DSM Composite Resins AG (Schaffhausen, Switzerland) and BÜFA (Oldenburg, Germany) announced the completion of two joint venture agreements: Euroresins, the first comprehensive pan-European distribution and support network for the composites industry; and BÜFA Gelcoat+, a developer and manufacturer of gel coats, adhesives, pigment pastes and fire retardant products. Both companies will operate a shared business structure, with DSM having a majority share in the distribution business of Euroresins and BÜFA taking the lead in the business for gel coats, fire retardants and adhesives. DSM says the agreements herald an important change for the composites industry in Europe because small- to midsized customers will gain access, through Euroresins, to the combined know-how and product range of DSM and BÜFA, as well as from a growing number of other major industry suppliers of other materials, such as glass, peroxides and auxiliaries. This means smaller firms can harness this expertise to use technologies previously only available to larger producers. DSM also says that it will soon introduce a bioresin comprising 50 percent biobased feedstock. Because its patents are pending, the company would not reveal the nature of the biomaterial except to say that it's not been used previously in a bioresin for composites use.
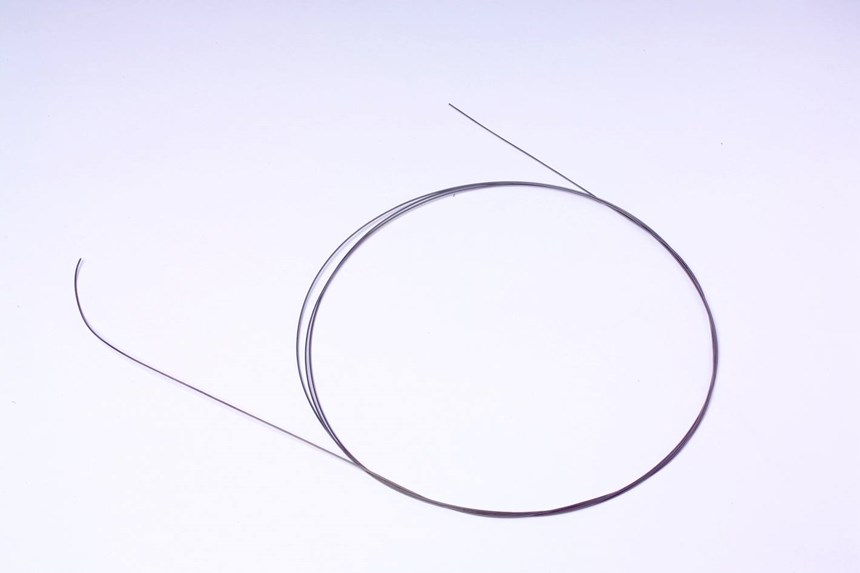
Glass-reinforced component for heart catheters
For the medical industry, Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft (Darmstadt, Germany) announced the development, with Philips and University Hospital Aachen, of a guide wire for heart catheter procedures that is made of glass-reinforced composite. The wire enables surgeons to image a patient’s arteries with magnetic resonance tomography instead of computer tomography, which requires the use of X-ray radiation. The 2m/6.6-ft guide wires are pultruded to a diameter of less than 0.5 mm/0.02 inch.
Laser projection/cutting system integration
Gerber Technology (Tolland, Conn.) announced a new program that will integrate the laser projection software technology of its subsidiary, Virtek Vision International Inc. (Waterloo, Ontario, Canada), with the capabilities of Gerber’s DCS 2500 GT cutting table technology, for high-speed cutting and kitting applications, says the company. (See Virtek Vision item, below.)
Initiative targets ocean energy turbine development
Gurit UK (Isle of Wight, U.K.) held a press conference to announce its new initiative to target ocean energy. The company is positioning itself as a Tier 1 supplier to ocean wave and tidal current power developers and will offer them a range of materials and design expertise, says Tom Royle, Gurit’s head of strategic business development. The company believes that, although ocean energy is 20 years behind wind energy in terms of development, the former will prove to be a lucrative market because greater power output can be realized with wave/tidal turbines than with wind turbines, using much smaller devices. Also announced were similar initiatives for the wind energy and automotive markets. For wind, the company is partnering with aerodynamics design firm Garrad Hassan (Bristol, U.K.) to reduce the cost of blade manufacturing by way of innovative designs and materials. On the automotive side, the company intends to develop tooling improvements and in-line paintable composite parts for superior Class A finishes with cost-effective investment.
Prepregs for wind energy & automotive markets
Hexcel (Dublin, Calif. and Duxford, U.K.) called attention to the two new plants in Tianjin, China and Windsor, Colo. that will support its long-established wind energy prepreg facility in Neumarkt, Austria, and the company promoted its composite products for wind blades. New items included a surfacing prepreg, trademarked HexPly XF2P, that reportedly provides a tough, durable and ready-to-paint surface that does not require a gel coat, saving time and reducing labor and material costs. Hexcel also touted materials tailored for the automotive industry: HexPly M49 prepreg for car body parts and interiors; and HexPly XF3, a surfacing film that reportedly provides a ready-to-paint surface finish with minimum preparation and is compatible with most epoxy prepregs and adaptable to a wide range of cure cycles, from 100°C to 140°C (212°F to 284°F).On display in the stand was a bonnet (hood) for the Lamborghini Gallardo, manufactured by ACE GmbH (Immenstad, Germany) using resin transfer molding with HexForce NC2 multiaxial carbon fabric, said to permit full resin infusion and provide a very smooth surface that reduces the print-through effect of the carbon. The Gallardo gear selector is manufactured with HexMC carbon fiber/epoxy that facilitates layup of parts with complex shapes.
Also of interest to automotive customers is the HexForce PrimeTex range of fabrics that have been processed for a smooth, closed weave and uniform cosmetic appearance. The fiber tows are spread via patented processes in both the warp and weft for unique aesthetic appeal. Trademarked PrimeTex fabrics are being used by automaker BMW on the inner and outer skins of the carbon/epoxy roof of the current M3 and M6 models.
Resins for fuel cells & aircraft interiors
Huntsman Advanced Materials (The Woodlands, Texas) received a JEC Innovation award in the “Raw Materials” category for two new resin systems based on benzoxazine and bismaleimide chemistries. The new resins allowed Huntsman’s award partners GrafTech International (Parma, Ohio) and Ballard Power Systems (Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada) to produce next-generation bipolar plates for fuel cell applications. The company says the family of Araldite benzoxazine resins is also targeted to future structural applications and aircraft interiors. Also on display were the company’s new Araldite Digitalis rapid prototyping resins for fast manufacturing.
Ultrasonic camera for real-time NDI
Imperium Inc. (Silver Spring, Md.), a provider of ultrasonic camera solutions for nondestructive inspection (NDI), reported that Hexcel Corp. (Stamford, Conn.) has selected Imperium's Acoustocam I-500 for use by its Dublin, Calif., research lab to support application engineering efforts related to composite material inspection and evaluation of its HexMC molding material and other composite materials. Alfonso Lopez, application engineer for Hexcel, said, "Imperium's Acoustocam I-500 provides a terrific solution for non-NDI certified engineers to easily and effectively evaluate our composite materials in real time. Our investigation of other NDI equipment indicates that they do not offer such unique value."
Autoclave with external gas-fired furnace
Italmatic (Lucca, Italy) exhibited its line of autoclaves for composites curing. Company manager Roberto Frediani described a recent, highly efficient installation for Stork Fokker AESP (Papendrecht, The Netherlands) that uses an external gas furnace to heat the process air, rather than a direct combustion, electric heating source within the vessel itself. Hot air is transferred from the furnace via a closed loop to the pressure vessel through a heat exchanger; a ventilator inside distributes the hot air throughout the vessel to evenly heat the parts. The hot exhaust from the vessel stays in the closed loop to preheat incoming air and reduce the amount of heat energy required by the furnace. The system is designed for high thermal efficiency (82 percent), low-temperature exhaust, low NOX and CO2 emissions and minimum maintenance. The concept reportedly saves Stork Fokker significant energy costs while providing enough heating capacity for curing high-temperature thermoplastic parts. The system will be protected by an international patent.
Spray-on structural adhesives
ITW Plexus (Rushden, U.K. and Danvers, Mass.) exhibited its range of structural adhesives for composites, metals and plastics. On display was its Sta-Put pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA) formulation in canister form for a wide range of applications, including marine and laminate panels, as well as the company’s Plexus structural adhesives.
Nesting & NC-code software for cutting systems
JETCAM International (Monaco) announced a new suite of software applications at JEC, including JETCAM Expert, which provides a nesting engine and NC-code output for cutting systems used on composites. As part of this rollout, the company challenged visitors to provide CAD files of existing parts along with a DXF file of their best attempt to nest those parts. JETCAM then provided a comparison, using its High Performance Nesting engine, which reportedly can provide material savings of 5 to 15 percent. The company also launched its Material Life Management (MLM) software, which stores and then provides users with real-time data about available materials, including material stock levels, material left on a roll, material location, expiration date, how long each material has been out of the freezer, and other data.
New roving for SMC compounders
Johns Manville Corp. (Denver, Colo. and Trnava, Slovakia) showed a large number of innovative products, among them its new SMC Roving 272, aimed at compounders of sheet molding compound (SMC). The roving reportedly improves the surface finish of SMC parts molded for Class A applications while still delivering good mechanical performance. Also on the stand: new ThermoFlow CS671 densified chopped strand reinforcement, designed for use with polyamides. The product reportedly delivers improved mechanical performance and greater hydrolysis resistance.
In-mold painting for LFT molding process
KraussMaffei (Munich, Germany) emphasized at its stand an in-mold painting process that was used in production of tractor engine covers that went into operation at Harita TVS Technologies Ltd. (Bangalore, India) in late 2008. The company produces ~500 engine covers a month for the Tiger 10 tractor made by Same Deutz-Fahr (Teviglio, Italy). Made of fiber-reinforced PUR (polyurethane) in a long-fiber injection (LFI) process, the covers are given their high-gloss surface finish in the mold. The LFI process differs from other polyurethane processes in that the long glass reinforcing fibers are wet out in the mixing head. The high-gloss surface of the LFI parts is achieved by spraying the paint directly onto the surface of the mold. Endurance tests have shown that the engine covers can withstand temperatures up to 100°C/212°F and still exhibit acceptable mechanical properties. Applications for in-mold painting for LFI include parts for buses, construction machinery, agricultural vehicles and boats.
Epoxy syntactic & potting adhesives
High-performance epoxy specialist Magnolia Plastics Inc. (Chamblee, Ga.) came to Paris to publicize two materials for use in aircraft interiors: Magnolia 85-3 A/B is a lightweight, rapid-curing, epoxy syntactic, designed for edge fill in honeycomb panels. It has a pot life of three minutes, sets in 15 minutes and cures fully in seven days. Magnolia 121-146 A/B is a lightweight epoxy potting and filling adhesive, designed to be dispensed from side-by-side cartridges. It sets in 15 to 30 minutes and cures in seven days.
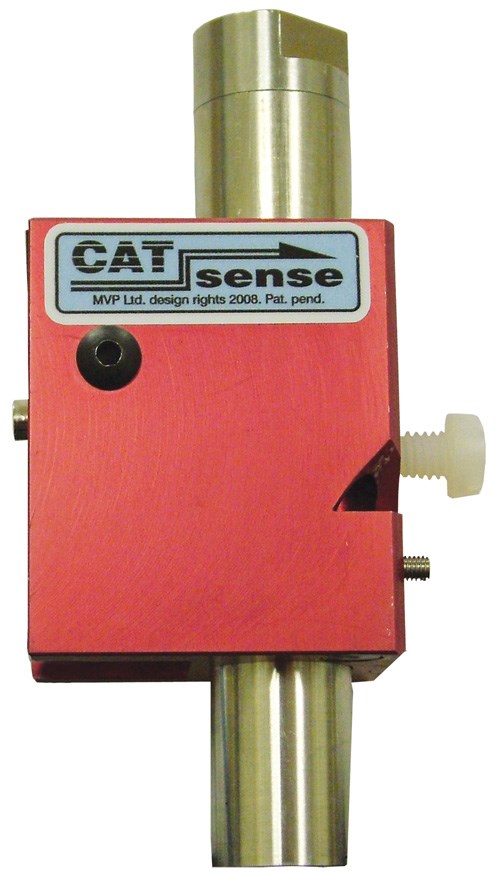
Catalyst flow alarm for meter/mix pumps
Magnum Venus Plastech (MVP, Kent, Wash.) introduced its Cat Sense catalyst flow alarm. As a pneumatically powered system (requires no electricity or batteries), it is designed for use on any MVP meter/mix system and reportedly is quick and simple to install. The system provides an audible alarm when catalyst flow drops below the flow threshold predetermined by the operator. It is said to be accurate regardless of line pressure. The system’s fluid section flow tube is manufactured from 316 stainless steel and is rated as safe to working pressures of up to 200 bar/3,000 psi.
The company also attracted crowds of visitors to its stand for demonstrations of infusion and resin transfer molding (RTM) technology. The product demo this year featured infusion of a female tool (made with tooling material provided by DSM Composite Resins, Schaffhausen, Switzerland) for the cover on a car-mounted ski rack. Glass fabric was provided by SAERTEX USA LLC (Huntersville, N.C.), and resin injection was provided by an MVP Patriot mix/meter pump. Resin flow was adjusted manually during the demo, but MVP officials report that the process will soon be automated.
SMC with integral heating wire
Menzolit Compounds International GmbH (Heidelberg, Germany) announced at its busy stand a new method for incorporating heating wires into slabs of sheet molding compound (SMC) to make integrally molded heated trays, heating elements or similar parts for home heating. Although metal inserts in SMC aren’t new, the company says that incorporating fragile heating wires without destroying them takes expertise. Menzolit now offers the technology to its SMC customers. The company was recently purchased by the German investor group All-Finanz.
Fiber-reinforced polyurethane foam core
Milliken & Co. (Spartanburg, S.C.) attracted interest from showgoers with its NexCore fiber-reinforced polyurethane foam core product for composite sandwich constructions. The product, now commercially available, is made in a continuous process, with triangular closed-cell foam elements encased in noncrimp E-glass fabric. The “truss” design, when infused as part of a sandwich structure, gives the core high toughness and durability and equal stiffness at a lower weight than comparable cores, reports the company.
Collaboration to automate wind blade production
MTorres (Torres de Elorz, Navarra, Spain) announced a breakthrough agreement with wind turbine developer Gamesa (Vitoria, Alava, Spain) for a research and development project to automate wind blade production. The new production concept is expected to significantly decrease blade manufacturing cycle times and overall manufacturing cost. The collaboration is also expected to produce a new family of Gamesa blade designs. The first prototyped automated units are slated for availability in the first quarter of 2010 (see “Work in Progress” on p. 27, this issue). Airbus (Toulouse, France) has signed a multiyear contract making MTorres its only source of tape laying technology to produce wingskins, stringers, spars and other components. GKN Aerospace (Bristol, U.K.) will use MTorres’ automated fiber placement machines for the A350 XWB rear wing spar fabrication, and Spirit Aerosystems Inc. (Wichita, Kan.) will use the same type of machine to produce the A350’s front wing spar. The company reports that 43 of its automated tape-laying machines are currently in operation or on order.
3-D through-stitched isotropic core
Nida-Core Corp. (Port St. Lucie, Fla.) introduced a new product called NidaFusion SXO/SXF, a three-dimensional, through-stitched isotropic core with fiberglass facings designed for closed molding sandwich construction applications where isotropic properties are highly desirable, such as wind turbine blades. The z-directional stitches, when infused with resin, form a pyramidal truss network inside a closed cell foam for high strength. The company also distributes a unique honeycomb foam core product, termed 3D Core, that features scored channels around each cell. The scoring makes the core pliable and conformable and forms resin channels during infusion. When cured, the resin in the scored channels forms the cell “walls” around the foam cells, creating a foam-filled honeycomb core with very high shear, flexural and compression strengths.
Vinyl/glass commingled fiber reinforcement
Owens Corning Composite Materials LLC (Toledo, Ohio) focused on recent applications of its products, including the JEC Innovation Award-winning window lineal part made with the company’s trademarked Twintex commingled glass fiber/polymer fiber reinforcement. The windows, as originally fabricated by a French window specialist using vinyl reinforced with steel rods, were not as thermally efficient as they could be because the steel caused thermal bridging. A specially formulated grade of Twintex replaced the steel rods. Made with polyvinylchloride (PVC) fiber rather than the typical polypropylene fiber, the Twintex reinforcement was, therefore, compatible with the manufacturer’s vinyl resin and could be inserted into the vinyl extrusion line without changes in any of the window tooling. The finished windows exhibited 30 percent higher thermal efficiency, says the company.
Funding fuels manufacturing startup
Quickstep Technologies Pty. Ltd. (North Coogee, Western Australia) reiterated that on March 10 it received an additional funding injection to bolster the company’s growth, consisting of binding commitments under a convertible note placement. Philippe Odouard, Quickstep’s chief executive officer, said the funds will be used to provide further working capital as the company prepares to start aerospace-grade composites manufacturing from its headquarters in North Coogee, Western Australia.
Water-based release for high-gloss parts
REXCO Mold Care Products’ (Conyers, Ga.) Partall POWER liquid mold release made its debut. The water-based, nonhazardous, silicone-free, semipermanent external mold release agent is designed to form a high-gloss finish on molded parts. Designed for use on most mold substrates (e.g., composite, aluminum and steel), the product reportedly provides multiple releases, yet offers ease of application with superior wet polishing and minimal fouling of tooling during processing. Recommended for use with most thermoset resins, it can be wiped on or spray applied over a sealed mold to form a smooth, durable, glossy film with excellent adhesion to the interfacial coating. Odorless, nonhazardous, and nonflammable, the product contains no hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) or volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Inductively heated molding system demonstrated
Roctool (Le Bourget du Lac, France and Atlanta, Ga.) periodically demonstrated its high-speed thermoplastic composite molding process, producing composite laptop computer covers on the company’s Cage System. The Cage System features an inductive heating system that heats only the thickness of the mold surface, providing for rapid ramp to molding temperature and fast cooldown cycling. A blank of material can be elevated from 50°C/122°F to 250°C/482°F in 70 seconds before forming, enabling users to achieve part production cycles of just over two minutes. Material for the covers was provided by Roctool partner Performance Materials Corp. (PMC, Camarillo, Calif.) and consists of unidirectional carbon fiber (12K and 24K) in a PET resin matrix. The covers, designed to compete with magnesium versions, have wall thickness of only 0.8 mm/0.03 inch, offer competitive cost and stiffness and emerge from the mold ready to paint. PMC is a licensee of the Roctool Cage System process and is working with laptop manufacturers on supply agreements.
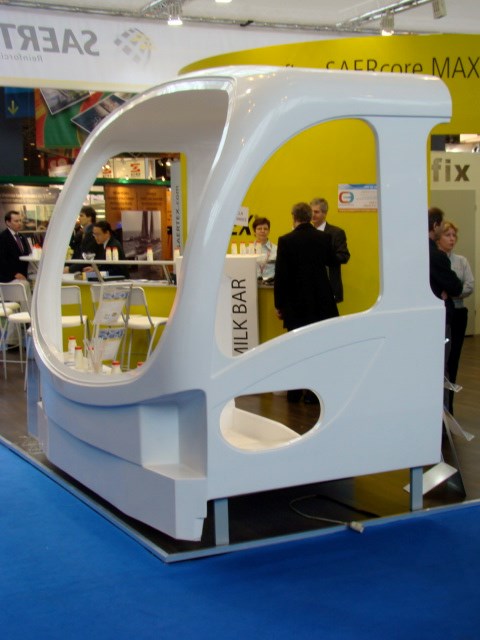
Bus cab section shows off reinforcements line
SAERTEX USA LLC (Huntersville, N.C.) attracted much attention at the show for the cab section (see photo) of a new all-composite fuel-cell-powered shuttle bus for which the company provided design assistance and reinforcement fabrics. The bus is being manufactured by Proterra LLC (Golden, Colo.). Details of SAERTEX’s involvement are available in CT’s “Inside Manufacturing” feature on this project, in this issue (click here).
Resins for pultrsuion & closed molding
Scott Bader Co. Ltd. (Northamptonshire, U.K.) introduced several new products in Paris. Crestapol 1210 and 1212 are tough, low-viscosity, high-reactivity resins based on urethane acrylate chemistry that are designed for use in pultrusion and closed-mold processes. Designed for use in rail, truck, bus, and building applications, they feature fast pultrusion haul-off rates and reportedly can be cycled in a closed mold in as few as seven minutes. Crystic RTR 4000PA is a new rapid tooling resin that cures using an MEKP catalyst. It offers good shrinkage control and is compatible with the brush-on tooling gel coat Crystic 14PA and Crystic VE 679PA, a vinyl ester skin coat. Crystic 967 is an improved sanitaryware gel coat that reportedly eliminates microporosity and provides high gloss as well as a 40 percent increase in thermal shock resistance, compared to competitive products. Finally, a new polyester gel coat for use with epoxies accommodates wet layup or prepreg systems. It reportedly applies quickly, has a fast demold time (tack-free in less than 75 minutes) and offers UV and weather resistance.
New name, new stitch-bonded reinforcements
Scott & Fyfe Composites Ltd. (Kilmarnock, Ayrshire, U.K.) exhibited under the company’s new moniker, following the January 2009 rebranding of its composites division, formerly known as Flemings Textiles Ltd. The company emphasized the benefits of its POLYMAT Hi-Flow product, a mechanically stitch-bonded reinforcement that features a flexible engineered thermoplastic core between layers of chopped strand glass when used in structural laminates, such as in wind turbine blades or marine applications. Notably, when used in VARTM processes, the material reportedly contributes to a 50 percent reduction mold-fill time and 20 percent less resin consumption. On display were two new Hi-Flow products designed for excellent surface finish.
Carbon/PEEK thermoplastic prepregs
TenCate Advanced Composites USA Inc. (Morgan Hill, Calif.) offered an alternative to thermosetting composites in high-performance applications. Its new prepregging line is producing trademarked CETEX carbon fiber/PEEK (polyetheretherketone) and glass fiber/PEEK thermoplastic prepregs. According to the company, the new material is intended for structural applications, has an extremely low void content (less then 1 percent) and is suitable for press lamination, thermoforming or autoclave processing.
Boron-free chopped strand glass
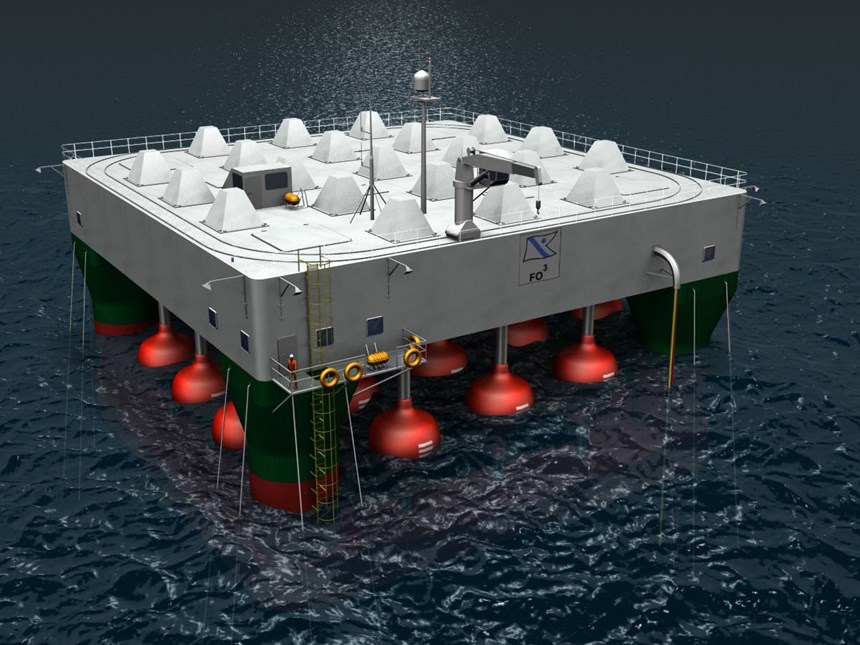
3B – The Fibreglass Company (Battice, Belgium and Birkeland, Norway), reportedly the largest fiberglass producer in Europe, introduced its new DS 2200-13P dry chopped strand for polypropylene and polyethylene reinforcement. Made from new boron-free Advantex glass, the product is targeted to metal replacement and incorporation into existing reinforced thermoplastics that are used in demanding automotive and consumer applications. The product has high density and good dispersion capability at high (>50 percent) loading concentrations in plastic compounds. The company also provided Advantex E-glass fiber and HiPer-tex high-performance glass fiber to Fred Olsen Ltd. (Oslo, Norway), a cowinner of a 2009 JEC Innovation Award for a composites-intensive ocean wave energy converter (see a rendering the converter system, at right).
Reinforced PPS in oil & gas pipe
Ticona (Kelsterbach, Germany) emphasized use of its Fortron PPS with fiber reinforcement in pipe manufacturer PolyFlow Inc.’s (Oaks, Pa.) Thermoflex tubing for oil and gas applications. Thermoflex tubing, designed to replace metal tubing, uses a three-layer design. The inner layer is neat Fortron PPS; on top of that is a layer of high-performance fibers (usually aramid), with another layer of Fortron PPS on top of that. The tubing, which has a diameter of 2.5 to 11 cm (1 to 4.3 inches), has operating pressure of 17.24 to 172 bar (36,000 to 359,000 psi) and tensile force limit of 4,500 kg/9,900 lb.
24K carbon fiber for industrial applications
Toho Tenax Europe GmbH (Wuppertal, Germany) introduced its new trademarked Tenax-E IMS65 24K fiber, commercially produced on one of the newest production lines in Germany. Also showcased was Tenax-E UTS55 24K, an ultrahigh-tenacity fiber still under development that offers enhanced tensile properties and is targeted for high performance industrial applications, such as offshore oil piping and pressure vessels as well as for aerospace use. The fiber will be produced on a new line in Germany, currently under construction, which the company says will be finalized in August this year. Also available is a short fiber type specifically designed for high temperature resin systems. Tenax-A HT C723 (6 mm/0.24 inch) has thermal stability approaching 500°C/932°F, making it applicable for reinforcing high-temperature thermoplastics from PPS up to PEEK.
Restructuring effort increases marketing potential
Umeco Composites (Leamington Spa, U.K.), one of the two divisions within Umeco plc, has restructured its operations into two subsidiaries, Process Materials and Structural Materials, reportedly to give “greater focus to these value-added services for customers and ensure it meets its full potential to capture market opportunities.” Umeco Composites Process Materials (UCPM) will be headed by Tim Cooper, the former managing director of Aerovac Systems, and will comprise the newly acquired IPM in Italy along with Richmond Aerovac and Med-Lab. Umeco Composites Structural Materials (UCSM) will be led by Jon Mabbitt, managing director of Advanced Composites Group Ltd. (ACG, Heanor, Derbyshire, U.K.), and will include ACG as well as subsidiaries Advanced Composites Group Inc. (Tulsa, Okla.), J.D. Lincoln (Costa Mesa, Calif.) and GRP Materials Supplies Ltd. (Fareham, Hampshire, U.K.).
Laser templating systems sale announced
Virtek Vision International Inc. (Waterloo, Ontario, Canada), a subsidiary of Gerber Technology (Tolland, Conn.), signed an agreement at the show with Stork Fokker AESP (Hoogeveen, The Netherlands) for the latter’s purchase of laser templating systems over the course of the next five years. In the published announcement, Virtek’s VP for imaging and templating, Peter Richter, commented, “We are extremely pleased at having an important and prestigious aerospace manufacturer such as Stork Fokker place their long term trust in our products.”
Composites engineering software suite updated
VISTAGY Inc. (Waltham, Mass.) used the JEC show to debut the latest version of its suite of composites engineering software, FiberSIM 2009, which enables users to more easily define composite parts, provides improved functionality for resolving manufacturing issues and enhances the link between analysis and design. The new release reportedly simplifies composite part design with the addition of the global stagger profile, partial boundary editor and design checker as well as enhancements to zone-based design and core definition tools. Other features include improved tools for resolving manufacturability issues in FiberSIM 2009 with significant enhancements to the optional Automated Deposition Design (ADD) module. FiberSIM 2009 also features expanded integration of analysis and design with enhanced definition and interoperability between CAE and CAD for composite design.
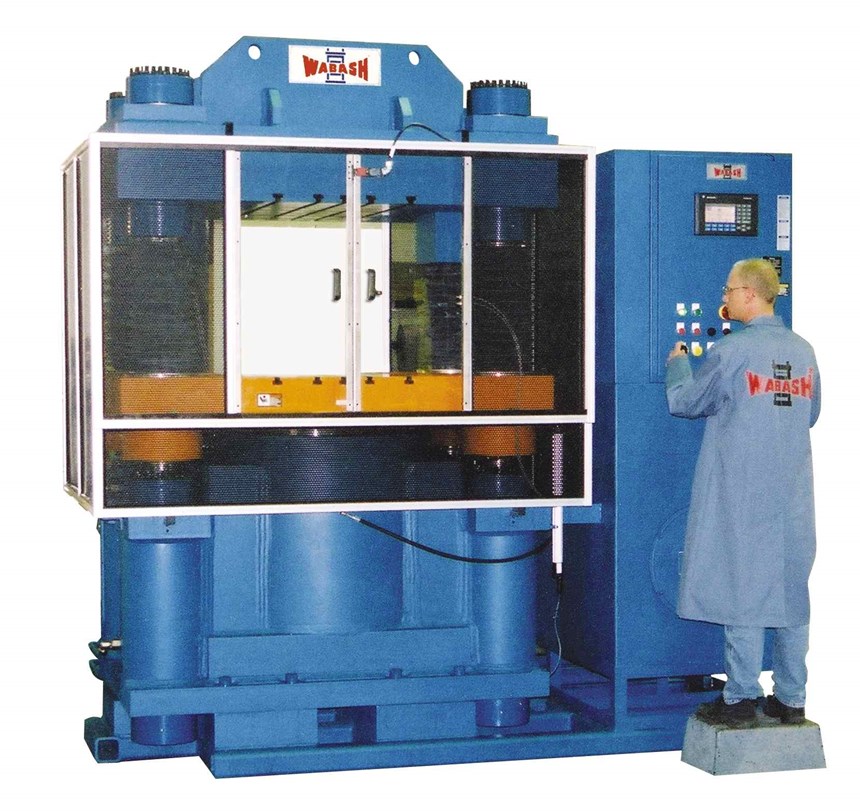
Presses for composites manufacturers
Wabash MPI (Wabash, Ind.) promoted its full line of production and laboratory presses, standard and custom, for composites applications, including equipment for compression molding, liquid injection molding, vacuum molding, ASTM/laboratory and R&D presses, as well as a series of all electric compression presses. Its Genesis Series Presses are available from 15 to 150 tons for compression molding of composites, rubber and plastics, while the Vantage Series ranges from 50 to 1000 tons fro molding SMC and other composite materials. C-Frame press configurations are also available for handling long work pieces.
Nickel-shell tooling for in- or out-of-autoclave processing
Weber Manufacturing Technologies Inc. (Midland, Ontario Canada) demonstrated its precision nickel-shell tooling for carbon fiber part production, including tools for Plasan Carbon Composites (Bennington, Vt.) that are used to produce autoclaved auto body panels for General Motors’ Corvette and Ford’s GT500KR Shelby Mustang models. The company also produces integrally heated nickel-shell tools for out-of-autoclave infusion processes and provides molds for high volume production applications (e.g., automotive interiors and residential doors) for a range of manufacturers. Weber has produced tools for Gurit UK (Isle of Wight, U.K.) to make out-of-autoclave, net-shape parts, using the latter’s patented SPRINT CBS (Car Body Sheet) technology.
Reconfigurable flatbed cutting/routing system
Zünd Systemtechnik AG (Altstätten, Switzerland) highlighted its award-winning new G3 digital table cutting/routing system, which is highly configurable for many materials thanks to its modular tool design. The G3 is available in nine different sizes, says the company, and can be easily customized to meet customer requirements. Its readily changed modular tool heads include rotary or oscillating knife blades or routers. Together with its cutters, Zünd also offers GTK “Autonester” nesting software for efficient ply cutting.Related Content
XlynX Materials BondLynx and PlastiLynx for low surface energy PP, PE substrates
Award-winning Xlynx materials use breakthrough “diazirine” technology to boost bond strength up to 950% as adhesives, primers and textile strengtheners.
Read MoreScott Bader, Oxeco partner for high-performance bonding solution
Joint technology breaks barriers to bonding lightweight flexible solar panels to roofing structures made from aluminum, coated steel and composites.
Read MorePro-Set named official materials supplier for New York Yacht Club American Magic
Competitive sailing team prepares for the 37th America’s Cup beginning in August 2024 with adhesives, resins and laminate testing services for its AC75 monohull construction.
Read MorePittsburgh engineers receive $259K DARPA award for mussel-inspired underwater adhesion
The proposed META GLUE takes inspiration from hydrogels, liquid crystal elastomers and mussels’ natural bioadhesives to develop highly architected synthetic systems.
Read MoreRead Next
Developing bonded composite repair for ships, offshore units
Bureau Veritas and industry partners issue guidelines and pave the way for certification via StrengthBond Offshore project.
Read More“Structured air” TPS safeguards composite structures
Powered by an 85% air/15% pure polyimide aerogel, Blueshift’s novel material system protects structures during transient thermal events from -200°C to beyond 2400°C for rockets, battery boxes and more.
Read MoreVIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read More