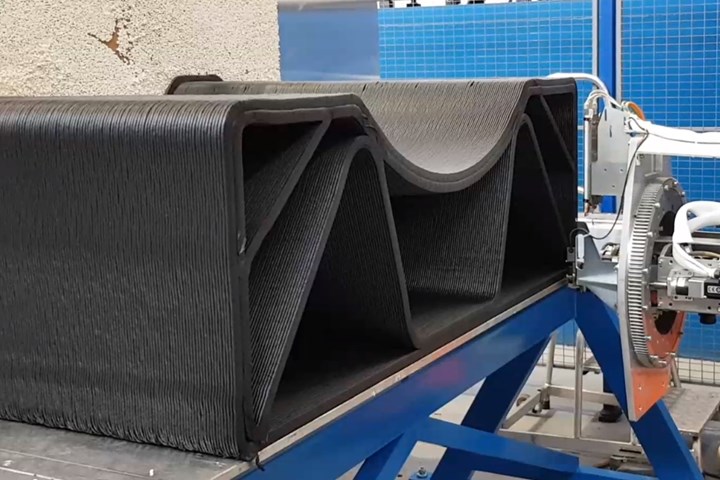
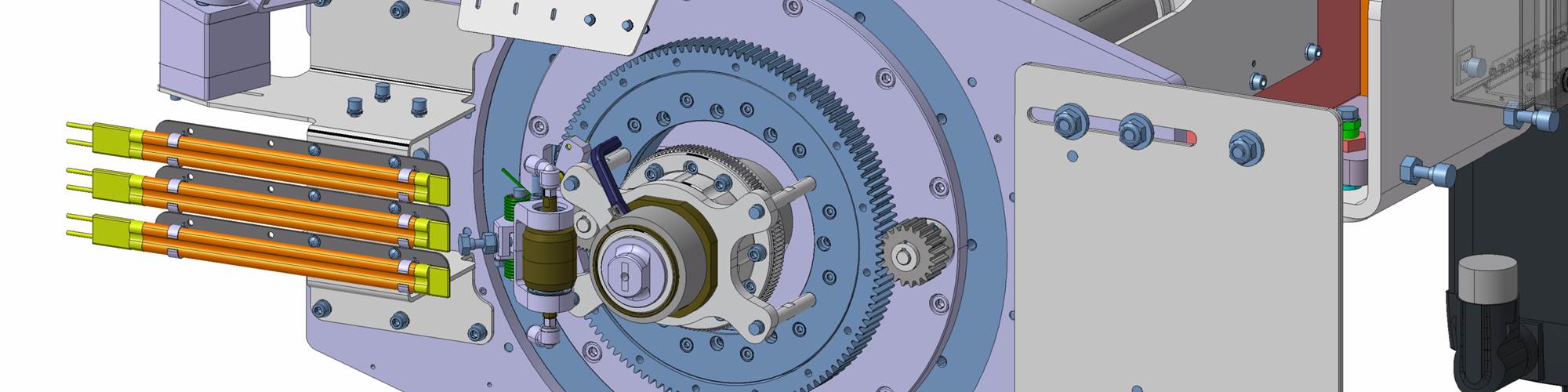
The MTorres large-format 3D printer features a six-axis robot that prints on the vertical axis. As each layer is placed, the part moves along the deposition table to make room for the next layer. Photo Credit: MTorres
Automation and fiber and tape placement specialist MTorres (Torres de Elorz, Navarra, Spain) is entering the large-format additive manufacturing (LFAM) space with a fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing system that extrudes polymer on a vertical axis. The system features a vertical deposition table attached to a longitudinally movable deposition platform and a six-axis robot at the end of the table with an extruder end effector. The robot extrudes material onto the vertical printbed and as each layer is placed, the deposition platform automatically indexes away from the robot, allowing the robot to begin placement of the next layer. In this way, the part moves down the table as it is built. The deposition table is 2 meters wide and is offered in lengths up to 25 meters, which also represents the current length limit of printed parts.
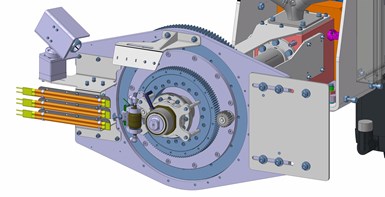
The extrusion head on the in-house developed extruder features three rotational axes — one to rotate the heating system, one to rotate the extruder cylinder and one to rotate the extruder nozzle. It offers deposition rates up to 35 kg/hr. Photo Credit: MTorres
The robot works to always keep the extruder axis in the horizontal position and perpendicular to the vertical deposition table. A seventh axis is also offered to increase the lateral working envelope. The extruder, which MTorres developed and produced in-house, can be used in other machine configurations, including on a gantry or attached to an XYZ Cartesian column machine. The extruder nozzle itself offers significant functionality and features several rotational axes — one to rotate the heating system, one to rotate the extruder cylinder and one to rotate the extruder nozzle.
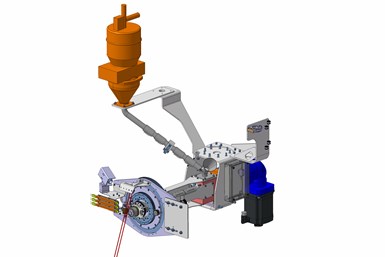
The MTorres-developed extruder comes with a resin dryer and offers process temperatures up to 350°C. The company has evaluated PPE/CF, ABS/CF, ABS/GF and PEI/CF material combinations. Photo Credit: MTorres
Valentín Forte, engineering team leader at MTorres, says the company has tested a variety of resin/fiber combinations on this system, including PPE/CF, ABS/CF, ABS/GF and PEI/CF, but other thermoplastics are compatible as well. Forte adds that the system also offers deposition rates up to 35 kilograms per hour, provides in-situ re-heating of the previous layer to promote z-direction adhesion, does not require a temperature-controlled chamber and provides overall better temperature control capabilities compared to competing systems. In addition, the deposition table can be equipped with a CNC system at the non-deposition end to facilitate part trimming and finishing as necessary. Finally, the MTorres AM system offers process temperatures up to 350°C, but higher-temperature capability is under development for processing of high-performance thermoplastics like PEEK, PEKK and PAEK.

The MTorres large-format printer is targeted toward production of tooling and fixtures. Finished part manufacturing is also possible. Photo Credit: MTorres
The slicing software used to govern operation of the system is derived from software developed for MTorres’ automated fiber placement (AFP) machines. In addition, the slicing software is designed to automate robot and extruder programming. “Our slicing software receives the final part to print as a CAD file, as well as the printing conditions — material width, starting point, etc.,” says Forte. “The application then analyzes the part and creates the necessary trajectories to print it, including movements to avoid collisions. It also manages the extrusion activation/deactivation, feed rates and the commands that define the material width.” Forte also says the final program includes the position for the robot and the table, and controls the roller position to compact the material, heater position and heater activation and deactivation.”
Potential applications for the MTorres system include production tooling for large parts or fixtures for machining/trimming where no temperature cycles are required. Building autoclave-capable molds is also possible, Forte says, as is finished parts manufacturing, although the latter is not currently a target of the technology.
Related Content
Manufacturing the MFFD thermoplastic composite fuselage
Demonstrator’s upper, lower shells and assembly prove materials and new processes for lighter, cheaper and more sustainable high-rate future aircraft.
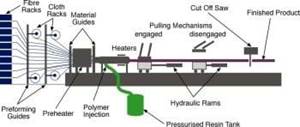
Read MorePultrusion: The basics
A primer describing what pultrusion is, its advantages and disadvantages, and typical applications.
Read MorePlant tour: Spirit AeroSystems, Belfast, Northern Ireland, U.K.
Purpose-built facility employs resin transfer infusion (RTI) and assembly technology to manufacture today’s composite A220 wings, and prepares for future new programs and production ramp-ups.
Read MoreLarge-format 3D printing enables toolless, rapid production for AUVs
Dive Technologies started by 3D printing prototypes of its composite autonomous underwater vehicles, but AM became the solution for customizable, toolless production.
Read MoreRead Next
VIDEO: High-volume processing for fiberglass components
Cannon Ergos, a company specializing in high-ton presses and equipment for composites fabrication and plastics processing, displayed automotive and industrial components at CAMX 2024.
Read MorePlant tour: Daher Shap’in TechCenter and composites production plant, Saint-Aignan-de-Grandlieu, France
Co-located R&D and production advance OOA thermosets, thermoplastics, welding, recycling and digital technologies for faster processing and certification of lighter, more sustainable composites.
Read MoreAll-recycled, needle-punched nonwoven CFRP slashes carbon footprint of Formula 2 seat
Dallara and Tenowo collaborate to produce a race-ready Formula 2 seat using recycled carbon fiber, reducing CO2 emissions by 97.5% compared to virgin materials.
Read More