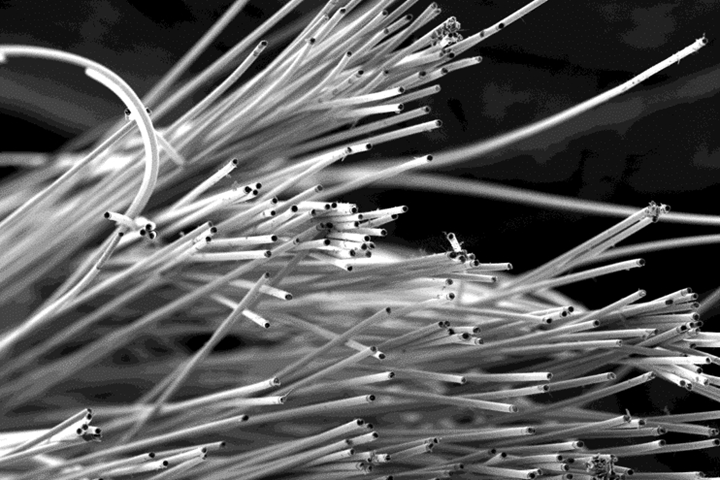
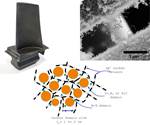
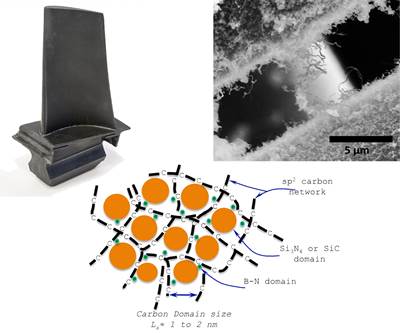
This group of silicon-converted PAN carbon fiber filaments, passed through ACF’s Direct Conversion Process, are the basis for the company’s CMC materials designed for extreme environments. The base carbon fiber can be seen as the black center of each filament, and the uniform, white outer layers are silicon carbide (SiC). Each individual filament has been converted, which ACF says enables them to move freely within the matrix. Photo Credit, all images: Advanced Ceramic Fibers LLC
Editor’s note: Information contained herein may be related to SBIR Phase II Contract No.: N0001416C2020. The content of the information does not reflect the position or policy of the government and no official endorsement should be inferred.
NASA’s Interstellar Probe (ISP) concept study, led by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL, Laurel, Md., U.S.), would be the first mission intentionally sent to explore the space beyond our solar system, requiring it to travel faster and farther than any other spacecraft, including the Voyager probes. To be able to reach very long distances at very high speeds, the Interstellar Probe may need to perform an “Oberth maneuver,” which would swing the probe close to the sun and use the sun’s gravity to slingshot the probe toward deep space. To enable this effort, research is being done to develop a lightweight, ultra-high-temperature material for use on the probe’s protective solar shield.
In response, high-temperature materials developer Advanced Ceramic Fibers LLC (ACF, Idaho Falls, Idaho, U.S.) recently conducted a seven-month project with APL to develop potential materials able to withstand temperatures up to 3,500°C (6,332°F). The project, which took place from February to August 2020, showed promising initial results for ACF’s ultra-high-temperature ceramic matrix composite (CMC) materials.
CMCs, often used in aircraft engine and other high-temperature applications (see “Commercialization of CMCs and developments for next-gen performance” and “Bridging the gap between CFRP and CMC”), showed the most promise for investigation, given their light weight and ability to withstand high temperatures. After initial testing, coupons made of ACF’s proprietary CMC materials showed potential for reaching or exceeding NASA’s temperature targets, with low vapor pressures and while maintaining mechanical strength requirements.
Direct fiber conversion
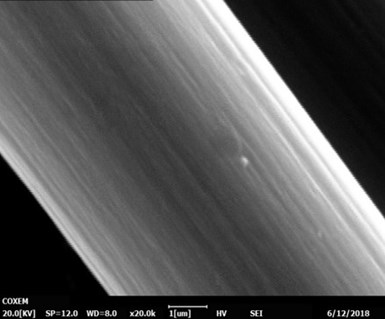
Micrograph of a carbon fiber filament encased in silicon carbide.
Founded in 2012, ACF has developed and patented what it calls its Direct Conversion Process (DCP), which works by passing a carbon fiber tow through a continuous (proprietary) process to convert the outer layer of each individual carbon fiber filament into a metallic carbide, such as silicon carbide (SiC/C). According to Ken Koller, CEO of ACF, what differentiates this process compared to other CMCs is that it’s a fiber conversion process, not a coating.
The resulting fiber tows are called Fi-Bar, so named because “it acts like rebar when incorporated in materials like metals and ceramics,” Koller says. Combined with a ceramic matrix and additional proprietary materials, Fi-Bar is the basis for ACF’s CMC materials, designed for use in extreme temperature environments.
“Our CMCs can be modified using different materials (or recipes) depending on the specific application,” Koller says. “ACF holds a U.S. patent covering 35 of the metallic carbides in the periodic table. That means we can, theoretically, process our Fi-Bar using titanium, hafnium, zirconium, etc., as our metallic carbide using the Direct Conversion Process.”
Ultra-high-temp CMCs for military and space applications
ACF’s first major foray into applications of UHT CMCs came out of a SBIR Phase II project that took place from 2016-2021 with the U.S. Office of Naval Research (ONR). ACF was tasked with the development of advanced, fiber-reinforced CMCs able to withstand up to 2,700°F (1,371°C). The resulting material, which is ACF’s patented Quad-XE product, would be used to build turbine engine components for military aircraft structures, which previously were limited to an operating temperature of about 2,500°F, Koller says.

As part of a research program ACF conducted with ONR, five NASA-designed turbine engine vanes were temperature-tested in fall 2020. Each vane, made with different iterations of ACF’s Fi-Bar interior core in a CMC matrix, was tested up to 2,900°F (1,371°C), and one version was capable of reaching 3,120°F with no external damage and the interior Fi-Bar carbon fiber core remained intact.
He adds that, upon testing at a U.S. research center affiliated with an unnamed U.S. turbine engine manufacturer, one of the test components was actually able to reach an operating temperature of 3,100°F (1,704°C). “The significance of this is that the hotter you can run a turbine engine, the more efficient it is,” he says, which saves on operating costs and enables pilots to fly faster.
Compared to the ONR project, the Interstellar Probe concept required even higher temperatures — more than 3,000°C for several hours — and more complex geometries. Light weight, structural integrity, mechanical strength and shield size were all key considerations as well. Tungsten, a UHT material that has been used for heat shields in the past, would be too heavy for the initial, foam-filled sandwich shield design listed in the concept.
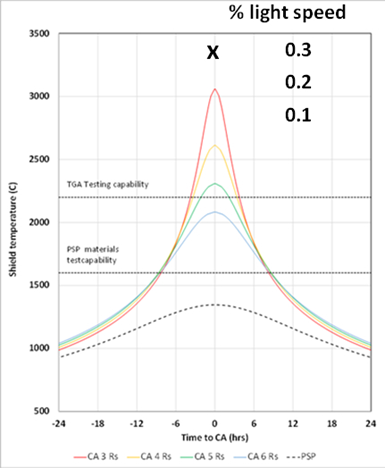
As part of the Interstellar Space Probe research project, near-sun pass shield temperature profiles and testing capabilities are shown for five test materials.
Building on ACF’s ONR work with SiC CMC materials, the focus of the new APL study was to see if ACF’s processing techniques could be extended to the development of CMCs based on several other metal carbides known for their ultra-high temperature capabilities. ACF’s proprietary process produced metal carbide CMC samples said to have very low vapor pressure and low density.
The samples were tested using torch testing and vacuum heating. According to Koller, the materials showed potential for lightweight, low-vapor pressure materials extending the current 2,000°C (3,632°F) upper limit for carbon fiber materials, and that the materials retained mechanical strength to temperatures up to at least 2,900°C (5,252°F), with potential for higher temperatures.
APL’s initial report concludes, “The results of this Phase I project have demonstrated the potential for development of an entirely new class of materials with UHT capability.”
Related Content
ORNL, Sierra Space create novel C/SiC TPS for reusable space vehicles
CMC tiles will be used on the Sierra Space DC100 Dream Chaser spaceplane carrying critical supplies and science experiments to and from NASA’s ISS.
Read MoreArceon introduces novel CMC materials for space, defense
Carbeon C/C-SiC ceramic matrix composites are being developed and tested for rocket nozzles, onboard the International Space Station and in electric aviation, metal treatment and reactor applications.
Read MoreBombardier begins manufacture of Global 8000 business jet
Ultra-long range business jet featuring CMC-intensive engine and a range of 8,000 nautical miles is set to enter service in second half of 2025 as it remains on track for flight testing.
Read MoreGE Aerospace awarded demonstration contract for NASA HyTEC project
Turbofan engine small core technology development with CMC-coated components targets enhanced fuel efficiency in single-aisle aircraft by mid-2030s.
Read MoreRead Next
Composites in the race to space
Advanced materials use in current and upcoming NASA missions.
Read MoreBridging the gap between CFRP and CMC
Novel composites offer performance up to 1000°C with faster processing.
Read MoreCommercialization of CMCs and developments for next-gen performance
As industrial production of parts begins, new developments offer promise for higher-temperature and more damage-tolerant ceramic matrix composite (CMCs).
Read More

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)